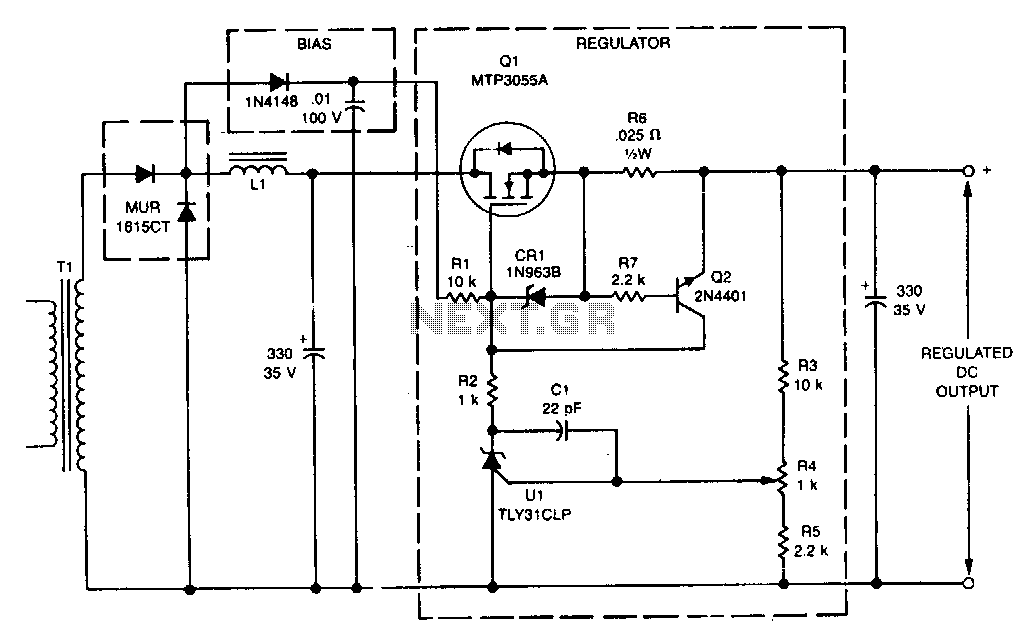
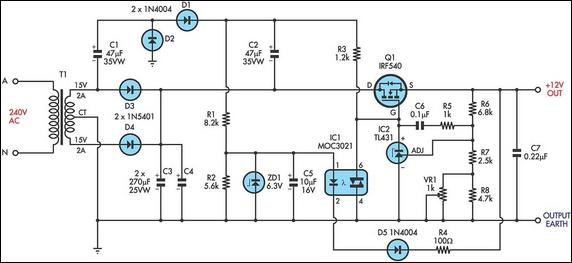
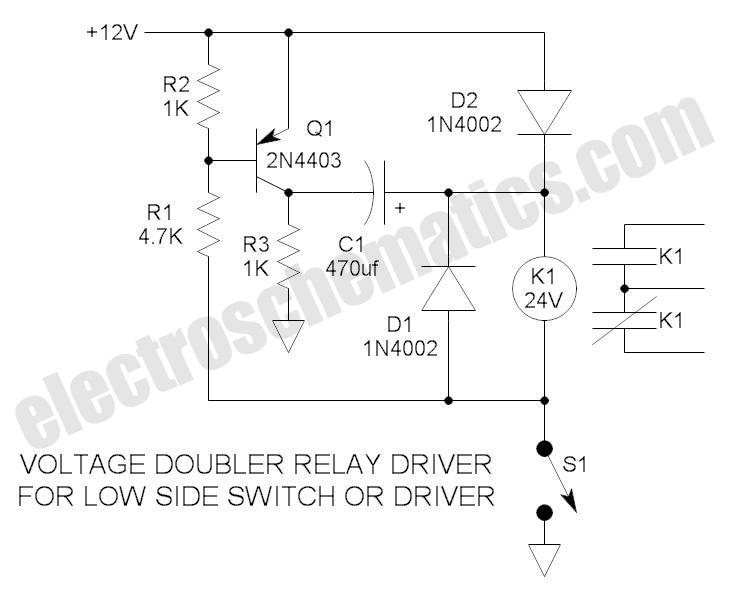
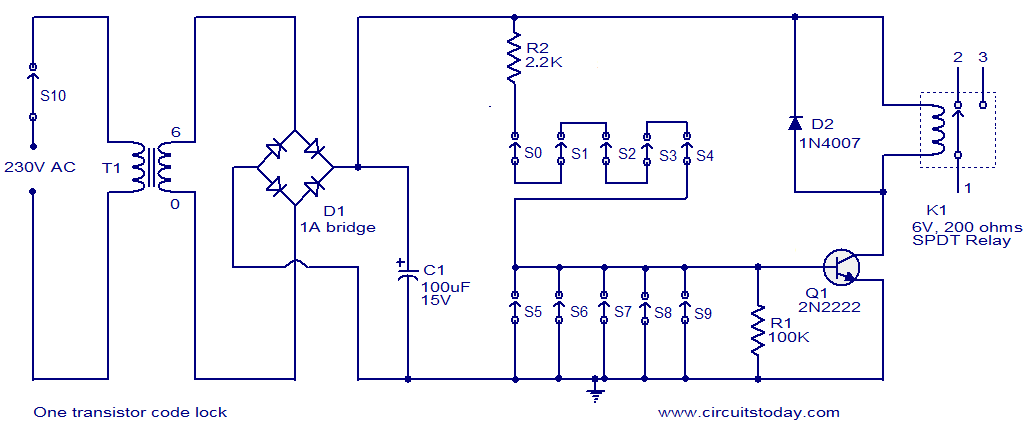
Transistor Buffer for Zener Diode Voltage Regulator
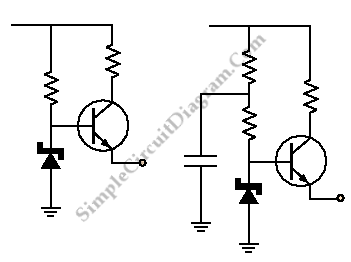
Buffering for the zener diode is achieved through the impedance matching and current amplifying features of the emitter follower, which draws less current from the zener.
Buffering in electronic circuits is essential for ensuring that the performance of one component does not adversely affect another, particularly in sensitive applications like zener diode voltage regulation. The emitter follower configuration, also known as a common-collector amplifier, serves as an effective buffer due to its high input impedance and low output impedance. This configuration allows the circuit to maintain the voltage level provided by the zener diode while minimizing the load it experiences.
In this setup, the zener diode regulates the voltage across its terminals, providing a stable reference voltage. The emitter follower, connected to the zener's output, takes this reference voltage and buffers it, allowing for higher current drive capabilities without drawing significant current from the zener itself. This is particularly important in applications where the zener diode needs to maintain its voltage regulation under varying load conditions.
The emitter follower's current amplification characteristics enable it to supply sufficient current to the load while keeping the zener diode operating within its specified parameters. This arrangement not only enhances the overall stability of the circuit but also improves the response time, making it suitable for dynamic applications where rapid changes in load current may occur.
In summary, utilizing an emitter follower to buffer a zener diode effectively combines the benefits of impedance matching and current amplification, ensuring reliable performance and improved efficiency in voltage regulation circuits.Buffering for the zener is provided by the impedance matching and current amplifying characteristics of the emitter follower and draw less current from it. To.. 🔗 External reference
Buffering in electronic circuits is essential for ensuring that the performance of one component does not adversely affect another, particularly in sensitive applications like zener diode voltage regulation. The emitter follower configuration, also known as a common-collector amplifier, serves as an effective buffer due to its high input impedance and low output impedance. This configuration allows the circuit to maintain the voltage level provided by the zener diode while minimizing the load it experiences.
In this setup, the zener diode regulates the voltage across its terminals, providing a stable reference voltage. The emitter follower, connected to the zener's output, takes this reference voltage and buffers it, allowing for higher current drive capabilities without drawing significant current from the zener itself. This is particularly important in applications where the zener diode needs to maintain its voltage regulation under varying load conditions.
The emitter follower's current amplification characteristics enable it to supply sufficient current to the load while keeping the zener diode operating within its specified parameters. This arrangement not only enhances the overall stability of the circuit but also improves the response time, making it suitable for dynamic applications where rapid changes in load current may occur.
In summary, utilizing an emitter follower to buffer a zener diode effectively combines the benefits of impedance matching and current amplification, ensuring reliable performance and improved efficiency in voltage regulation circuits.Buffering for the zener is provided by the impedance matching and current amplifying characteristics of the emitter follower and draw less current from it. To.. 🔗 External reference