Three reversing operation of the reverse brake circuit
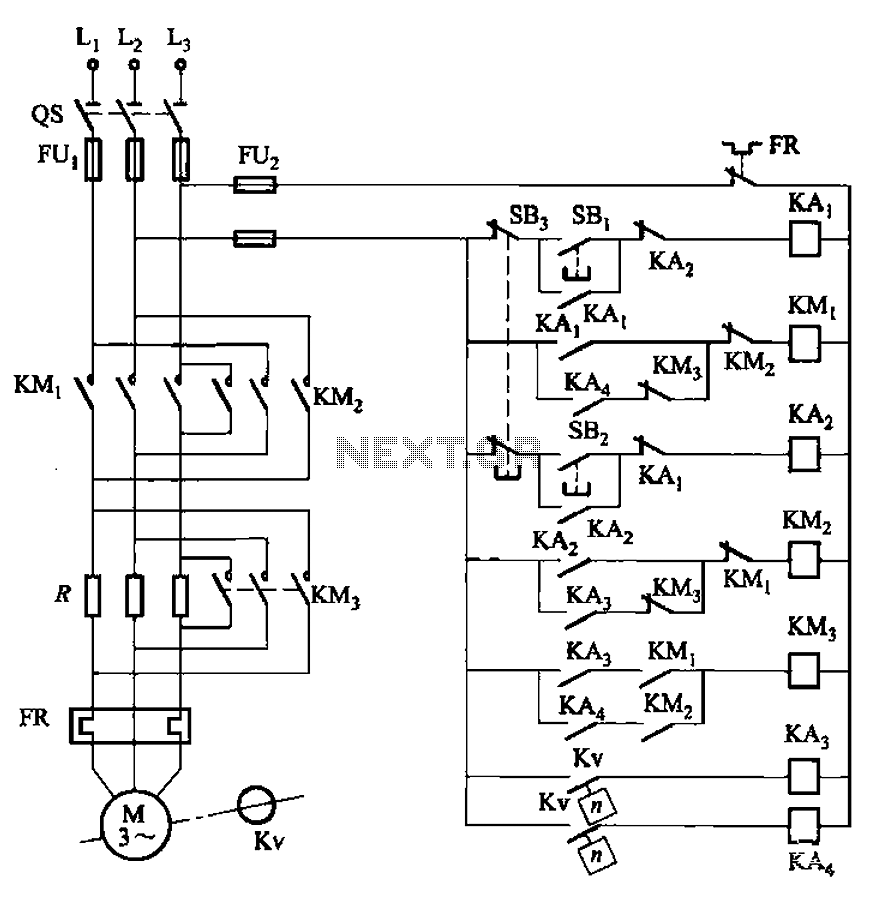
The circuit illustrated in Figure 3-130 differs from the circuit in Figure 3-129 in that when the stop button SB3 is pressed, the electric motor initiates braking. Furthermore, during both the startup and braking phases, the motor power lines are connected in series with a current limiting resistor.
The circuit in question employs a straightforward control mechanism for an electric motor, integrating a stop button (SB3) that triggers the braking process. When SB3 is activated, the circuit alters the flow of current to the motor, facilitating a controlled deceleration. The inclusion of a current limiting resistor in series with the motor power lines serves a dual purpose: it protects the motor from excessive current during startup and braking, and it ensures a gradual change in motor speed, which can prevent mechanical stress and enhance the longevity of the motor.
The configuration of the circuit allows for efficient operation by managing the electrical characteristics of the motor. During startup, the current limiting resistor restricts the amount of current flowing into the motor, reducing the inrush current, which is critical for preventing damage to the windings and associated components. When the motor is required to stop, pressing SB3 activates a braking mechanism that likely involves reversing the current flow or applying a braking resistor, thereby dissipating energy safely and effectively.
This circuit design is particularly useful in applications where precise control of motor speed and torque is necessary, such as in conveyor systems, automated machinery, or any system requiring reliable motor control. The careful selection of the current limiting resistor value is essential to balance performance and protection, ensuring that the motor operates within its specified parameters throughout its operational range. Circuit shown in Figure 3-130. The line differs from FIG 3-129 line that press the stop button SB3, the electric motor begins braking. In addition, start-up and braking, the mo tor power lines are in series with the current limiting resistor.
The circuit in question employs a straightforward control mechanism for an electric motor, integrating a stop button (SB3) that triggers the braking process. When SB3 is activated, the circuit alters the flow of current to the motor, facilitating a controlled deceleration. The inclusion of a current limiting resistor in series with the motor power lines serves a dual purpose: it protects the motor from excessive current during startup and braking, and it ensures a gradual change in motor speed, which can prevent mechanical stress and enhance the longevity of the motor.
The configuration of the circuit allows for efficient operation by managing the electrical characteristics of the motor. During startup, the current limiting resistor restricts the amount of current flowing into the motor, reducing the inrush current, which is critical for preventing damage to the windings and associated components. When the motor is required to stop, pressing SB3 activates a braking mechanism that likely involves reversing the current flow or applying a braking resistor, thereby dissipating energy safely and effectively.
This circuit design is particularly useful in applications where precise control of motor speed and torque is necessary, such as in conveyor systems, automated machinery, or any system requiring reliable motor control. The careful selection of the current limiting resistor value is essential to balance performance and protection, ensuring that the motor operates within its specified parameters throughout its operational range. Circuit shown in Figure 3-130. The line differs from FIG 3-129 line that press the stop button SB3, the electric motor begins braking. In addition, start-up and braking, the mo tor power lines are in series with the current limiting resistor.