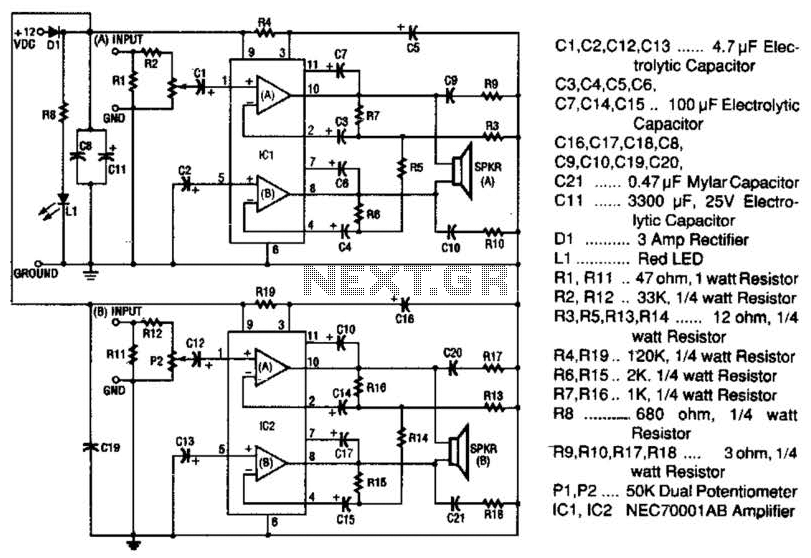
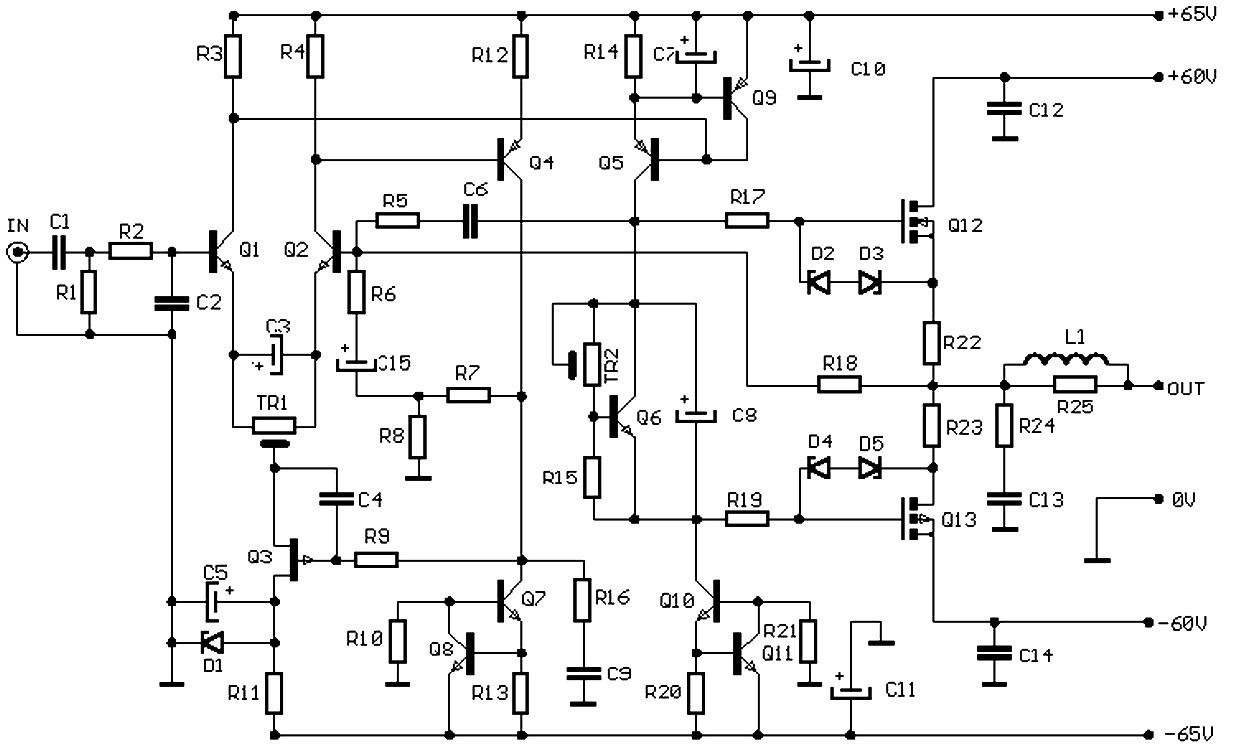
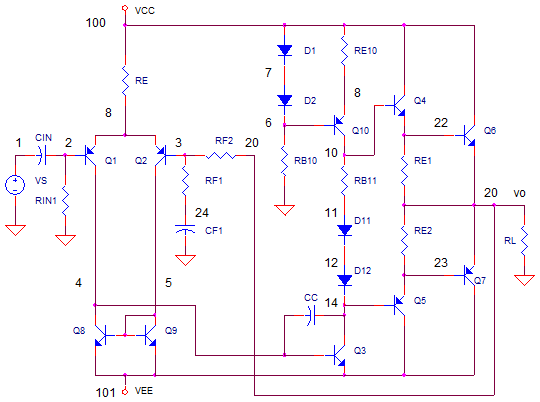
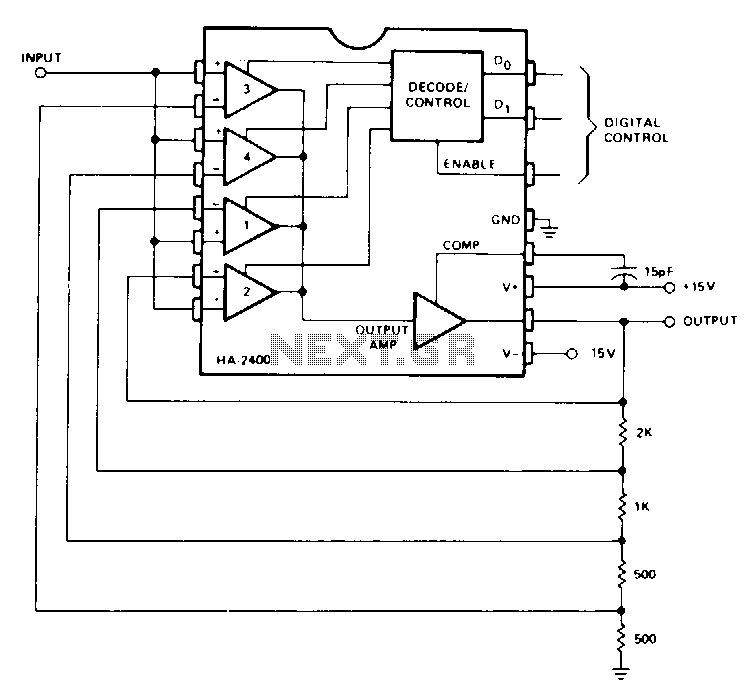
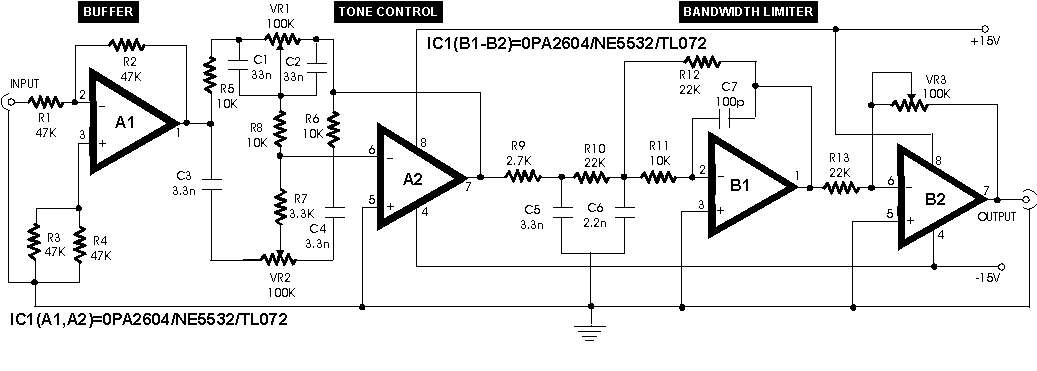
250mw 16 db vhf amplifier
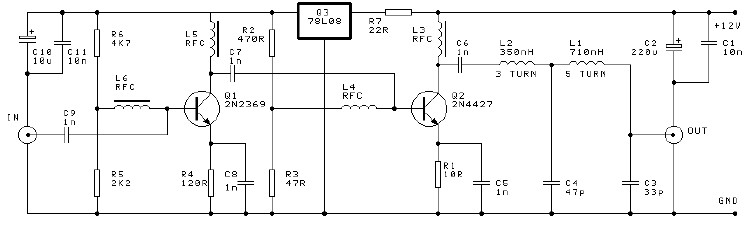
This project involves a 250mW RF power amplifier circuit. It is designed to amplify the output of approximately 7mW wideband FM transmitters to a final output level of about 250mW. The circuit utilizes a simple two-transistor VHF power amplifier configuration, providing a gain of around 16dB, and does not require any tuning or alignment procedures. Wideband techniques have been implemented in the design, and the circuit includes a low-pass filter to ensure good output spectral purity. The project is intended for assembly on a single-sided printed circuit board and is specifically designed to amplify the output of 7mW to 10mW wideband FM transmitters to a final output level of 250mW to 300mW after the filter.
The 250mW RF power amplifier circuit is structured around two transistors configured in a push-pull arrangement to enhance efficiency and output power. The choice of components is critical; transistors with suitable frequency response and power handling capabilities are selected to ensure optimal performance in the VHF range. The circuit is designed to operate within the frequency range typically used for FM broadcasting, which is between 88 MHz and 108 MHz.
The amplifier circuit exhibits a significant gain of approximately 16dB, which allows for the effective amplification of the relatively low output power from wideband FM transmitters. The use of wideband techniques ensures that the amplifier maintains consistent performance across the entire operational bandwidth, minimizing distortion and maximizing fidelity.
To further enhance the quality of the output signal, a low-pass filter is integrated into the design. This filter is essential for removing unwanted harmonic frequencies generated during amplification, thereby ensuring that the output signal maintains good spectral purity. The inclusion of this filter not only improves the quality of the transmitted signal but also helps to comply with regulatory standards regarding spectral emissions.
The layout of the circuit is optimized for assembly on a single-sided printed circuit board (PCB), which simplifies the manufacturing process and reduces production costs. The PCB design minimizes the length of signal paths, which is important for maintaining signal integrity and reducing potential interference. Careful attention is given to the placement of components to ensure proper thermal management and to prevent signal degradation.
In summary, this RF power amplifier project is a well-engineered solution for amplifying the output of low-power wideband FM transmitters. Its design incorporates effective amplification techniques, filtering for spectral purity, and considerations for practical assembly, making it a reliable choice for applications requiring increased RF output power.This is an 250mW RF power amplifier project. This circuit is designed to amplify the output of about 7mW wide band FM transmitters to a final level of about 250mW. This electronic circuit is a simple 2-transistor VHF power amplifier, with about 16dB gain, and requires no tuning or alignment procedures.
Wideband techniques have been used in the design and the circuit is equipped with a lowpass filter to ensure good output spectral purity. The project has been designed for assembly on a single-sided printed circuit board. The circuit is specifically designed to amplify the output of 7mW to 10mW WBFM transmitters (wide band) to a final level of 250mW to 300mW, after the filter. 🔗 External reference
The 250mW RF power amplifier circuit is structured around two transistors configured in a push-pull arrangement to enhance efficiency and output power. The choice of components is critical; transistors with suitable frequency response and power handling capabilities are selected to ensure optimal performance in the VHF range. The circuit is designed to operate within the frequency range typically used for FM broadcasting, which is between 88 MHz and 108 MHz.
The amplifier circuit exhibits a significant gain of approximately 16dB, which allows for the effective amplification of the relatively low output power from wideband FM transmitters. The use of wideband techniques ensures that the amplifier maintains consistent performance across the entire operational bandwidth, minimizing distortion and maximizing fidelity.
To further enhance the quality of the output signal, a low-pass filter is integrated into the design. This filter is essential for removing unwanted harmonic frequencies generated during amplification, thereby ensuring that the output signal maintains good spectral purity. The inclusion of this filter not only improves the quality of the transmitted signal but also helps to comply with regulatory standards regarding spectral emissions.
The layout of the circuit is optimized for assembly on a single-sided printed circuit board (PCB), which simplifies the manufacturing process and reduces production costs. The PCB design minimizes the length of signal paths, which is important for maintaining signal integrity and reducing potential interference. Careful attention is given to the placement of components to ensure proper thermal management and to prevent signal degradation.
In summary, this RF power amplifier project is a well-engineered solution for amplifying the output of low-power wideband FM transmitters. Its design incorporates effective amplification techniques, filtering for spectral purity, and considerations for practical assembly, making it a reliable choice for applications requiring increased RF output power.This is an 250mW RF power amplifier project. This circuit is designed to amplify the output of about 7mW wide band FM transmitters to a final level of about 250mW. This electronic circuit is a simple 2-transistor VHF power amplifier, with about 16dB gain, and requires no tuning or alignment procedures.
Wideband techniques have been used in the design and the circuit is equipped with a lowpass filter to ensure good output spectral purity. The project has been designed for assembly on a single-sided printed circuit board. The circuit is specifically designed to amplify the output of 7mW to 10mW WBFM transmitters (wide band) to a final level of 250mW to 300mW, after the filter. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713