1 hour LM122 timer circuit
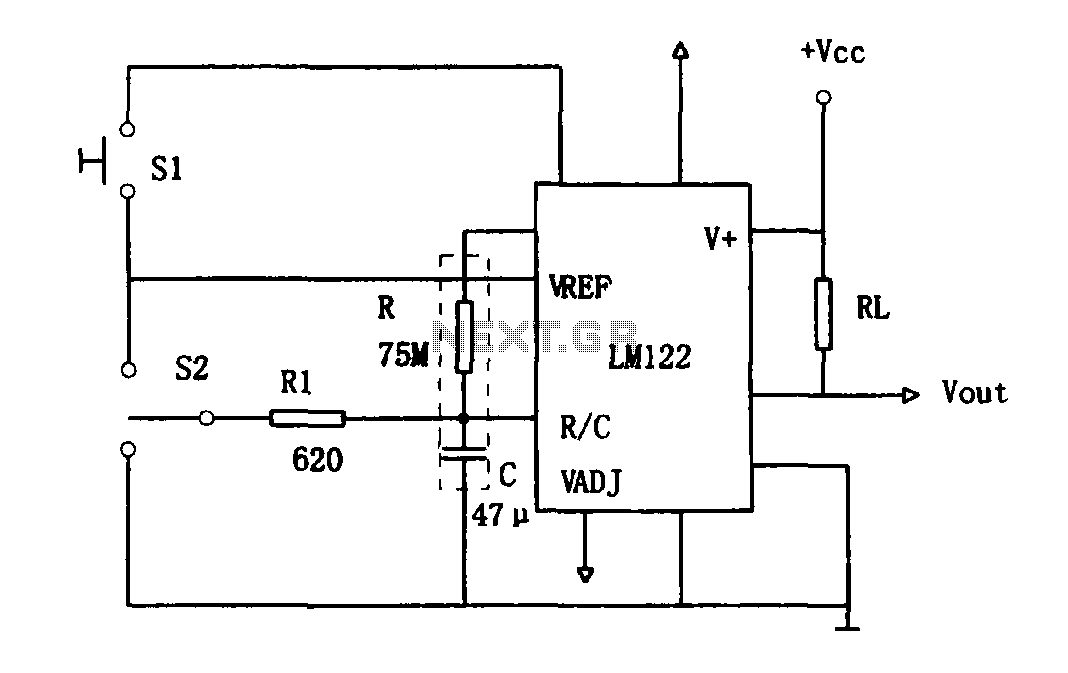
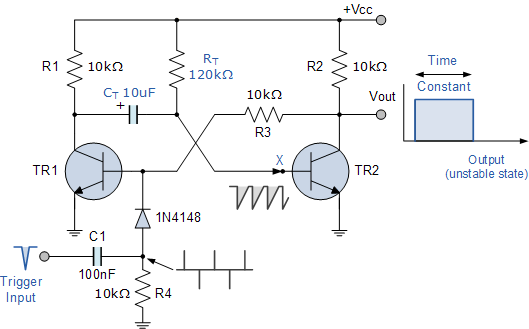
As illustrated in Figure 1, the circuit utilizes an LM122 timer. The circuit's start, reset, and stop functions are managed through switching operations. Switch S1 initiates the timing sequence when the timer is activated; thereafter, this switch has no further effect. S2 serves as the central "off" switch, allowing the timer to transition through its operational states: charge, open, and discharge. If the charging process is halted midway, the timer will revert to its active state even if the set time has not been reached. When capacitor C discharges, the voltage at the R/C terminal drops to zero, placing the discharge component in a waiting state for the start signal from S1. Even when in recovery mode, the timer output remains unchanged. Consequently, the timer retains its output state during the reset process, and at this point, capacitor C begins charging again, prompting the timer to adjust its working hours.
The LM122 timer circuit operates based on a combination of charging and discharging cycles controlled by the state of the switches. The circuit is designed to function in different modes, which are initiated by the action of S1 and S2. When switch S1 is pressed, the timer begins its timing cycle, allowing capacitor C to charge. The charging phase continues until the timer reaches the predetermined time or until S2 is activated to stop the timing process.
During the charging phase, the capacitor accumulates voltage, which is monitored at the R/C terminal. Once the voltage reaches a specific threshold, the timer transitions to the open state, allowing for the discharge of capacitor C. If the timing needs to be stopped before the set duration is completed, activating switch S2 interrupts the charging process, and the circuit enters a standby mode. In this mode, the voltage at the R/C terminal drops to zero, indicating that capacitor C is fully discharged and ready to receive a new start signal.
The reset function of the circuit is critical to its operation, as it allows the timer to maintain its output state regardless of the charging status of capacitor C. This ensures that when the timer is reset, it does not disrupt the ongoing processes and can resume operation smoothly when the start signal is received again. The design of this timer circuit provides flexibility in timing applications, making it suitable for various electronic projects where precise timing control is essential. The LM122 timer's integrated features, combined with the manual switching options, create a versatile and efficient timing solution.As shown in Figure 1 hour using a LM122 timer circuit. Start of the circuit, reset and stop halfway, etc. are converted by the switching operation. Figure, S1 to start timing when the timer is started, then this switch has no effect. S2 is centrally located in the "off" switch, the timer can switch through the conversion is completed: Charge - open - discharge. Since midway stop charging, even if not to the timer set time, the charging station will return to work status timer output lines.
When the C discharge, R / C terminal voltage is zero, the discharge position waiting for start signal S1. Even if the recovery position. Work status timer output line does not change, therefore, the timer is reset when the work which the state remains the same output line, in this moment, C starts charging again, start a timer to change working hours.
The LM122 timer circuit operates based on a combination of charging and discharging cycles controlled by the state of the switches. The circuit is designed to function in different modes, which are initiated by the action of S1 and S2. When switch S1 is pressed, the timer begins its timing cycle, allowing capacitor C to charge. The charging phase continues until the timer reaches the predetermined time or until S2 is activated to stop the timing process.
During the charging phase, the capacitor accumulates voltage, which is monitored at the R/C terminal. Once the voltage reaches a specific threshold, the timer transitions to the open state, allowing for the discharge of capacitor C. If the timing needs to be stopped before the set duration is completed, activating switch S2 interrupts the charging process, and the circuit enters a standby mode. In this mode, the voltage at the R/C terminal drops to zero, indicating that capacitor C is fully discharged and ready to receive a new start signal.
The reset function of the circuit is critical to its operation, as it allows the timer to maintain its output state regardless of the charging status of capacitor C. This ensures that when the timer is reset, it does not disrupt the ongoing processes and can resume operation smoothly when the start signal is received again. The design of this timer circuit provides flexibility in timing applications, making it suitable for various electronic projects where precise timing control is essential. The LM122 timer's integrated features, combined with the manual switching options, create a versatile and efficient timing solution.As shown in Figure 1 hour using a LM122 timer circuit. Start of the circuit, reset and stop halfway, etc. are converted by the switching operation. Figure, S1 to start timing when the timer is started, then this switch has no effect. S2 is centrally located in the "off" switch, the timer can switch through the conversion is completed: Charge - open - discharge. Since midway stop charging, even if not to the timer set time, the charging station will return to work status timer output lines.
When the C discharge, R / C terminal voltage is zero, the discharge position waiting for start signal S1. Even if the recovery position. Work status timer output line does not change, therefore, the timer is reset when the work which the state remains the same output line, in this moment, C starts charging again, start a timer to change working hours.