Voltage follower with 1G ohm input resistances
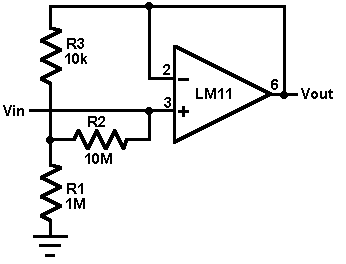
This circuit utilizes an LM11 operational amplifier configured as a voltage follower with an input resistance of 1 GΩ, constructed using standard resistor values. When the input is left disconnected, the input offset voltage is amplified by the same factor as R2; however, this additional error is minimal due to the low offset voltage characteristic of the LM11. Connecting the input to a source with a resistance of less than 1 GΩ further reduces this error. In the case of an AC-coupled input, a second 10 MΩ resistor can be added in series with the inverting input to effectively eliminate bias current error; removing this resistor would result in negligible noise.
The described circuit employs the LM11 operational amplifier, a precision device known for its low offset voltage and high input impedance, making it suitable for applications requiring minimal signal distortion. The configuration as a voltage follower allows the circuit to maintain the input signal while providing high input resistance, which is essential when interfacing with high-impedance sources.
The use of a 1 GΩ resistor in conjunction with the LM11 ensures that the circuit does not load the signal source, preserving the integrity of the input signal. The input offset voltage, while typically small, can introduce errors in precision applications. By multiplying this offset by the feedback resistor R2, the circuit can account for this error, although the overall impact remains low due to the LM11's specifications.
When the input is connected to a source with a resistance lower than 1 GΩ, the error introduced by the input offset voltage is further minimized, enhancing the accuracy of the output signal. To accommodate AC signals, the addition of a 10 MΩ resistor in series with the inverting input is an effective strategy to mitigate bias current errors, which can otherwise distort the signal. This configuration allows for a more stable and reliable operation, particularly in sensitive applications.
If the series resistor is bypassed, the circuit remains functional with minimal noise, maintaining signal fidelity. This design approach is particularly advantageous in high-precision measurement systems, sensor applications, and any scenario where signal integrity is paramount. Overall, the circuit exemplifies a careful balance of component selection and configuration to achieve high performance in voltage follower applications.This circuit uses an LM11 to form a voltage follower with 1G ohm input resistance built using standard resistor values. With the input disconnected, the input offset voltage is multiplied by the same factor as R2; but the added error is small because the offset voltage of the LM11 is so low.
When the input is connected to a source less than 1G ohm , this error is reduced. For an ac-coupled input a second 10M resistor could be connected in series with the inverting input to virtually eliminate bias current error; bypassing it would give minimal noise. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit employs the LM11 operational amplifier, a precision device known for its low offset voltage and high input impedance, making it suitable for applications requiring minimal signal distortion. The configuration as a voltage follower allows the circuit to maintain the input signal while providing high input resistance, which is essential when interfacing with high-impedance sources.
The use of a 1 GΩ resistor in conjunction with the LM11 ensures that the circuit does not load the signal source, preserving the integrity of the input signal. The input offset voltage, while typically small, can introduce errors in precision applications. By multiplying this offset by the feedback resistor R2, the circuit can account for this error, although the overall impact remains low due to the LM11's specifications.
When the input is connected to a source with a resistance lower than 1 GΩ, the error introduced by the input offset voltage is further minimized, enhancing the accuracy of the output signal. To accommodate AC signals, the addition of a 10 MΩ resistor in series with the inverting input is an effective strategy to mitigate bias current errors, which can otherwise distort the signal. This configuration allows for a more stable and reliable operation, particularly in sensitive applications.
If the series resistor is bypassed, the circuit remains functional with minimal noise, maintaining signal fidelity. This design approach is particularly advantageous in high-precision measurement systems, sensor applications, and any scenario where signal integrity is paramount. Overall, the circuit exemplifies a careful balance of component selection and configuration to achieve high performance in voltage follower applications.This circuit uses an LM11 to form a voltage follower with 1G ohm input resistance built using standard resistor values. With the input disconnected, the input offset voltage is multiplied by the same factor as R2; but the added error is small because the offset voltage of the LM11 is so low.
When the input is connected to a source less than 1G ohm , this error is reduced. For an ac-coupled input a second 10M resistor could be connected in series with the inverting input to virtually eliminate bias current error; bypassing it would give minimal noise. 🔗 External reference