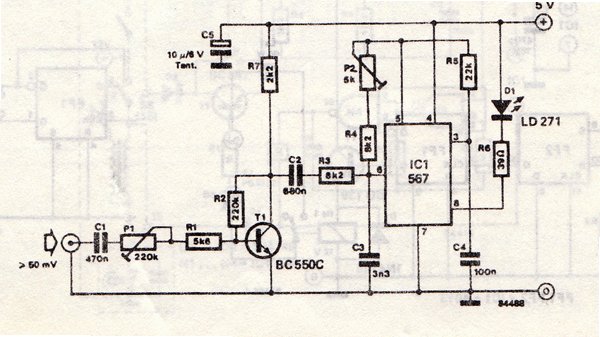
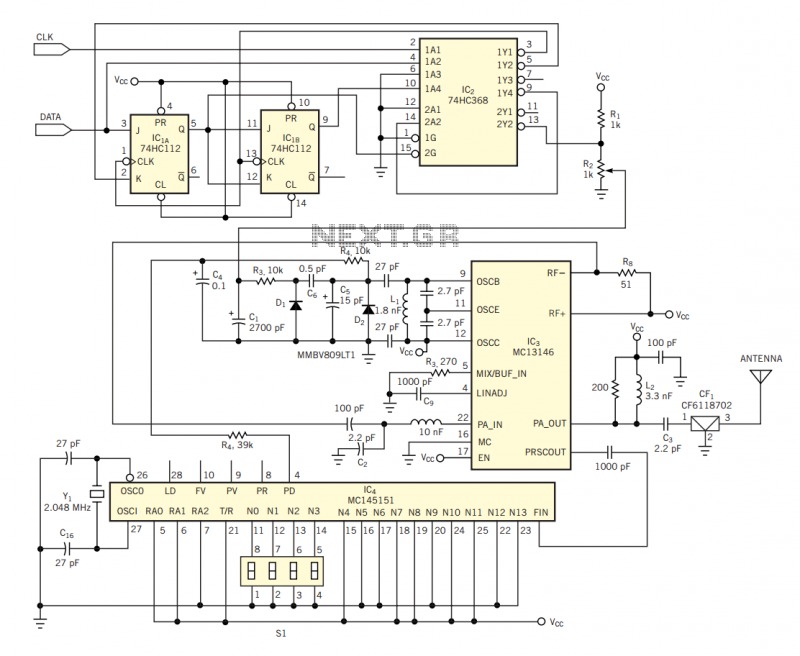
4W FM Transmitter
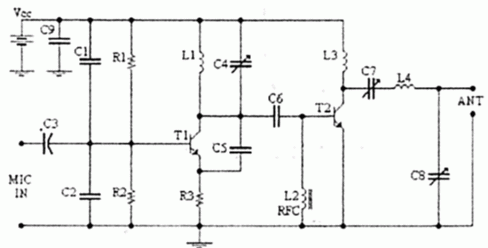
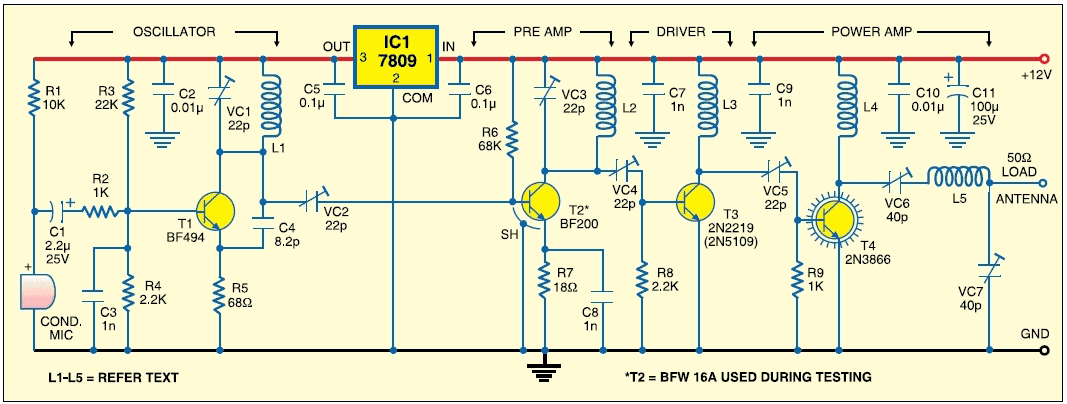
4W FM Transmitter. Technical Characteristics: Stabilized power supply: Vcc = 12~16V. Emission frequency: 88~108MHz. Current consumption: 100~400mA.
The 4W FM transmitter is designed to operate within a frequency range of 88 to 108 MHz, which is the standard FM broadcast band. This device requires a stabilized power supply voltage ranging from 12 to 16 volts, ensuring consistent performance across various operating conditions. The transmitter's current consumption varies between 100 to 400 mA, depending on the output power and operational mode.
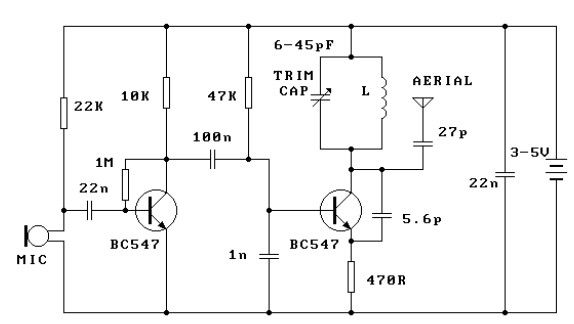
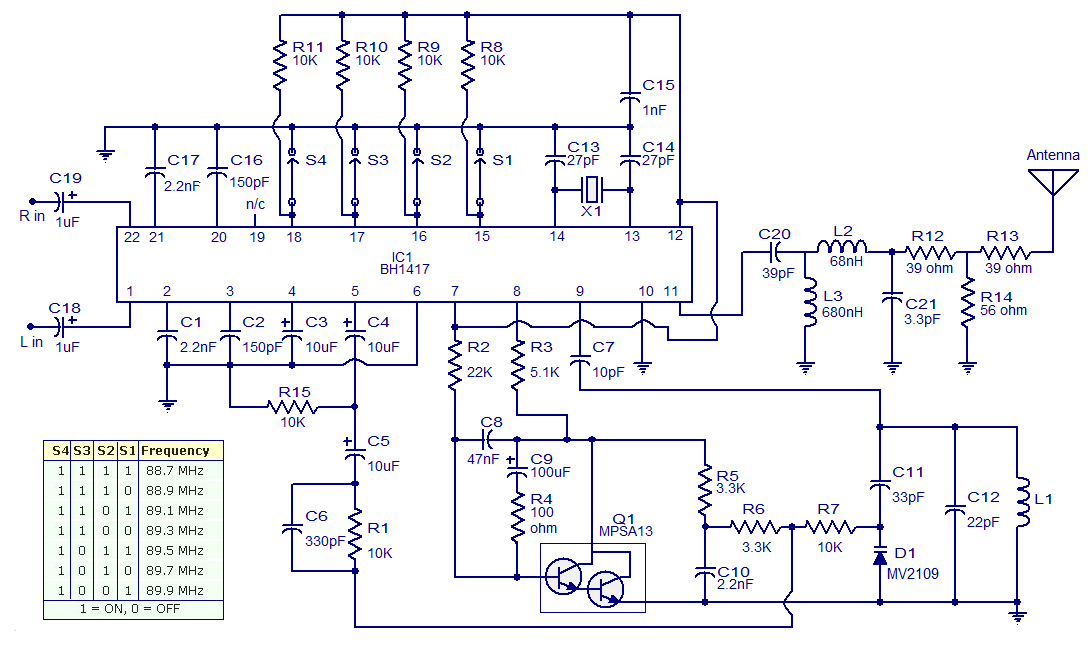
The circuit typically includes a modulation stage, an oscillator, and a power amplifier. The oscillator generates the carrier frequency, which is modulated by the audio signal input. The modulation can be achieved using various techniques such as frequency modulation (FM) or phase modulation (PM), with FM being the most common for broadcasting applications.
The power amplifier stage boosts the modulated signal to a level suitable for transmission. Careful attention must be paid to the design of this stage to minimize distortion and ensure high linearity, which is crucial for maintaining audio quality. The output stage may also include a low-pass filter to suppress unwanted harmonic frequencies, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards for emissions.
In addition, the transmitter may incorporate features such as an audio preamplifier, which enhances the audio input signal before modulation, and a feedback loop for automatic gain control (AGC) to maintain consistent output levels despite variations in input signal strength.
Additional components may include capacitors for coupling and bypassing, inductors for tuning, and resistors for biasing and load matching. The overall layout of the circuit should adhere to best practices in RF design, including proper grounding, shielding, and component placement to minimize interference and optimize performance.
This FM transmitter can be utilized in various applications, including community radio stations, educational projects, and personal broadcasting, making it a versatile component in the field of electronic communications.4W FM Transmitter. TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS: Stabilised tendency of catering: Vcc=12~16V Frequency of emission: 88~108MHz Consumption: 100~400mA Materially: The. 🔗 External reference
The 4W FM transmitter is designed to operate within a frequency range of 88 to 108 MHz, which is the standard FM broadcast band. This device requires a stabilized power supply voltage ranging from 12 to 16 volts, ensuring consistent performance across various operating conditions. The transmitter's current consumption varies between 100 to 400 mA, depending on the output power and operational mode.
The circuit typically includes a modulation stage, an oscillator, and a power amplifier. The oscillator generates the carrier frequency, which is modulated by the audio signal input. The modulation can be achieved using various techniques such as frequency modulation (FM) or phase modulation (PM), with FM being the most common for broadcasting applications.
The power amplifier stage boosts the modulated signal to a level suitable for transmission. Careful attention must be paid to the design of this stage to minimize distortion and ensure high linearity, which is crucial for maintaining audio quality. The output stage may also include a low-pass filter to suppress unwanted harmonic frequencies, ensuring compliance with regulatory standards for emissions.
In addition, the transmitter may incorporate features such as an audio preamplifier, which enhances the audio input signal before modulation, and a feedback loop for automatic gain control (AGC) to maintain consistent output levels despite variations in input signal strength.
Additional components may include capacitors for coupling and bypassing, inductors for tuning, and resistors for biasing and load matching. The overall layout of the circuit should adhere to best practices in RF design, including proper grounding, shielding, and component placement to minimize interference and optimize performance.
This FM transmitter can be utilized in various applications, including community radio stations, educational projects, and personal broadcasting, making it a versatile component in the field of electronic communications.4W FM Transmitter. TECHNICAL CHARACTERISTICS: Stabilised tendency of catering: Vcc=12~16V Frequency of emission: 88~108MHz Consumption: 100~400mA Materially: The. 🔗 External reference