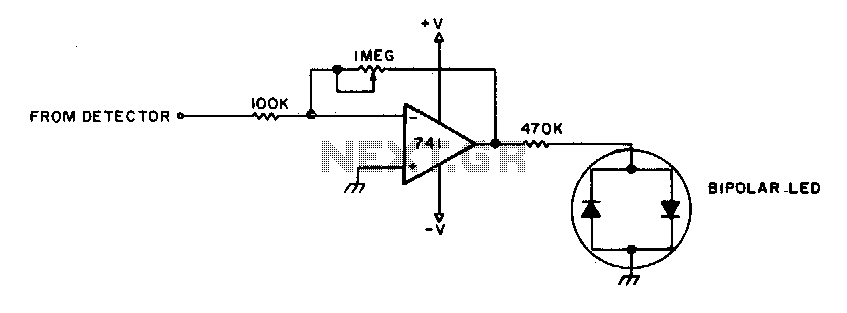
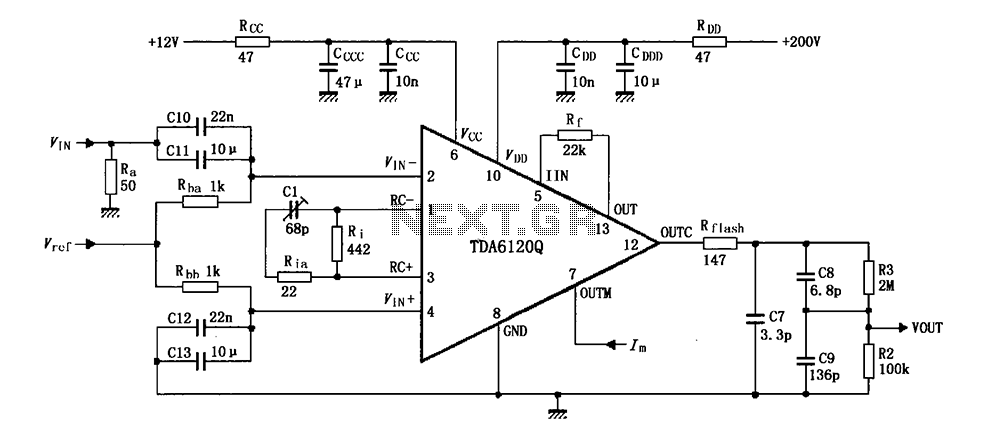
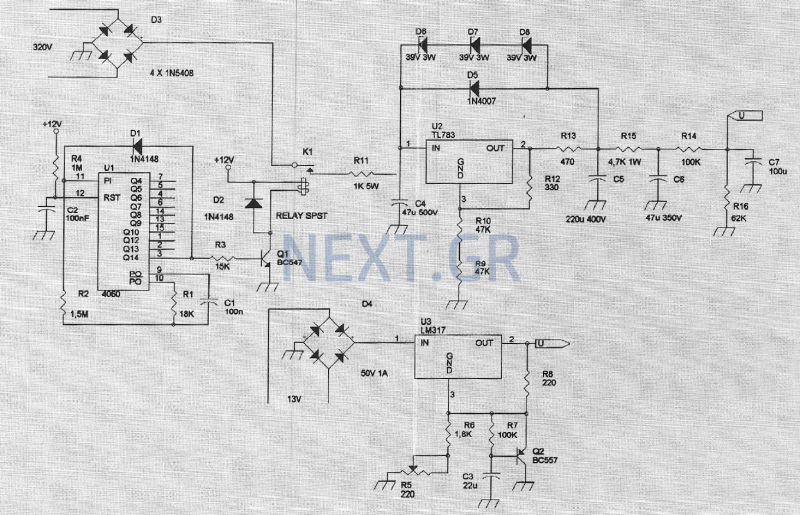
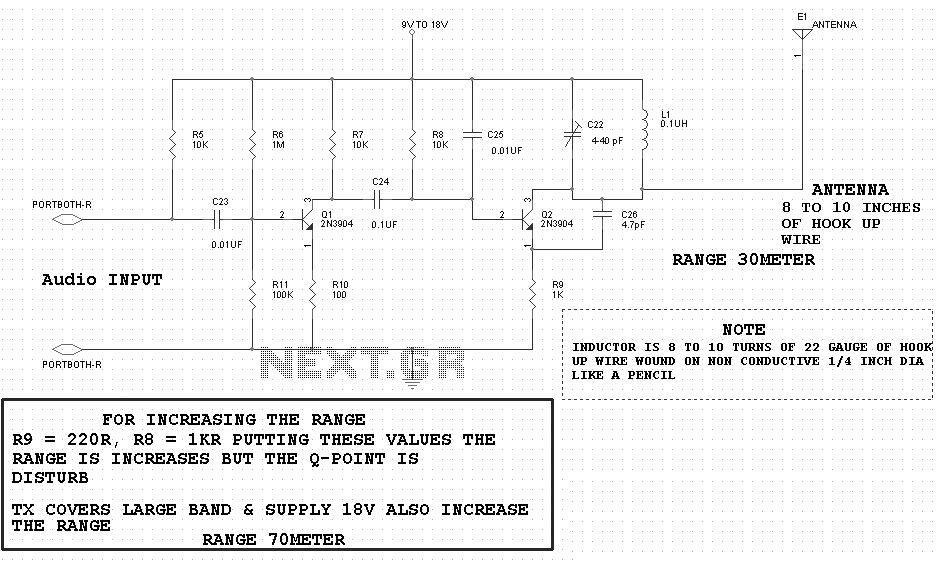
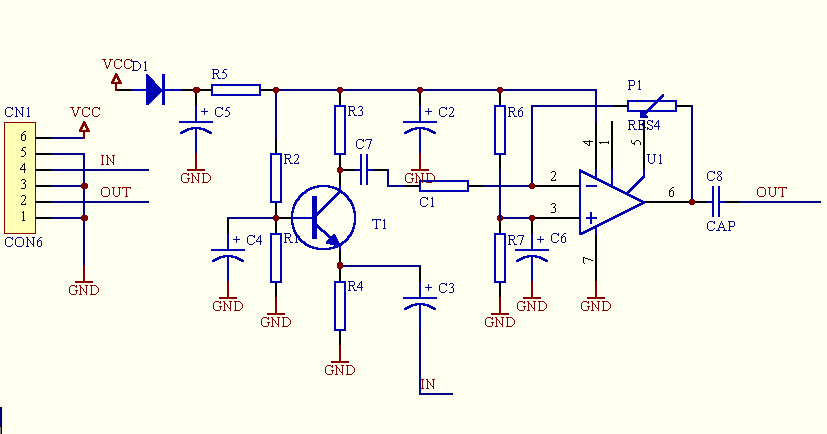
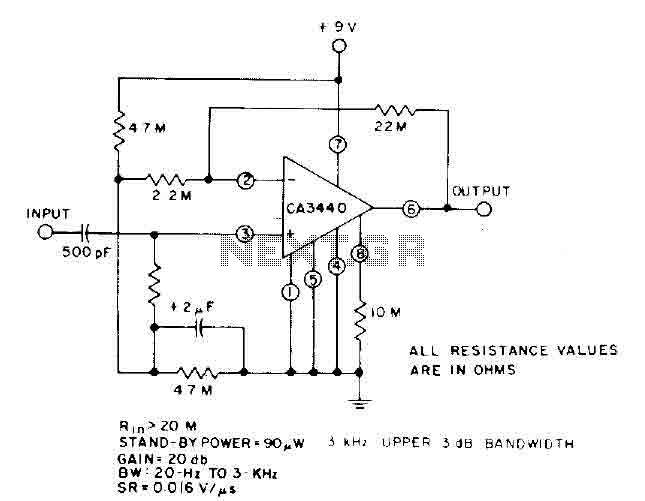
Zero Feedback Impedance Amplifiers
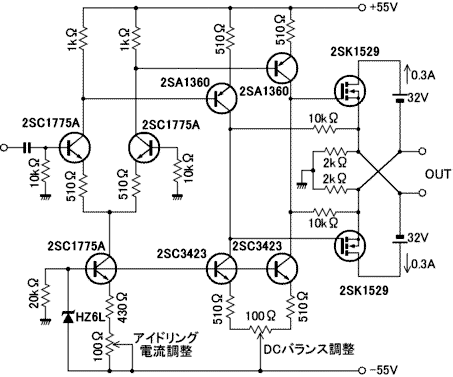
The amplifier in question is comparable to another model that has a lower parts count. It is worthy of construction.
The amplifier under discussion features a simplified design that maintains high performance while reducing the number of components required for assembly. This can lead to easier troubleshooting, lower manufacturing costs, and potentially improved reliability.
Key components typically include operational amplifiers, resistors, capacitors, and transistors, arranged in a configuration that optimizes signal amplification. The schematic may show a power supply stage, input stage, and output stage, with each section designed to handle specific tasks such as filtering, gain adjustment, and output drive.
The power supply section is crucial, as it provides the necessary voltage and current to the amplifier. It may involve a transformer, rectifier, and smoothing capacitors to ensure a stable DC supply.
The input stage usually consists of a differential amplifier configuration to minimize noise and improve signal integrity. This stage might include input coupling capacitors to block DC offsets while allowing AC signals to pass through.
The gain stage amplifies the input signal, typically using a combination of transistors and feedback resistors to set the gain level. This stage must be carefully designed to avoid distortion and maintain linearity across the desired frequency range.
Lastly, the output stage is responsible for driving the load, which could be a speaker or another circuit. It may employ a push-pull configuration to enhance efficiency and reduce heat generation.
In summary, this amplifier design, with its lower parts count, is not only feasible but also advantageous for those looking to build an efficient and effective audio amplification solution.Dear Susan, your amp is similar to this one which has even a lower parts number. It deserves to be built!.. 🔗 External reference
The amplifier under discussion features a simplified design that maintains high performance while reducing the number of components required for assembly. This can lead to easier troubleshooting, lower manufacturing costs, and potentially improved reliability.
Key components typically include operational amplifiers, resistors, capacitors, and transistors, arranged in a configuration that optimizes signal amplification. The schematic may show a power supply stage, input stage, and output stage, with each section designed to handle specific tasks such as filtering, gain adjustment, and output drive.
The power supply section is crucial, as it provides the necessary voltage and current to the amplifier. It may involve a transformer, rectifier, and smoothing capacitors to ensure a stable DC supply.
The input stage usually consists of a differential amplifier configuration to minimize noise and improve signal integrity. This stage might include input coupling capacitors to block DC offsets while allowing AC signals to pass through.
The gain stage amplifies the input signal, typically using a combination of transistors and feedback resistors to set the gain level. This stage must be carefully designed to avoid distortion and maintain linearity across the desired frequency range.
Lastly, the output stage is responsible for driving the load, which could be a speaker or another circuit. It may employ a push-pull configuration to enhance efficiency and reduce heat generation.
In summary, this amplifier design, with its lower parts count, is not only feasible but also advantageous for those looking to build an efficient and effective audio amplification solution.Dear Susan, your amp is similar to this one which has even a lower parts number. It deserves to be built!.. 🔗 External reference