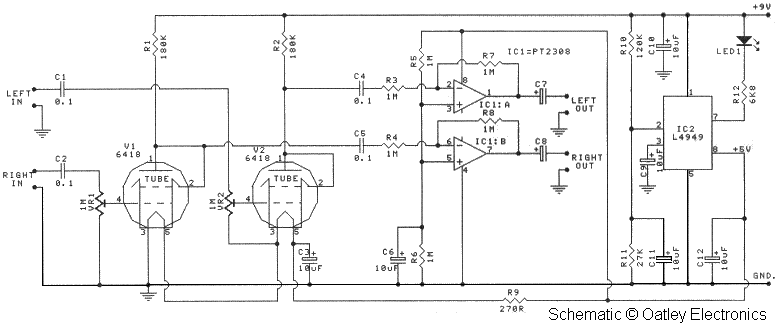
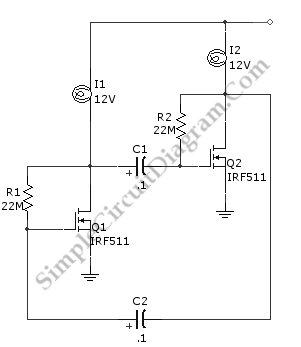
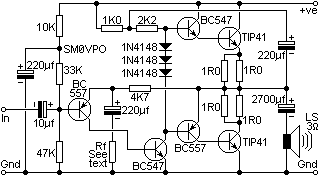
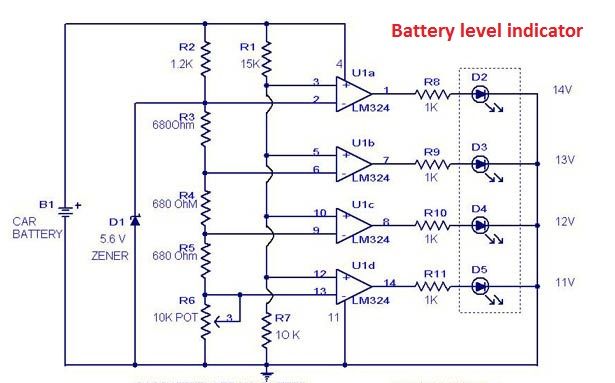
12V 6-12 Watt Fluorescent Tube (Neon) Lamp Inverter
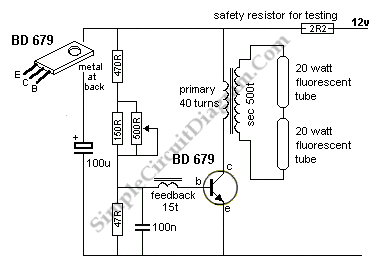
A 40-watt fluorescent tube lamp or two 20-watt tubes in series will be driven by this circuit; however, this circuit will produce less brightness than usual, since...
This circuit is designed to operate a 40-watt fluorescent tube lamp or two 20-watt tubes connected in series. The operation of fluorescent lamps involves the ionization of gas within the tube, which emits ultraviolet light that is subsequently converted to visible light by the phosphor coating inside the tube.
In this circuit configuration, the input voltage is typically rectified and regulated to ensure a stable current flow through the tubes. The circuit may include a ballast, which is a critical component that limits the current flowing through the fluorescent tubes, preventing them from drawing excessive current that could lead to overheating or failure.
The reduced brightness mentioned in the description can be attributed to several factors, including the type of ballast used, the voltage supplied to the circuit, and the overall efficiency of the circuit design. If an electronic ballast is utilized, it may provide better performance and efficiency compared to a magnetic ballast; however, if the circuit is designed with suboptimal components or configurations, it may result in lower light output than expected.
To achieve optimal performance, it is essential to ensure that the circuit is designed with appropriate ratings for the ballast and that the tubes are compatible with the circuit specifications. Additionally, the circuit should be protected against overcurrent conditions and have provisions for thermal management to enhance longevity and reliability.
Overall, careful consideration of the circuit design and component selection is necessary to ensure that the fluorescent tubes operate efficiently while providing adequate illumination.A 40 watt fluorescent tube lamp or two 20-watt tubes in series will be driven by this circuit but this circuit will produce less brightness than usual, since.. 🔗 External reference
This circuit is designed to operate a 40-watt fluorescent tube lamp or two 20-watt tubes connected in series. The operation of fluorescent lamps involves the ionization of gas within the tube, which emits ultraviolet light that is subsequently converted to visible light by the phosphor coating inside the tube.
In this circuit configuration, the input voltage is typically rectified and regulated to ensure a stable current flow through the tubes. The circuit may include a ballast, which is a critical component that limits the current flowing through the fluorescent tubes, preventing them from drawing excessive current that could lead to overheating or failure.
The reduced brightness mentioned in the description can be attributed to several factors, including the type of ballast used, the voltage supplied to the circuit, and the overall efficiency of the circuit design. If an electronic ballast is utilized, it may provide better performance and efficiency compared to a magnetic ballast; however, if the circuit is designed with suboptimal components or configurations, it may result in lower light output than expected.
To achieve optimal performance, it is essential to ensure that the circuit is designed with appropriate ratings for the ballast and that the tubes are compatible with the circuit specifications. Additionally, the circuit should be protected against overcurrent conditions and have provisions for thermal management to enhance longevity and reliability.
Overall, careful consideration of the circuit design and component selection is necessary to ensure that the fluorescent tubes operate efficiently while providing adequate illumination.A 40 watt fluorescent tube lamp or two 20-watt tubes in series will be driven by this circuit but this circuit will produce less brightness than usual, since.. 🔗 External reference