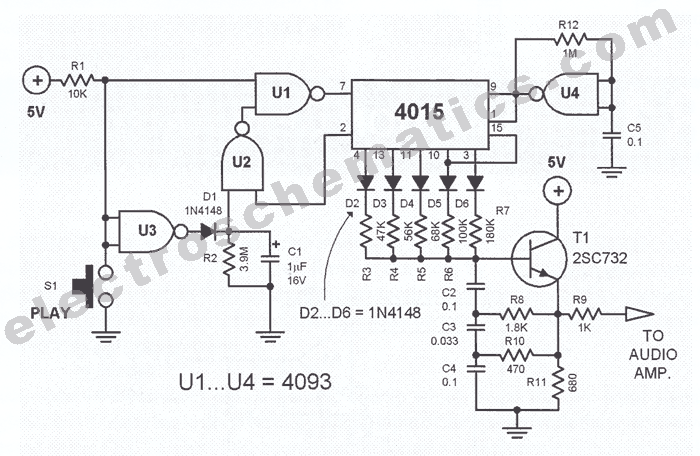
10 to 1000 MHz Oscillator circuit with RF2506
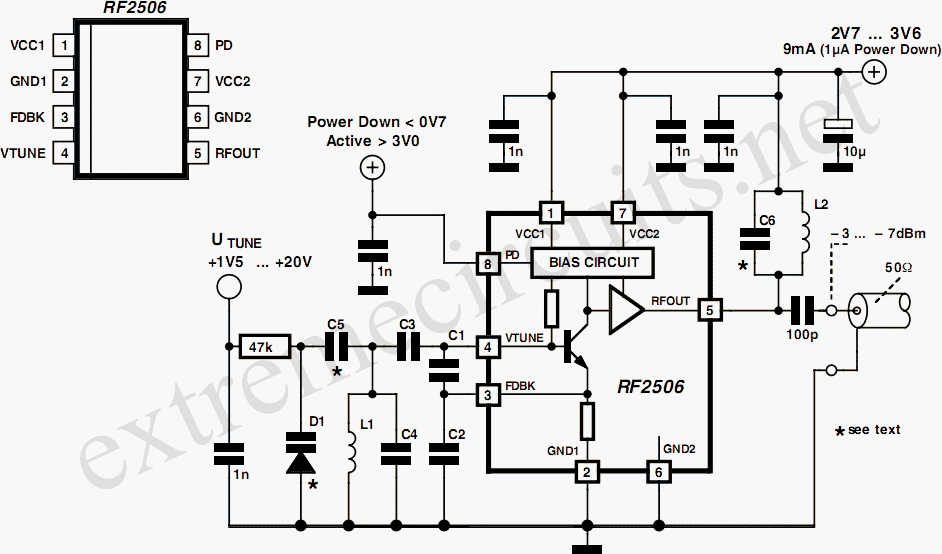
Today, it is no longer necessary to use discrete components for constructing oscillators. Many manufacturers now offer ready-made voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) integrated circuits (ICs) that require only a few external components to determine the frequency. An example of such an IC is the RF Micro Devices RF2506, which operates with a supply voltage ranging from 2.7 to 3.6 V (3.3V nominal) and features a low-noise oscillator transistor with an integrated DC bias setting. Additionally, it includes an isolating buffer amplifier that significantly reduces the impact of load variations on the oscillator. If a voltage lower than 0.7V is applied to the power-down input (pin 8), the oscillator is disabled, and the current consumption drops from 9mA to less than 1 µA. The VCO is activated when the voltage on pin 8 is at least +3V. By connecting feedback capacitors C1 and C2 to pins 3 (FDBK) and 4 (VTUNE), the internal transistor is configured as a Colpitts oscillator. A resonator, consisting of C4 and L1, is coupled via C3. To achieve a low level of phase noise, it is crucial to maintain a high Q factor for the coil, which can be accomplished by using an air-core coil. For applications requiring a tunable oscillator, a varicap diode (D1), such as BBY40, BBY51, or BB804, can be employed to adjust the resonant frequency. The tuning voltage (UTune) is applied through a high resistance, and its value depends on both the desired frequency range and the variable-capacitance diode used. A table provides suggestions for selecting frequency-determining components. For narrow frequency ranges, a parallel-resonant circuit should be connected between the output pin and +Vcc to serve as the collector load for the output transistor, using the same components as the oscillator resonator. In contrast, a broadband VCO should utilize a high-frequency choke with values ranging from a few microhenries to a few nanohenries, depending on the frequency band, eliminating the need for C6. The output level of this circuit is 3dBm with an LC load and 7 dBm with a choke load. Accompanying the schematic diagram is a table that provides approximate component values for various frequencies, serving as a starting point for experimentation. The coupling between the variable-capacitance diode and C5 determines the tuning range of the VCO. More information about this oscillator IC can be found on the manufacturer's website.
The RF Micro Devices RF2506 is designed for applications where compactness and efficiency are paramount. The architecture of this VCO integrates several critical components that enhance its performance. The isolation provided by the buffer amplifier is particularly advantageous, as it minimizes the load pulling effects that can distort oscillator performance. The Colpitts configuration is chosen for its stability and ease of tuning, making it suitable for a wide range of RF applications.
In terms of component selection, the external components play a vital role in defining the operational characteristics of the oscillator. The feedback capacitors and resonator components must be chosen carefully to achieve the desired frequency response. The Q factor of the resonator is essential for maintaining signal integrity, as a higher Q factor results in lower phase noise and better overall performance. The use of an air-core coil is recommended to maximize Q factor, as it avoids the losses associated with ferromagnetic materials.
The varicap diode adds another layer of versatility, allowing for dynamic frequency adjustments. The tuning voltage must be calibrated according to the specific diode characteristics and the operational frequency range. The suggested table for component values provides a useful reference for engineers looking to optimize their designs.
In conclusion, the RF2506 VCO offers a robust solution for modern oscillator applications, combining ease of use with high performance. Its design allows for flexibility in tuning and frequency selection, making it an ideal choice for a variety of electronic projects. The integration of critical components into a single IC simplifies the design process while maintaining high standards of performance.Nowadays, it is no longer necessary to use discrete components to build oscillators. Instead, many manufacturers provide ready-made voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) ICs that need only a few frequency-determining external components. One example is the RF Micro Devices RF2506. This IC operates with a supply voltage between 2. 7 and 3. 6 V (3. 3V no minal) and provides a low-noise oscillator transistor with integrated DC bias setting. In addition, it has an isolating buffer amplifier that strongly reduces the effects of load variations (load pulling) on the oscillator. If a voltage less than 0. 7V is applied to the power-down input (pin 8), the oscillator is shut down and the current consumption drops from 9mA to less than 1 µA.
The VCO is enabled when the voltage on pin 8 is at least +3V. Connecting the feedback capacitors C1 and C2 to pins 3 (FDBK) and 4 (VTUNE) transforms the internal transistor into a Colpitts oscillator. A resonator is also needed; here this consists of C4 and L1, and it is coupled via C3. Keep the Q factor of the coil as high as possible (by using an air-core coil, for example), to ensure a low level of phase noise.
Since most applications require a tuneable oscillator, the varicap diode D1 (BBY40, BBY51, BB804 etc) can be used to adjust the resonant frequency. The tuning voltage UTune is applied via a high resistance. The value of the tuning voltage naturally depends on the desired frequency range and the variable-capacitance diode (D1) that is used.
The table shows a number of suggestions for selecting the frequency-determining components. If the frequency range is narrow, a parallel-resonant circuit should be connected between the output pin and +Vcc, to form the collector load for the output transistor. This can be built using the same components as the oscillator resonator. With a broadband VCO, use a HF choke instead, with a value of a few microhenries to a few nanohenries, depending on the frequency band.
In this case C6 is not needed. The output level of this circuit is 3dBm with an LC load and 7 dBm with a choke load. The table that accompanies the schematic diagram provides rough indications of component values for various frequencies. It is intended to provide a starting point for experimentation. The coupling between the variable-capacitance diode and C5 determines the tuning range of the VCO. The manufacturer maintains an Internet site at where you cannd more information about this interesting oscillator IC.
🔗 External reference
The RF Micro Devices RF2506 is designed for applications where compactness and efficiency are paramount. The architecture of this VCO integrates several critical components that enhance its performance. The isolation provided by the buffer amplifier is particularly advantageous, as it minimizes the load pulling effects that can distort oscillator performance. The Colpitts configuration is chosen for its stability and ease of tuning, making it suitable for a wide range of RF applications.
In terms of component selection, the external components play a vital role in defining the operational characteristics of the oscillator. The feedback capacitors and resonator components must be chosen carefully to achieve the desired frequency response. The Q factor of the resonator is essential for maintaining signal integrity, as a higher Q factor results in lower phase noise and better overall performance. The use of an air-core coil is recommended to maximize Q factor, as it avoids the losses associated with ferromagnetic materials.
The varicap diode adds another layer of versatility, allowing for dynamic frequency adjustments. The tuning voltage must be calibrated according to the specific diode characteristics and the operational frequency range. The suggested table for component values provides a useful reference for engineers looking to optimize their designs.
In conclusion, the RF2506 VCO offers a robust solution for modern oscillator applications, combining ease of use with high performance. Its design allows for flexibility in tuning and frequency selection, making it an ideal choice for a variety of electronic projects. The integration of critical components into a single IC simplifies the design process while maintaining high standards of performance.Nowadays, it is no longer necessary to use discrete components to build oscillators. Instead, many manufacturers provide ready-made voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) ICs that need only a few frequency-determining external components. One example is the RF Micro Devices RF2506. This IC operates with a supply voltage between 2. 7 and 3. 6 V (3. 3V no minal) and provides a low-noise oscillator transistor with integrated DC bias setting. In addition, it has an isolating buffer amplifier that strongly reduces the effects of load variations (load pulling) on the oscillator. If a voltage less than 0. 7V is applied to the power-down input (pin 8), the oscillator is shut down and the current consumption drops from 9mA to less than 1 µA.
The VCO is enabled when the voltage on pin 8 is at least +3V. Connecting the feedback capacitors C1 and C2 to pins 3 (FDBK) and 4 (VTUNE) transforms the internal transistor into a Colpitts oscillator. A resonator is also needed; here this consists of C4 and L1, and it is coupled via C3. Keep the Q factor of the coil as high as possible (by using an air-core coil, for example), to ensure a low level of phase noise.
Since most applications require a tuneable oscillator, the varicap diode D1 (BBY40, BBY51, BB804 etc) can be used to adjust the resonant frequency. The tuning voltage UTune is applied via a high resistance. The value of the tuning voltage naturally depends on the desired frequency range and the variable-capacitance diode (D1) that is used.
The table shows a number of suggestions for selecting the frequency-determining components. If the frequency range is narrow, a parallel-resonant circuit should be connected between the output pin and +Vcc, to form the collector load for the output transistor. This can be built using the same components as the oscillator resonator. With a broadband VCO, use a HF choke instead, with a value of a few microhenries to a few nanohenries, depending on the frequency band.
In this case C6 is not needed. The output level of this circuit is 3dBm with an LC load and 7 dBm with a choke load. The table that accompanies the schematic diagram provides rough indications of component values for various frequencies. It is intended to provide a starting point for experimentation. The coupling between the variable-capacitance diode and C5 determines the tuning range of the VCO. The manufacturer maintains an Internet site at where you cannd more information about this interesting oscillator IC.
🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713