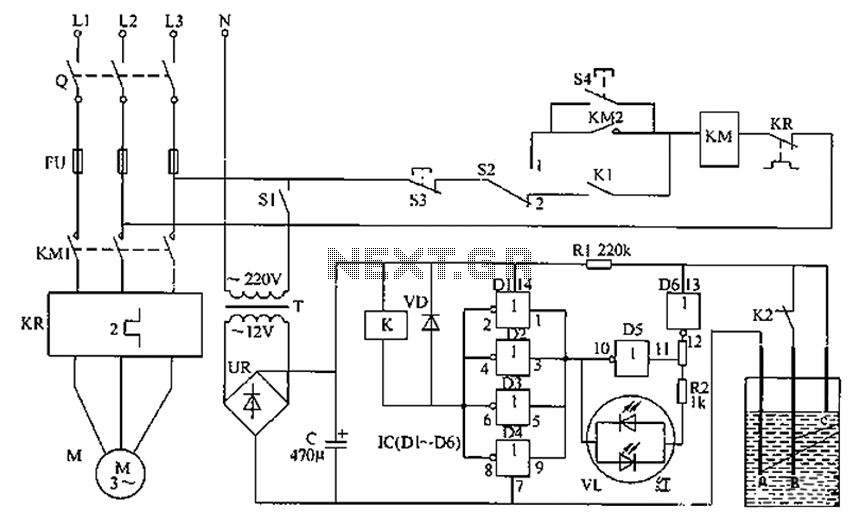
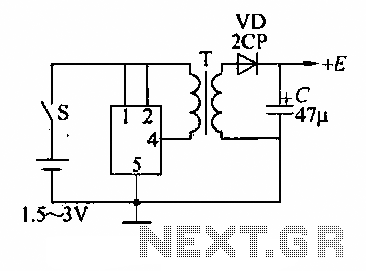
120v to 3.7v circuit
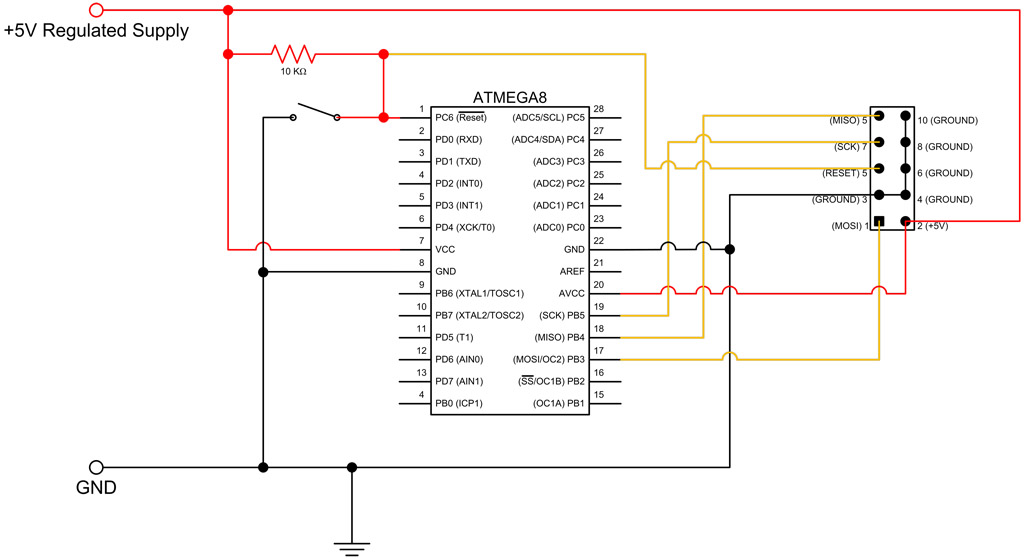
One aspect that was overlooked regarding the battery circuit is the attempt to salvage the circuit and integrate it with the new battery.
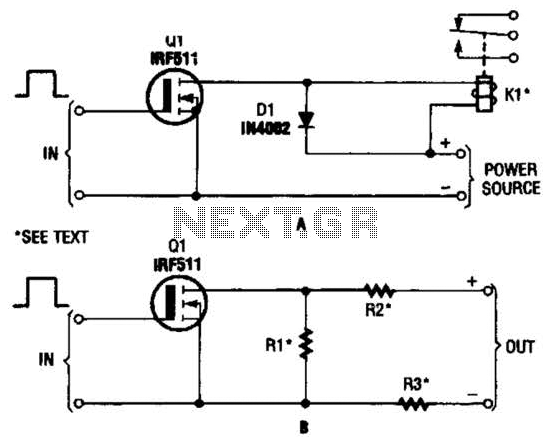
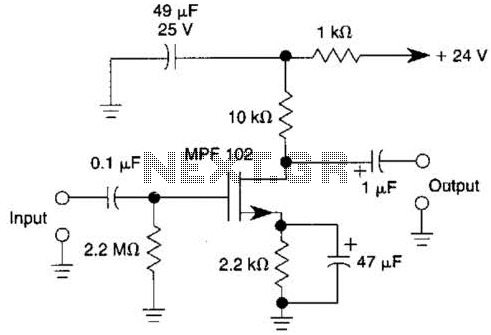
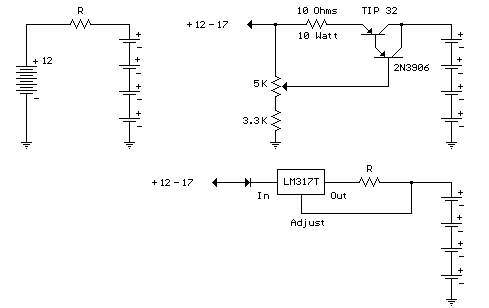
The battery circuit in question likely involves several key components that are essential for proper functionality. Typically, such circuits include a battery, a charging module, and various protection elements to ensure safe operation. The salvaging process may involve reusing components such as resistors, capacitors, or integrated circuits that were previously part of a functioning system.
When integrating a salvaged circuit with a new battery, it is crucial to ensure compatibility in voltage and current ratings to prevent damage. The circuit should also include a method for monitoring the battery's state of charge, which can be accomplished through voltage dividers or dedicated battery management ICs.
Protection features, such as overcurrent protection, overvoltage protection, and thermal management, are vital to enhance the reliability and safety of the battery circuit. These can be implemented using MOSFETs, fuses, and thermistors, respectively.
Additionally, the layout of the circuit board should be carefully designed to minimize resistance and inductance, which can affect performance. Proper grounding techniques and the use of decoupling capacitors can help mitigate noise and ensure stable operation of the circuit.
In summary, salvaging a battery circuit and integrating it with a new battery requires careful consideration of component compatibility, safety features, and circuit design principles to achieve a reliable and efficient power supply solution.Oh, one thing I forgot to mention about the battery ""circuit"" I attempted to salvage the circuit and put it inline with the new battery,.. 🔗 External reference
The battery circuit in question likely involves several key components that are essential for proper functionality. Typically, such circuits include a battery, a charging module, and various protection elements to ensure safe operation. The salvaging process may involve reusing components such as resistors, capacitors, or integrated circuits that were previously part of a functioning system.
When integrating a salvaged circuit with a new battery, it is crucial to ensure compatibility in voltage and current ratings to prevent damage. The circuit should also include a method for monitoring the battery's state of charge, which can be accomplished through voltage dividers or dedicated battery management ICs.
Protection features, such as overcurrent protection, overvoltage protection, and thermal management, are vital to enhance the reliability and safety of the battery circuit. These can be implemented using MOSFETs, fuses, and thermistors, respectively.
Additionally, the layout of the circuit board should be carefully designed to minimize resistance and inductance, which can affect performance. Proper grounding techniques and the use of decoupling capacitors can help mitigate noise and ensure stable operation of the circuit.
In summary, salvaging a battery circuit and integrating it with a new battery requires careful consideration of component compatibility, safety features, and circuit design principles to achieve a reliable and efficient power supply solution.Oh, one thing I forgot to mention about the battery ""circuit"" I attempted to salvage the circuit and put it inline with the new battery,.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713