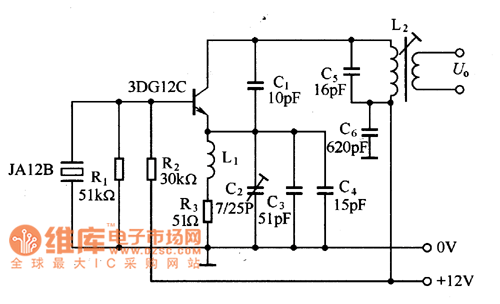
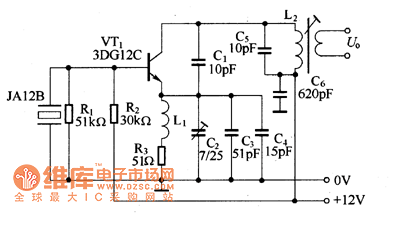
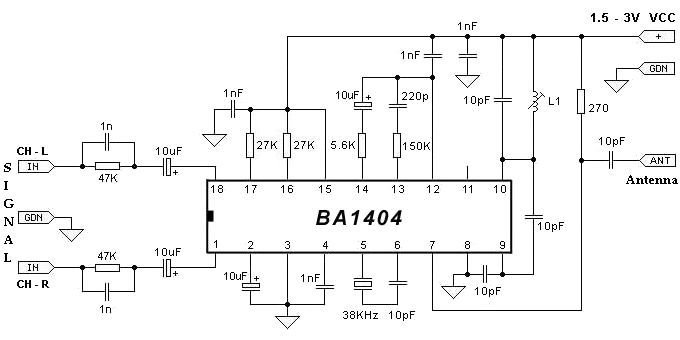
walkie talkie circuit research project

For example, I do not understand the process of demodulation or the modulation itself, and so on. Is there someone who can understand this circuit? Could you please assist me?
The circuit in question likely involves a modulation and demodulation process, which is essential in communication systems for transmitting information over various media. Modulation refers to the technique of varying a carrier signal's properties, such as amplitude, frequency, or phase, to encode the information being sent. Common modulation techniques include Amplitude Modulation (AM), Frequency Modulation (FM), and Phase Modulation (PM).
Demodulation is the reverse process, where the modulated signal is converted back into its original form for interpretation. This process typically involves filtering, amplification, and signal detection to retrieve the encoded information. The circuit may include components such as mixers, filters, amplifiers, and demodulators tailored to the specific modulation technique used.
A detailed understanding of the circuit's schematic is crucial for grasping the modulation and demodulation processes. Key components to examine include the input signal source, the modulator stage, which shapes the carrier signal based on the input, and the demodulator stage, which extracts the original signal from the modulated carrier. Additionally, analyzing the power supply, grounding, and signal paths within the circuit can provide insights into its operation and performance.
To gain a better understanding, it may be beneficial to study the specific type of modulation employed, the frequency ranges involved, and the intended application of the circuit. This knowledge will facilitate a clearer comprehension of how the circuit functions overall and the role each component plays in the modulation and demodulation processes.for example i dont get the way the demodulation is done or the modulation itself an so on please is someone able to understand this circuit could you give me a hand 🔗 External reference
The circuit in question likely involves a modulation and demodulation process, which is essential in communication systems for transmitting information over various media. Modulation refers to the technique of varying a carrier signal's properties, such as amplitude, frequency, or phase, to encode the information being sent. Common modulation techniques include Amplitude Modulation (AM), Frequency Modulation (FM), and Phase Modulation (PM).
Demodulation is the reverse process, where the modulated signal is converted back into its original form for interpretation. This process typically involves filtering, amplification, and signal detection to retrieve the encoded information. The circuit may include components such as mixers, filters, amplifiers, and demodulators tailored to the specific modulation technique used.
A detailed understanding of the circuit's schematic is crucial for grasping the modulation and demodulation processes. Key components to examine include the input signal source, the modulator stage, which shapes the carrier signal based on the input, and the demodulator stage, which extracts the original signal from the modulated carrier. Additionally, analyzing the power supply, grounding, and signal paths within the circuit can provide insights into its operation and performance.
To gain a better understanding, it may be beneficial to study the specific type of modulation employed, the frequency ranges involved, and the intended application of the circuit. This knowledge will facilitate a clearer comprehension of how the circuit functions overall and the role each component plays in the modulation and demodulation processes.for example i dont get the way the demodulation is done or the modulation itself an so on please is someone able to understand this circuit could you give me a hand 🔗 External reference