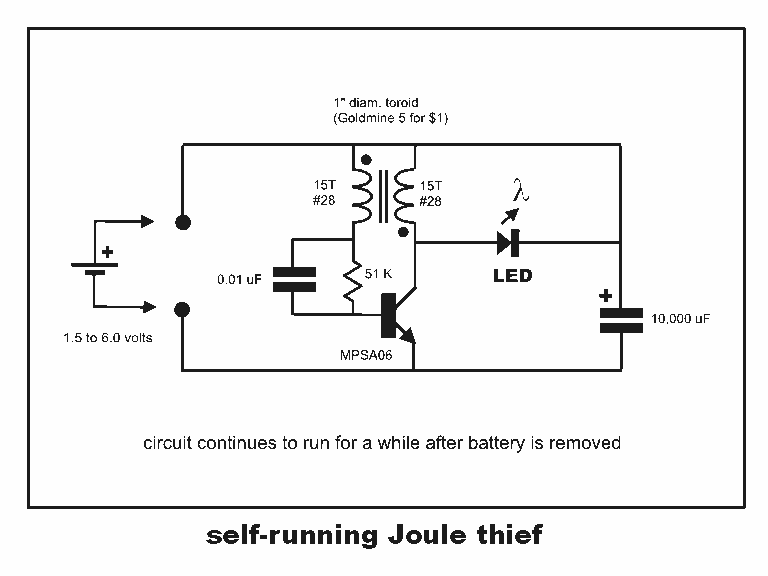
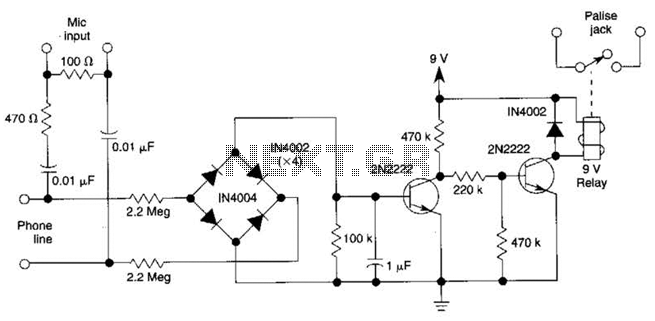
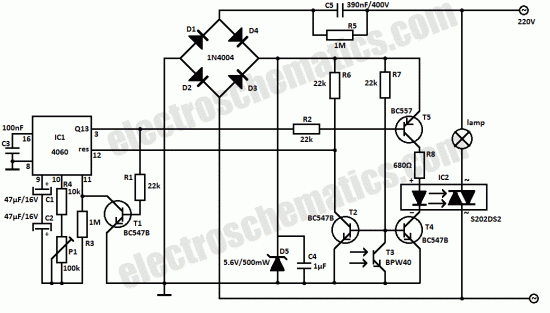
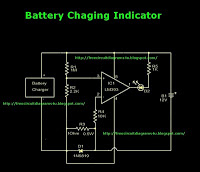
Vehicle lights at night rendezvous controlled circuit
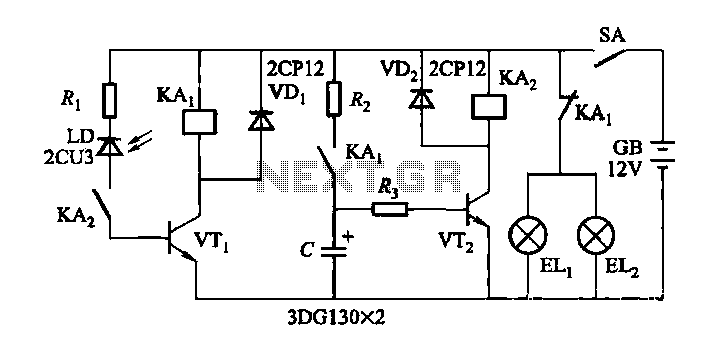
When driving at night and approaching another vehicle, traffic regulations dictate that the distance between the two vehicles should be maintained. This is achieved by alternately activating and deactivating the high beams, while utilizing either the wide lights or low beam lights to ensure the safety of passing vehicles. The circuit depicted in Figure 13-50 is designed to fulfill this function, with ELi and EL2 representing the high beams and SA functioning as a manual switch.
The circuit in Figure 13-50 operates by controlling the high beam lights (ELi and EL2) in response to the manual switch (SA). When the switch is activated, it sends a signal to the circuit that alternates the power supply to the high beams. This alternation is crucial for maintaining compliance with traffic regulations, which require that drivers do not dazzle oncoming vehicles with constant high beam usage.
The circuit may include additional components such as resistors to limit current flow, ensuring that the high beams operate within their specified voltage ratings. A relay could also be incorporated to handle the higher current required by the high beams, allowing the manual switch to control the relay instead of directly powering the lights.
Furthermore, the circuit can be designed with a timer or a microcontroller to automate the alternation process, enhancing convenience and ensuring compliance with regulations without requiring constant manual intervention. Safety features, such as diodes, may be included to prevent back EMF from damaging the circuit components when the relay is deactivated.
In summary, the described circuit effectively manages the operation of vehicle high beams in accordance with traffic regulations, enhancing safety during nighttime driving by ensuring that drivers can communicate their presence without compromising the visibility of other road users.Driving at night, when there is a vehicle rendezvous, according to traffic regulations prescribed distance should begin two vehicles alternately opening and closing the big lig ht, while OFF, showing the wide lights or low beam lights to ensure the safety of vehicles pass through. The circuit shown in Figure 13-50 to play this role. Figure, ELi and EL2 for the big lights, SA manual switch.
The circuit in Figure 13-50 operates by controlling the high beam lights (ELi and EL2) in response to the manual switch (SA). When the switch is activated, it sends a signal to the circuit that alternates the power supply to the high beams. This alternation is crucial for maintaining compliance with traffic regulations, which require that drivers do not dazzle oncoming vehicles with constant high beam usage.
The circuit may include additional components such as resistors to limit current flow, ensuring that the high beams operate within their specified voltage ratings. A relay could also be incorporated to handle the higher current required by the high beams, allowing the manual switch to control the relay instead of directly powering the lights.
Furthermore, the circuit can be designed with a timer or a microcontroller to automate the alternation process, enhancing convenience and ensuring compliance with regulations without requiring constant manual intervention. Safety features, such as diodes, may be included to prevent back EMF from damaging the circuit components when the relay is deactivated.
In summary, the described circuit effectively manages the operation of vehicle high beams in accordance with traffic regulations, enhancing safety during nighttime driving by ensuring that drivers can communicate their presence without compromising the visibility of other road users.Driving at night, when there is a vehicle rendezvous, according to traffic regulations prescribed distance should begin two vehicles alternately opening and closing the big lig ht, while OFF, showing the wide lights or low beam lights to ensure the safety of vehicles pass through. The circuit shown in Figure 13-50 to play this role. Figure, ELi and EL2 for the big lights, SA manual switch.