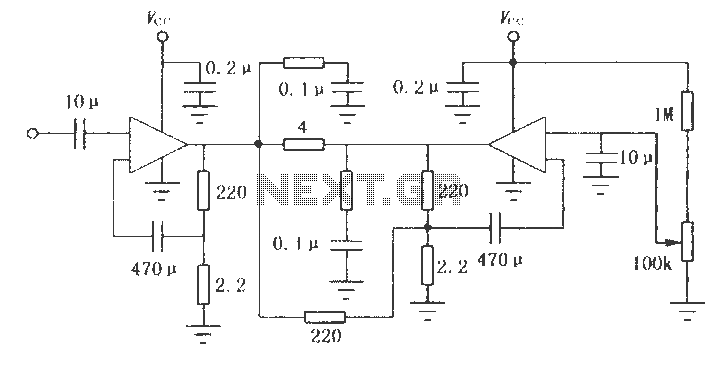
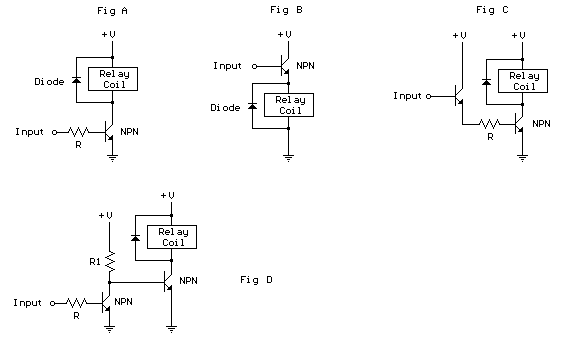
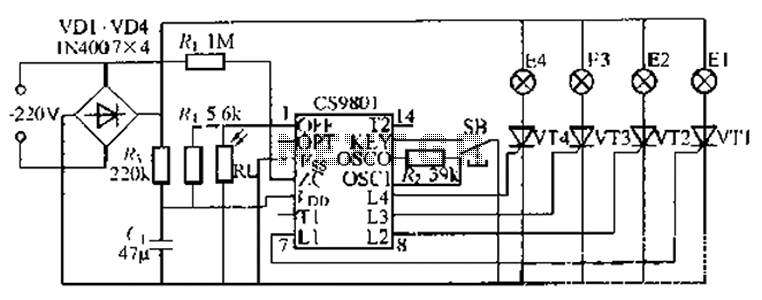
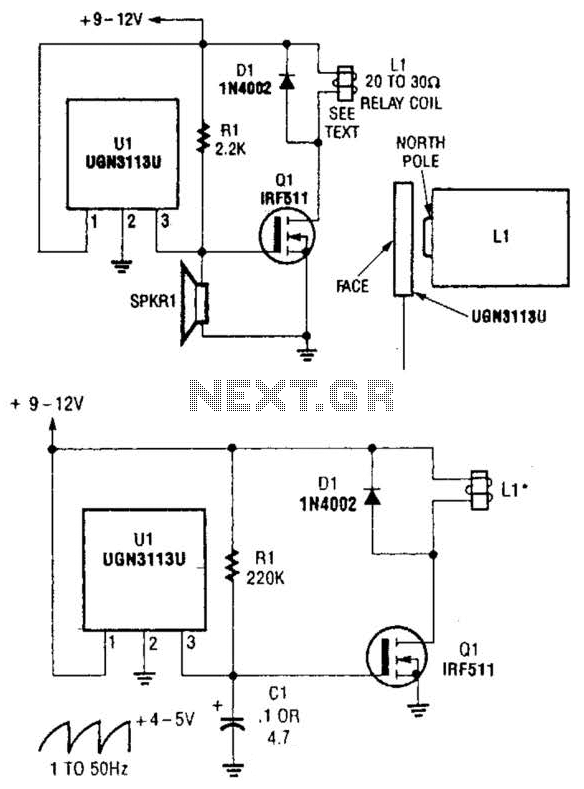
Third harmonic excitation device automatic circuit a thyristor
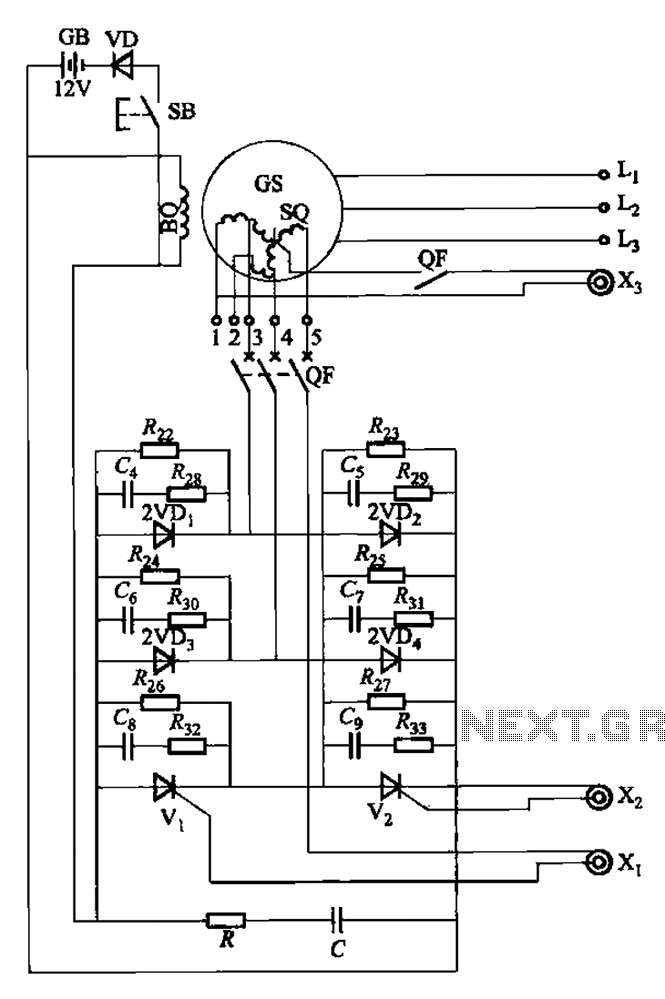
The setup is connected to separate stator windings of a harmonic generator, which leads to a thyristor rectifier supply for the third harmonic voltage, positioned after the motor field. The output voltage varies with changes in the winding harmonics generator load, necessitating automatic excitation adjustment. As the generator load increases, the power factor decreases, resulting in a corresponding increase in the third harmonic winding output voltage; conversely, when the generator load decreases and the power factor increases, the third harmonic winding voltage decreases. In the event of a short circuit on the grid, the output voltage from the third harmonic winding significantly increases, activating the force field generator. The circuit is illustrated in Figure 7-43, which depicts the sQ harmonic excitation winding.
The circuit design encompasses a harmonic generator that operates through dedicated stator windings, specifically tailored for third harmonic voltage generation. This configuration utilizes thyristor rectification to manage the output voltage effectively. The system is engineered to adapt to varying load conditions through automatic excitation control, which optimizes performance and stability.
The interaction between the generator load and the power factor is critical. When the generator experiences increased load, the power factor tends to diminish, leading to an elevation in the third harmonic output voltage. This response is vital for maintaining the operational integrity of the generator under varying electrical demands. Conversely, a reduction in load prompts an increase in the power factor, resulting in a proportional decrease in the third harmonic voltage. This dynamic adjustment ensures that the generator operates efficiently across a range of conditions.
In scenarios where a short circuit occurs on the grid, the output voltage from the third harmonic winding can experience a significant surge. This phenomenon triggers the force field generator, which serves as a protective and corrective mechanism, safeguarding the overall system from potential damage due to excessive voltage levels.
The schematic representation in Figure 7-43 provides a visual layout of the harmonic excitation winding, illustrating the interconnections and components involved in the system. This figure is essential for understanding the circuit's operational principles and for troubleshooting any issues that may arise during its operation. Overall, the design emphasizes reliability and adaptability in managing harmonic voltages within electrical systems. Attached to a separate harmonic generator stator windings, leads to the third harmonic voltage thyristor rectifier supply made after the motor field. Since the output voltage v aries with the winding harmonics generator load changes, and therefore with automatic adjustment of excitation. When the generator load and increase power factor decreases, the third harmonic winding output voltage corresponding increase; when the generator load decreases and the power factor increases, the third harmonic winding voltage correspondingly reduced.
When the grid a short circuit, the third harmonic winding output voltage is greatly increased, the implementation of the force field generator. Circuit shown in Figure 7-43. Figure, sQ harmonic excitation winding.
The circuit design encompasses a harmonic generator that operates through dedicated stator windings, specifically tailored for third harmonic voltage generation. This configuration utilizes thyristor rectification to manage the output voltage effectively. The system is engineered to adapt to varying load conditions through automatic excitation control, which optimizes performance and stability.
The interaction between the generator load and the power factor is critical. When the generator experiences increased load, the power factor tends to diminish, leading to an elevation in the third harmonic output voltage. This response is vital for maintaining the operational integrity of the generator under varying electrical demands. Conversely, a reduction in load prompts an increase in the power factor, resulting in a proportional decrease in the third harmonic voltage. This dynamic adjustment ensures that the generator operates efficiently across a range of conditions.
In scenarios where a short circuit occurs on the grid, the output voltage from the third harmonic winding can experience a significant surge. This phenomenon triggers the force field generator, which serves as a protective and corrective mechanism, safeguarding the overall system from potential damage due to excessive voltage levels.
The schematic representation in Figure 7-43 provides a visual layout of the harmonic excitation winding, illustrating the interconnections and components involved in the system. This figure is essential for understanding the circuit's operational principles and for troubleshooting any issues that may arise during its operation. Overall, the design emphasizes reliability and adaptability in managing harmonic voltages within electrical systems. Attached to a separate harmonic generator stator windings, leads to the third harmonic voltage thyristor rectifier supply made after the motor field. Since the output voltage v aries with the winding harmonics generator load changes, and therefore with automatic adjustment of excitation. When the generator load and increase power factor decreases, the third harmonic winding output voltage corresponding increase; when the generator load decreases and the power factor increases, the third harmonic winding voltage correspondingly reduced.
When the grid a short circuit, the third harmonic winding output voltage is greatly increased, the implementation of the force field generator. Circuit shown in Figure 7-43. Figure, sQ harmonic excitation winding.