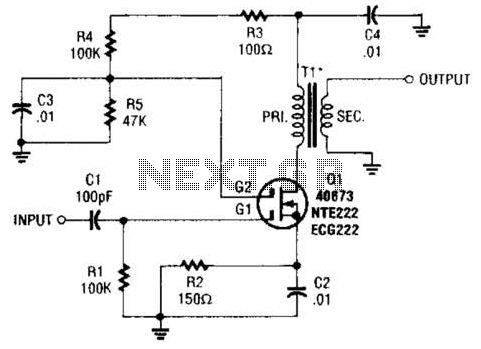
455-Khz Narrow-Band If Filter Circuit
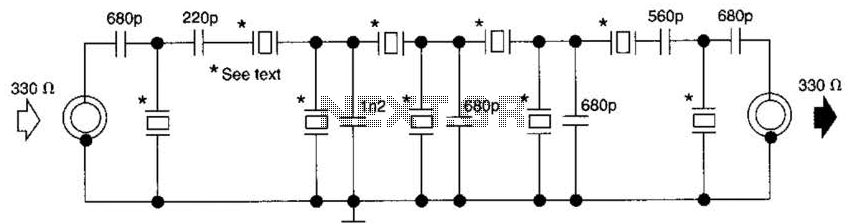
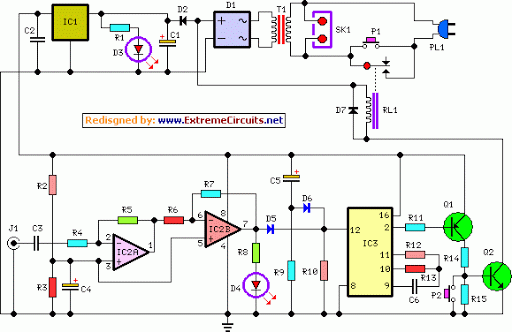
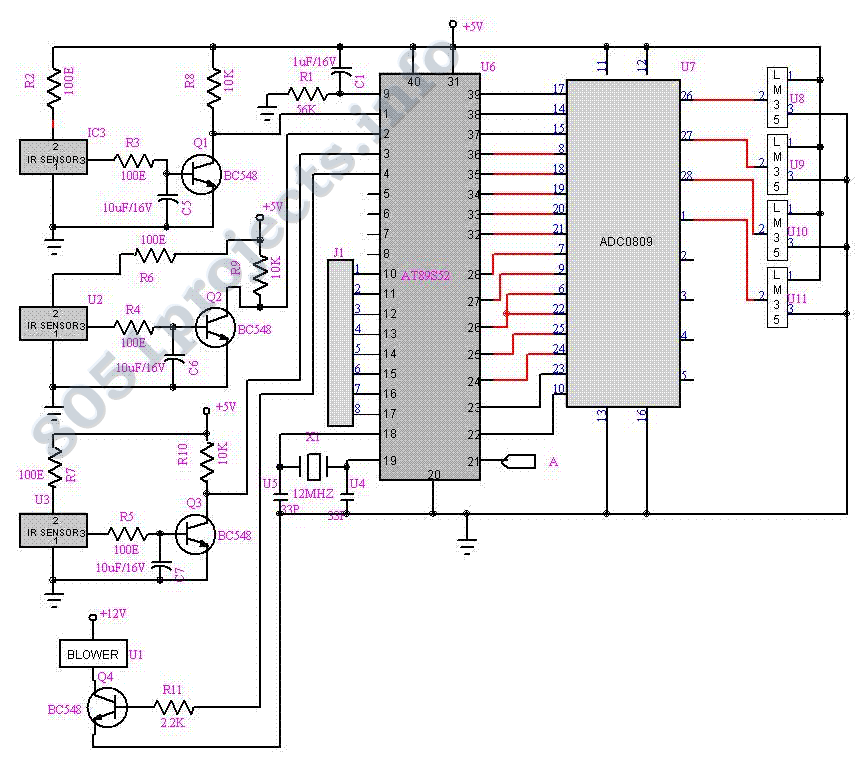
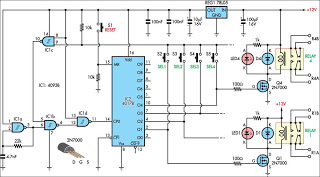
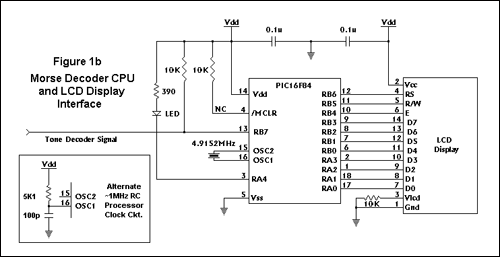
This filter utilizes five 455-kHz ceramic resonators. The impedance is 330 ohms, the bandwidth is 800 Hz, and the ultimate rejection is greater than 60 dB. Additionally, the ceramic resonators can be substituted with crystals.
The described filter is a highly specialized electronic component designed to operate at a frequency of 455 kHz, which is commonly used in applications such as radio frequency (RF) communication and signal processing. The use of five ceramic resonators in the design enhances the filter's selectivity and stability, allowing it to effectively isolate the desired frequency while attenuating unwanted signals.
The specified impedance of 330 ohms indicates the resistance that the filter presents to the connected circuitry, which is critical for ensuring optimal power transfer and minimizing signal reflections. The bandwidth of 800 Hz signifies the range of frequencies around the center frequency (455 kHz) that the filter allows to pass through with minimal attenuation. This relatively narrow bandwidth suggests that the filter is designed for applications requiring precise frequency discrimination.
The ultimate rejection of greater than 60 dB indicates the filter's ability to suppress signals outside its passband, providing a high level of attenuation for undesired frequencies. This characteristic is crucial in applications where signal integrity is paramount, such as in communication systems or audio processing.
The option to replace ceramic resonators with crystals offers flexibility in the design. Crystals typically provide even greater frequency stability and lower phase noise than ceramic resonators, making them suitable for applications where precision timing is essential. However, the choice between resonators and crystals will depend on the specific requirements of the application, including factors such as cost, size, and performance characteristics.
Overall, this filter design presents a robust solution for filtering applications at 455 kHz, with the potential for customization based on the components used. This filter uses five 455-kHz ceramic resonators. The impedance is 330, the bandwidth is 800 Hz, and the ultimate rejection >60 dB. The ceramic resonators could be replaced by crystals. 🔗 External reference
The described filter is a highly specialized electronic component designed to operate at a frequency of 455 kHz, which is commonly used in applications such as radio frequency (RF) communication and signal processing. The use of five ceramic resonators in the design enhances the filter's selectivity and stability, allowing it to effectively isolate the desired frequency while attenuating unwanted signals.
The specified impedance of 330 ohms indicates the resistance that the filter presents to the connected circuitry, which is critical for ensuring optimal power transfer and minimizing signal reflections. The bandwidth of 800 Hz signifies the range of frequencies around the center frequency (455 kHz) that the filter allows to pass through with minimal attenuation. This relatively narrow bandwidth suggests that the filter is designed for applications requiring precise frequency discrimination.
The ultimate rejection of greater than 60 dB indicates the filter's ability to suppress signals outside its passband, providing a high level of attenuation for undesired frequencies. This characteristic is crucial in applications where signal integrity is paramount, such as in communication systems or audio processing.
The option to replace ceramic resonators with crystals offers flexibility in the design. Crystals typically provide even greater frequency stability and lower phase noise than ceramic resonators, making them suitable for applications where precision timing is essential. However, the choice between resonators and crystals will depend on the specific requirements of the application, including factors such as cost, size, and performance characteristics.
Overall, this filter design presents a robust solution for filtering applications at 455 kHz, with the potential for customization based on the components used. This filter uses five 455-kHz ceramic resonators. The impedance is 330, the bandwidth is 800 Hz, and the ultimate rejection >60 dB. The ceramic resonators could be replaced by crystals. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713