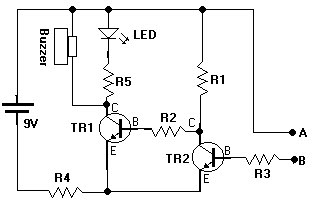
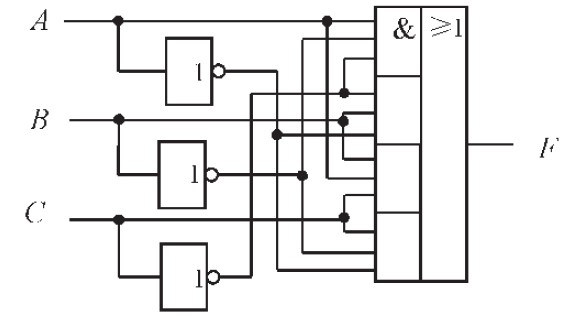
Light Bus speed detecting circuit diagrams
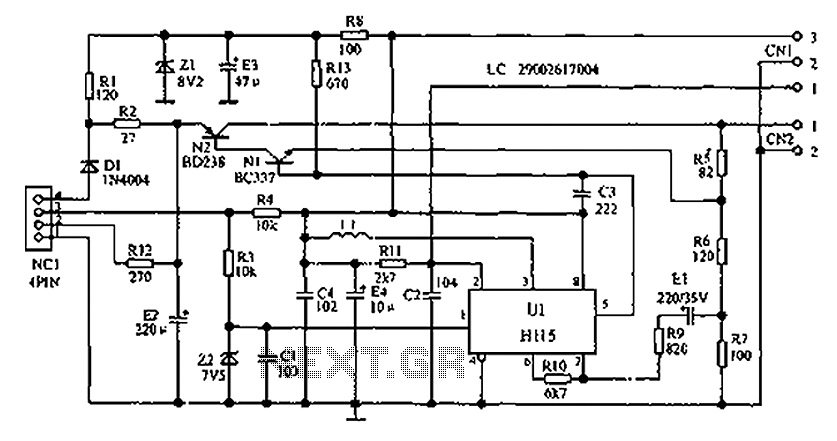
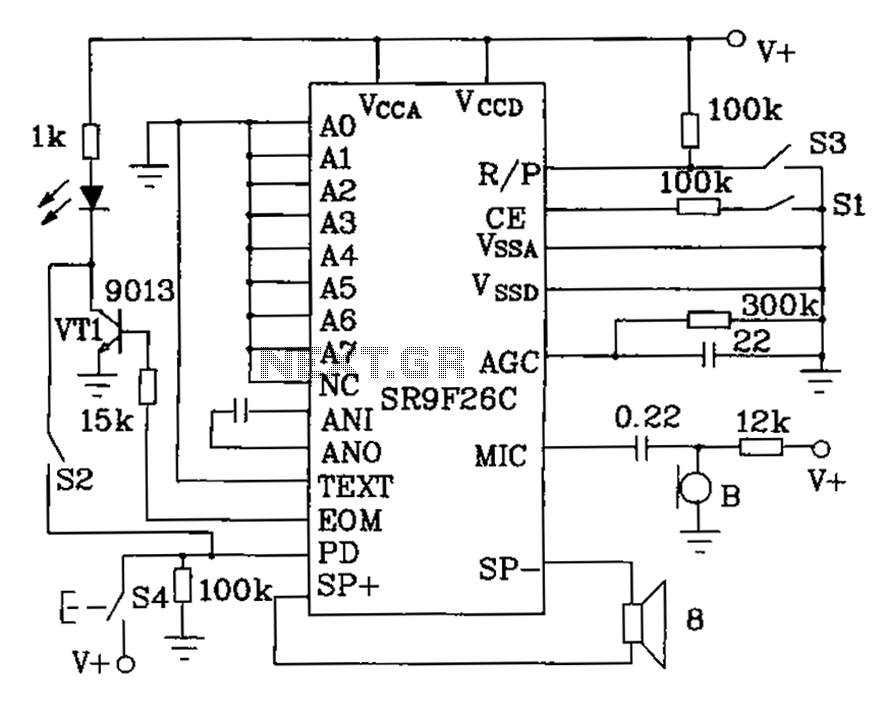
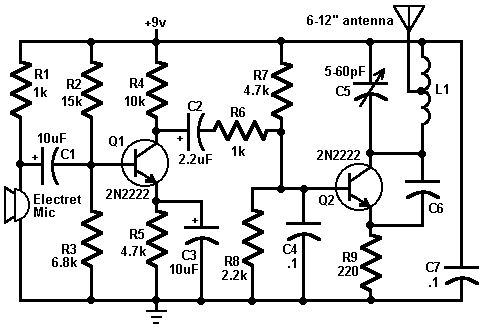
The following describes the circuits of a minibus odometer, which integrates electronic and mechanical components to form a new type of instrument for measuring distance and speed. Pulse signals are generated by the locomotive speed detection system and transmitted to the NC1 instrument cluster. These signals then pass through the dash panel to the core of the U1 electronic signal processing system for further processing, ultimately driving the electromagnetic meter to display mileage and speed.
The minibus odometer circuit operates by utilizing a combination of electronic and mechanical systems to accurately measure and display vehicle speed and distance traveled. The pulse signals generated by the speed detection mechanism are crucial for the proper functioning of the odometer and speedometer. These pulse signals are typically produced by a sensor that detects the rotation of the vehicle's wheels or transmission output shaft.
Upon generation, the pulse signals are sent to the NC1 instrument cluster, which serves as the primary interface for the driver. The signals travel through the dash panel, where they are routed to the U1 electronic signal processing unit. This processing unit is responsible for interpreting the incoming pulse signals, converting them into meaningful data that reflects the vehicle's speed and distance.
The U1 unit employs various electronic components, such as microcontrollers or dedicated signal processing ICs, to analyze the frequency and duration of the received pulse signals. This data is then used to calculate the vehicle's speed in real-time, which is displayed on the speedometer. Additionally, the odometer function accumulates these signals over time to compute the total distance traveled, which is shown on the odometer display.
The final output is then transmitted to an electromagnetic meter, which uses electromagnetic induction principles to visually represent the speed and distance. This combination of electronic processing and mechanical display provides a reliable and efficient means for drivers to monitor their vehicle's performance. Overall, the integration of these systems results in a modern odometer that enhances the driving experience by providing accurate and real-time information. As shown below, is described in a minibus odometer circuits, the odometer and speedometer is electronic, mechanical integration combination of new instruments. Pulse signal out put from the locomotive speed detecting means, away from the NC1 instrument cluster, after the dash panel through to the core of U1 electronic signal processing system for processing, driving the electromagnetic meter shows mileage and speed.
The minibus odometer circuit operates by utilizing a combination of electronic and mechanical systems to accurately measure and display vehicle speed and distance traveled. The pulse signals generated by the speed detection mechanism are crucial for the proper functioning of the odometer and speedometer. These pulse signals are typically produced by a sensor that detects the rotation of the vehicle's wheels or transmission output shaft.
Upon generation, the pulse signals are sent to the NC1 instrument cluster, which serves as the primary interface for the driver. The signals travel through the dash panel, where they are routed to the U1 electronic signal processing unit. This processing unit is responsible for interpreting the incoming pulse signals, converting them into meaningful data that reflects the vehicle's speed and distance.
The U1 unit employs various electronic components, such as microcontrollers or dedicated signal processing ICs, to analyze the frequency and duration of the received pulse signals. This data is then used to calculate the vehicle's speed in real-time, which is displayed on the speedometer. Additionally, the odometer function accumulates these signals over time to compute the total distance traveled, which is shown on the odometer display.
The final output is then transmitted to an electromagnetic meter, which uses electromagnetic induction principles to visually represent the speed and distance. This combination of electronic processing and mechanical display provides a reliable and efficient means for drivers to monitor their vehicle's performance. Overall, the integration of these systems results in a modern odometer that enhances the driving experience by providing accurate and real-time information. As shown below, is described in a minibus odometer circuits, the odometer and speedometer is electronic, mechanical integration combination of new instruments. Pulse signal out put from the locomotive speed detecting means, away from the NC1 instrument cluster, after the dash panel through to the core of U1 electronic signal processing system for processing, driving the electromagnetic meter shows mileage and speed.