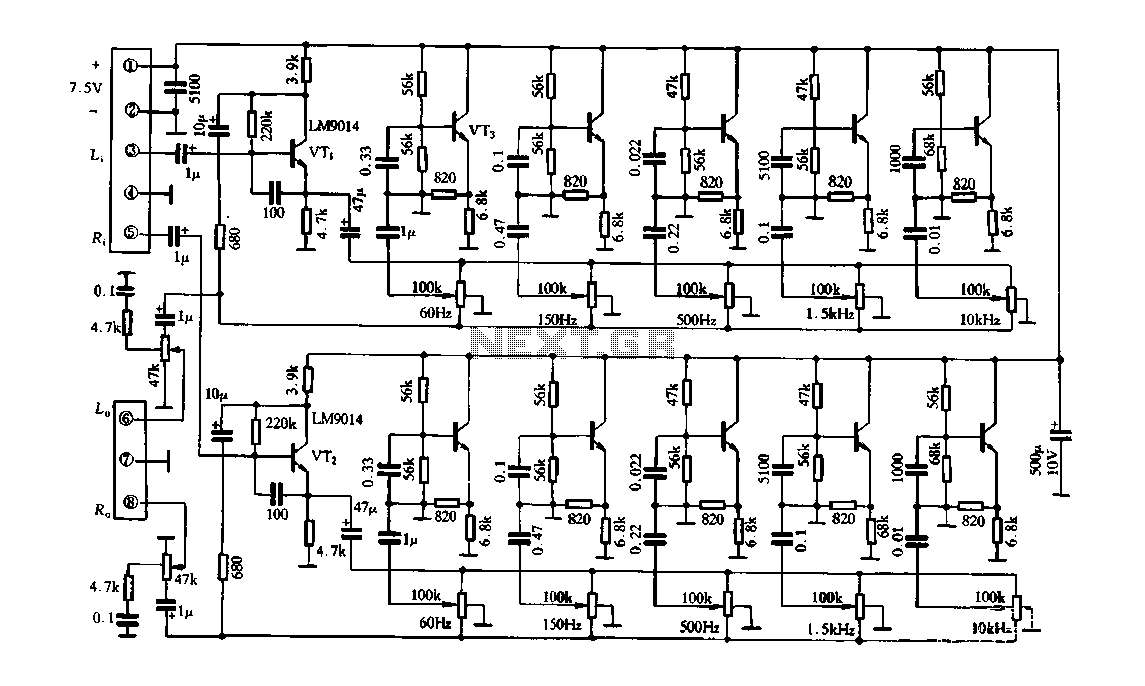
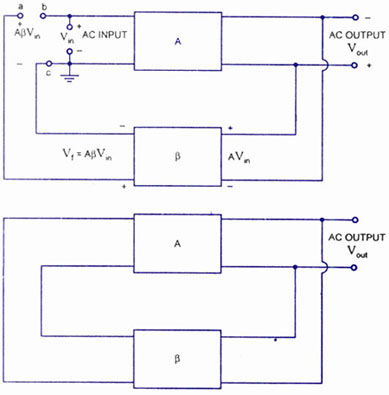
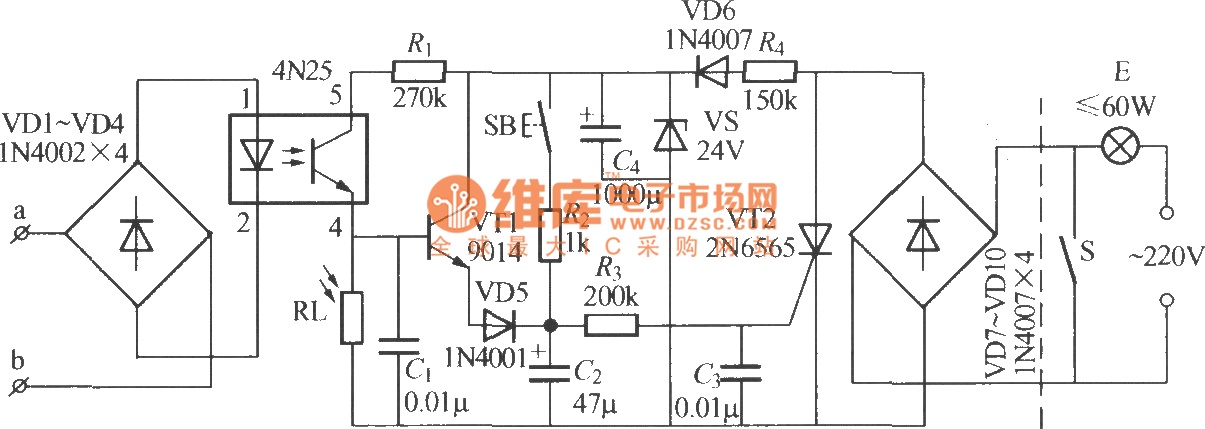
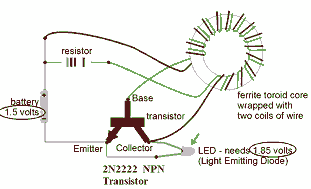
Variable Wein Bridge Oscillator Circuit
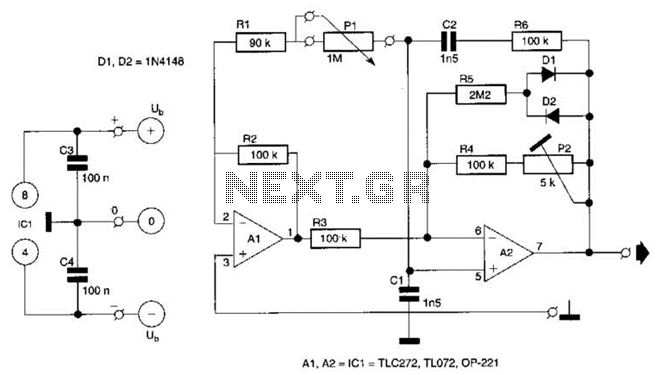
This circuit utilizes a single potentiometer to control a frequency range from 300 Hz to 3000 Hz. A FET operational amplifier is employed at stages A1 and A2. The upper frequency limit is dictated by the gain-bandwidth product of the operational amplifiers.
The circuit design incorporates a single potentiometer, which serves as a variable resistor, allowing for the adjustment of frequency within the specified range. The operational amplifiers (op-amps) used in this circuit are field-effect transistor (FET) types, known for their high input impedance and low noise characteristics, which are advantageous in frequency modulation applications.
At stage A1, the FET op-amp amplifies the input signal, with the gain set by the feedback network that includes the potentiometer. This stage is crucial for adjusting the amplitude of the output signal, ensuring that it remains within the optimal range for further processing.
Stage A2 continues the amplification process, further refining the signal. The gain-bandwidth product of the op-amps is a critical parameter, as it defines the maximum frequency at which the op-amps can effectively amplify the signal. In this circuit, the upper frequency limit of 3000 Hz is determined by this product, ensuring that the circuit can operate effectively across the entire frequency range.
Overall, the design emphasizes the importance of selecting appropriate components and configurations to achieve the desired frequency response. The use of a potentiometer for tuning provides flexibility, while the choice of FET op-amps ensures high performance and reliability in signal processing. This circuit uses a single potentiometer to time a 300- to 3000-Hz range. A FET op amp is used at A1 and A2. The upper frequency limit is determined by the gain-bandwidth product of the op amps.
The circuit design incorporates a single potentiometer, which serves as a variable resistor, allowing for the adjustment of frequency within the specified range. The operational amplifiers (op-amps) used in this circuit are field-effect transistor (FET) types, known for their high input impedance and low noise characteristics, which are advantageous in frequency modulation applications.
At stage A1, the FET op-amp amplifies the input signal, with the gain set by the feedback network that includes the potentiometer. This stage is crucial for adjusting the amplitude of the output signal, ensuring that it remains within the optimal range for further processing.
Stage A2 continues the amplification process, further refining the signal. The gain-bandwidth product of the op-amps is a critical parameter, as it defines the maximum frequency at which the op-amps can effectively amplify the signal. In this circuit, the upper frequency limit of 3000 Hz is determined by this product, ensuring that the circuit can operate effectively across the entire frequency range.
Overall, the design emphasizes the importance of selecting appropriate components and configurations to achieve the desired frequency response. The use of a potentiometer for tuning provides flexibility, while the choice of FET op-amps ensures high performance and reliability in signal processing. This circuit uses a single potentiometer to time a 300- to 3000-Hz range. A FET op amp is used at A1 and A2. The upper frequency limit is determined by the gain-bandwidth product of the op amps.