3 Digit Display Scoreboard
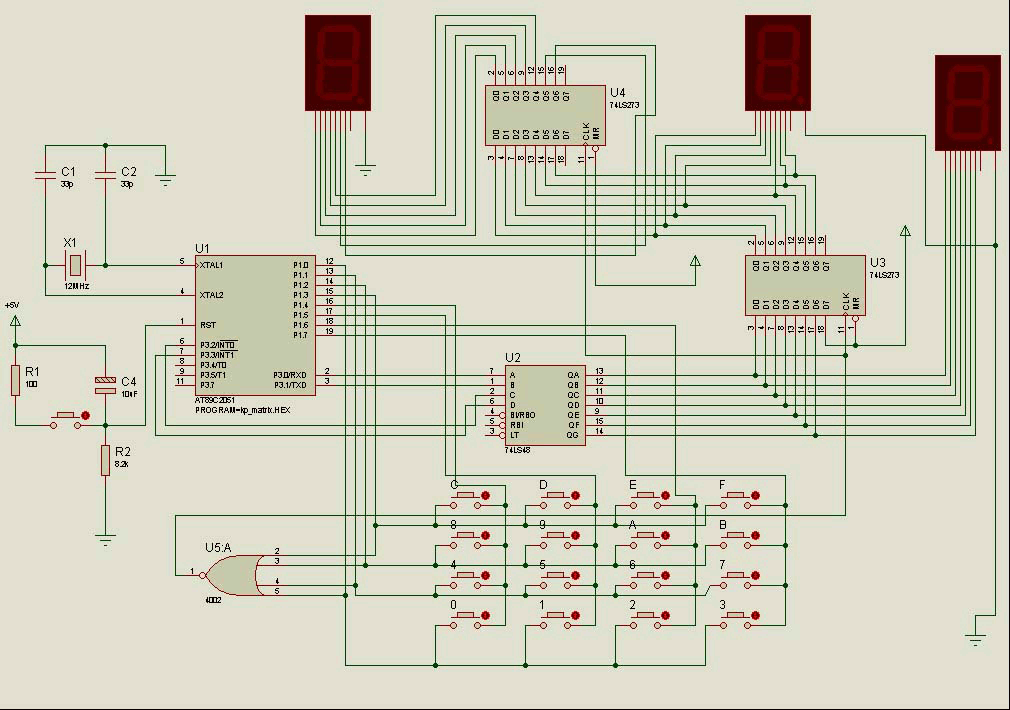
A few months ago, Milardo began studying the 8051 Microcontroller. From his research, Milardo designed a new circuit and named it the 3-Digit Display Scoreboard with a 4x4 Keypad Matrix.
The 3-Digit Display Scoreboard with a 4x4 Keypad Matrix is an electronic circuit that utilizes the 8051 Microcontroller to manage inputs and outputs effectively. The primary function of this circuit is to display scores or numerical values on a 7-segment display, allowing users to keep track of scores in games or other applications requiring numerical input and display.
The circuit comprises several key components: the 8051 Microcontroller, a 4x4 matrix keypad, and three 7-segment displays. The 4x4 matrix keypad serves as the user interface, allowing users to input scores or navigate through options. Each key press is detected by the microcontroller, which processes the input accordingly.
The 7-segment displays are connected to the microcontroller's output pins. The microcontroller is programmed to convert the numerical values from the keypad into a format suitable for display on the 7-segment units. This involves driving the segments of each display to represent the corresponding digits accurately.
Power supply considerations for the circuit include ensuring that the microcontroller and the displays receive appropriate voltage levels, typically 5V. Bypass capacitors may be included to filter any noise from the power supply, ensuring stable operation.
For the design, attention must be paid to the connections between the microcontroller, keypad, and displays. Proper debouncing techniques should be implemented in the software to avoid erroneous readings from the keypad. Additionally, the microcontroller's firmware should be optimized for efficiency, allowing for quick response times to user inputs.
Overall, the 3-Digit Display Scoreboard with a 4x4 Keypad Matrix represents a practical application of the 8051 Microcontroller, demonstrating its capabilities in handling user input and controlling output displays in a user-friendly manner.A few months ago Milardo starting to study the 8051 Microcontroller. From his research Miardo has designed a new circuit and called it 3-Digit Display Scoreboard with 4x4 Keypad Matrix.. 🔗 External reference
The 3-Digit Display Scoreboard with a 4x4 Keypad Matrix is an electronic circuit that utilizes the 8051 Microcontroller to manage inputs and outputs effectively. The primary function of this circuit is to display scores or numerical values on a 7-segment display, allowing users to keep track of scores in games or other applications requiring numerical input and display.
The circuit comprises several key components: the 8051 Microcontroller, a 4x4 matrix keypad, and three 7-segment displays. The 4x4 matrix keypad serves as the user interface, allowing users to input scores or navigate through options. Each key press is detected by the microcontroller, which processes the input accordingly.
The 7-segment displays are connected to the microcontroller's output pins. The microcontroller is programmed to convert the numerical values from the keypad into a format suitable for display on the 7-segment units. This involves driving the segments of each display to represent the corresponding digits accurately.
Power supply considerations for the circuit include ensuring that the microcontroller and the displays receive appropriate voltage levels, typically 5V. Bypass capacitors may be included to filter any noise from the power supply, ensuring stable operation.
For the design, attention must be paid to the connections between the microcontroller, keypad, and displays. Proper debouncing techniques should be implemented in the software to avoid erroneous readings from the keypad. Additionally, the microcontroller's firmware should be optimized for efficiency, allowing for quick response times to user inputs.
Overall, the 3-Digit Display Scoreboard with a 4x4 Keypad Matrix represents a practical application of the 8051 Microcontroller, demonstrating its capabilities in handling user input and controlling output displays in a user-friendly manner.A few months ago Milardo starting to study the 8051 Microcontroller. From his research Miardo has designed a new circuit and called it 3-Digit Display Scoreboard with 4x4 Keypad Matrix.. 🔗 External reference