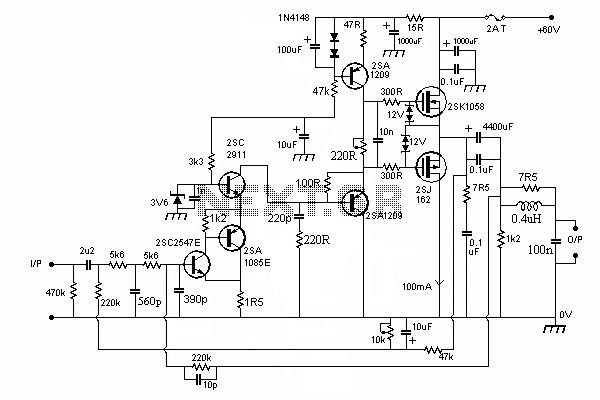
3-channel Audio Amplifier circuit
A careful examination of the amplifier photos reveals that the heatsink on the HY60 near-clone built using the TDA2050A is slightly shorter than that of the original HY60s. This unit is positioned at the rear of the amplifier, creating a gap that provides sufficient space for air circulation within the amplifier. No slots were cut into the bottom side of the top slab, which is secured firmly in place with three large wood screws driven through the middle tier upwards.
Safety is paramount when dealing with mains voltages. Each brass panel is connected with sturdy insulated wire to the brass panel on the power supply unit (PSU), to which the Earth from the mains supply is connected. This connection is made via a 100-ohm resistor to the 0V line of the PSU. Additionally, a similar wire connects the transformer pan base to Earth. For the 0V line on the PSU, a small-diameter brass bar is utilized, allowing connections from the amplifier at any point in a 360-degree orientation. The positive and negative connections are made using reasonably heavy (10 amp) insulated wire. Notably, a change of mind resulted in cross-connecting colors on the capacitors, leading to a RED negative wire and a BLUE positive wire—this is not advisable for others to replicate. To avoid a larger case, two sets of three 6800uF capacitors were used in place of two 20,000uF capacitors, with receptacles drilled in the base slab using a Forstner bit. The bridge rectifier is secured to one of the small brass panels with a bit of silicone grease to assist in cooling. The transformer pan cut-out is made slightly larger than the transformer itself to allow for air circulation around the periphery, facilitated by holes drilled in the pan base. The transformer, purchased from RS Components, did not come with a fitting kit, which was assumed to be included. As a solution, bottom and top gaskets were improvised from a silicone heat mat, and the top fixing plate was crafted from 22-gauge aluminum.
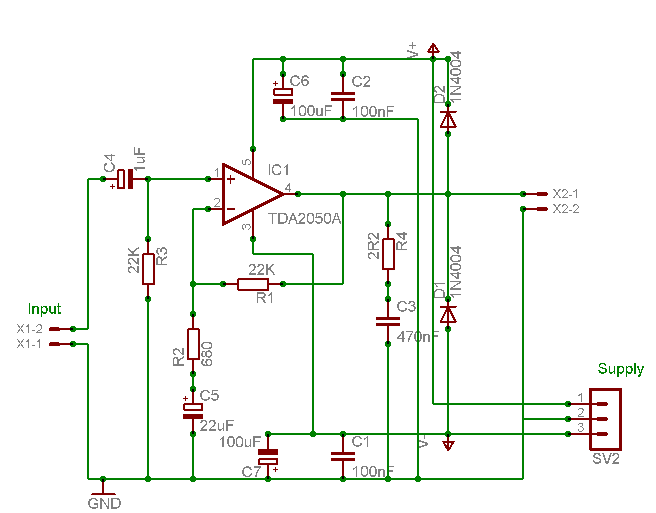
The described amplifier circuit incorporates a TDA2050A audio amplifier IC, which is known for its ability to deliver high-quality audio output while maintaining thermal efficiency. The heatsink, although shorter than the original design, is strategically placed to promote airflow, enhancing the overall thermal management of the amplifier. The choice of materials, such as brass for the panels and aluminum for the fixing plate, contributes to both the durability and aesthetic of the unit.
The power supply section is designed with safety as a primary concern, employing insulated wiring and a resistor to ensure proper grounding. The use of a small-diameter brass bar for the 0V line facilitates versatile connections, allowing for ease of assembly and maintenance. The decision to utilize multiple smaller capacitors instead of fewer larger ones reflects a practical approach to space management within the amplifier casing while still achieving the desired capacitance for stable power delivery.
The bridge rectifier's mounting with silicone grease indicates a focus on thermal dissipation, which is critical in preventing overheating during operation. The transformer pan's design, featuring a larger cut-out for airflow, further emphasizes the importance of thermal management within the circuit. Overall, these design choices reflect a thorough understanding of electronic principles while ensuring the functionality and safety of the amplifier circuit.Careful examination of the photos of the amplifier will reveal that the heatsink on the HY60 near-clone I built using the TDA2050A is slightly shorter than that on the original HY60s. I placed this unit at the rear of the amplifier, and the gap provides adequate space for a free-flow of air up the inside of the amplifier.
No slots were cut in the bottom-side of the top slab, this is lined up and held firmly in place with three large woodscrews driven through the middle-tier upwards. Safety should be paramount where mains voltages are concerned, and each Brass panel is connected with stoutish insulated wire to the brass panel on the PSU to which the Earth from the mains supply is connected. This was then connected via a 100 ohm resistor to the 0v line of the PSU. A similar wire connected to the transformer pan base is also connected to Earth. For the 0v line on the PSU I used a small-diameter brass bar, which allows connections from the amplifier at any point in 360 degs.
The +ve and -ve connections were done using reasonably heavy (10 amp) insulated wire. Look carefully at my photos of the PSU and you will see that a change of mind resulted in me cross-connecting colours on the capacitors, so that I ended up with a RED -ve wire and a BLUE +ve wire – don’t do this at home! To have fitted two 20,000uF capacitors would have resulted in a larger case, so I substituted these for two sets of 3 X 6800uF, and sited these by drilling receptacles in the base slab using a Forstner bit.
The bridge rectifier is fastened to one of the small Brass panels using a little silicone grease to aid cooling. Note that I made the transformer pan cut-out slightly larger than the Tx itself, to allow for the free flow of air around the periphery, via holes drilled in the pan base.
The transformer (which I bought from RS components) came without a fitting kit (I had assumed this was included). I improvised bottom and top gaskets cut from a cheap silcone heat mat, and the top fixing plate from 22 gauge Aluminium.
🔗 External reference
Safety is paramount when dealing with mains voltages. Each brass panel is connected with sturdy insulated wire to the brass panel on the power supply unit (PSU), to which the Earth from the mains supply is connected. This connection is made via a 100-ohm resistor to the 0V line of the PSU. Additionally, a similar wire connects the transformer pan base to Earth. For the 0V line on the PSU, a small-diameter brass bar is utilized, allowing connections from the amplifier at any point in a 360-degree orientation. The positive and negative connections are made using reasonably heavy (10 amp) insulated wire. Notably, a change of mind resulted in cross-connecting colors on the capacitors, leading to a RED negative wire and a BLUE positive wire—this is not advisable for others to replicate. To avoid a larger case, two sets of three 6800uF capacitors were used in place of two 20,000uF capacitors, with receptacles drilled in the base slab using a Forstner bit. The bridge rectifier is secured to one of the small brass panels with a bit of silicone grease to assist in cooling. The transformer pan cut-out is made slightly larger than the transformer itself to allow for air circulation around the periphery, facilitated by holes drilled in the pan base. The transformer, purchased from RS Components, did not come with a fitting kit, which was assumed to be included. As a solution, bottom and top gaskets were improvised from a silicone heat mat, and the top fixing plate was crafted from 22-gauge aluminum.
The described amplifier circuit incorporates a TDA2050A audio amplifier IC, which is known for its ability to deliver high-quality audio output while maintaining thermal efficiency. The heatsink, although shorter than the original design, is strategically placed to promote airflow, enhancing the overall thermal management of the amplifier. The choice of materials, such as brass for the panels and aluminum for the fixing plate, contributes to both the durability and aesthetic of the unit.
The power supply section is designed with safety as a primary concern, employing insulated wiring and a resistor to ensure proper grounding. The use of a small-diameter brass bar for the 0V line facilitates versatile connections, allowing for ease of assembly and maintenance. The decision to utilize multiple smaller capacitors instead of fewer larger ones reflects a practical approach to space management within the amplifier casing while still achieving the desired capacitance for stable power delivery.
The bridge rectifier's mounting with silicone grease indicates a focus on thermal dissipation, which is critical in preventing overheating during operation. The transformer pan's design, featuring a larger cut-out for airflow, further emphasizes the importance of thermal management within the circuit. Overall, these design choices reflect a thorough understanding of electronic principles while ensuring the functionality and safety of the amplifier circuit.Careful examination of the photos of the amplifier will reveal that the heatsink on the HY60 near-clone I built using the TDA2050A is slightly shorter than that on the original HY60s. I placed this unit at the rear of the amplifier, and the gap provides adequate space for a free-flow of air up the inside of the amplifier.
No slots were cut in the bottom-side of the top slab, this is lined up and held firmly in place with three large woodscrews driven through the middle-tier upwards. Safety should be paramount where mains voltages are concerned, and each Brass panel is connected with stoutish insulated wire to the brass panel on the PSU to which the Earth from the mains supply is connected. This was then connected via a 100 ohm resistor to the 0v line of the PSU. A similar wire connected to the transformer pan base is also connected to Earth. For the 0v line on the PSU I used a small-diameter brass bar, which allows connections from the amplifier at any point in 360 degs.
The +ve and -ve connections were done using reasonably heavy (10 amp) insulated wire. Look carefully at my photos of the PSU and you will see that a change of mind resulted in me cross-connecting colours on the capacitors, so that I ended up with a RED -ve wire and a BLUE +ve wire – don’t do this at home! To have fitted two 20,000uF capacitors would have resulted in a larger case, so I substituted these for two sets of 3 X 6800uF, and sited these by drilling receptacles in the base slab using a Forstner bit.
The bridge rectifier is fastened to one of the small Brass panels using a little silicone grease to aid cooling. Note that I made the transformer pan cut-out slightly larger than the Tx itself, to allow for the free flow of air around the periphery, via holes drilled in the pan base.
The transformer (which I bought from RS components) came without a fitting kit (I had assumed this was included). I improvised bottom and top gaskets cut from a cheap silcone heat mat, and the top fixing plate from 22 gauge Aluminium.
🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713