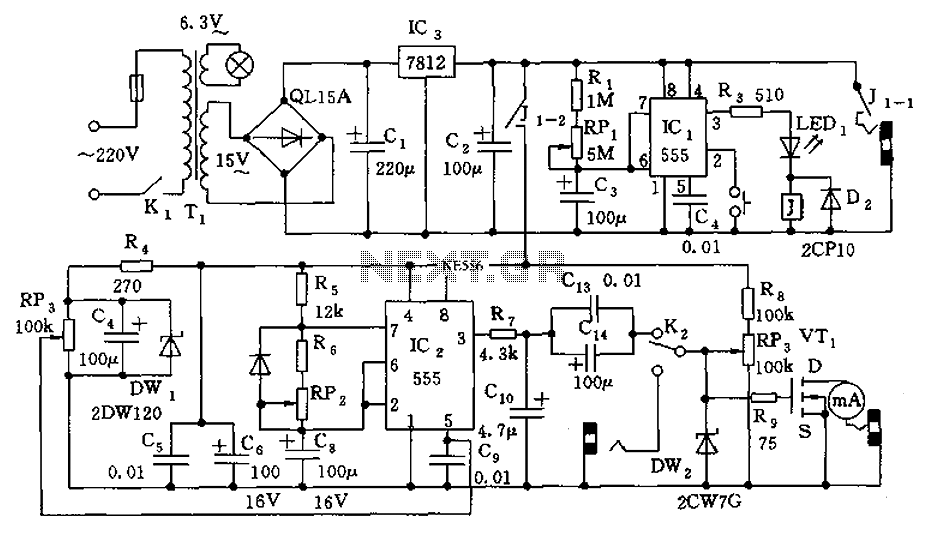
555 the DC capacitor tester
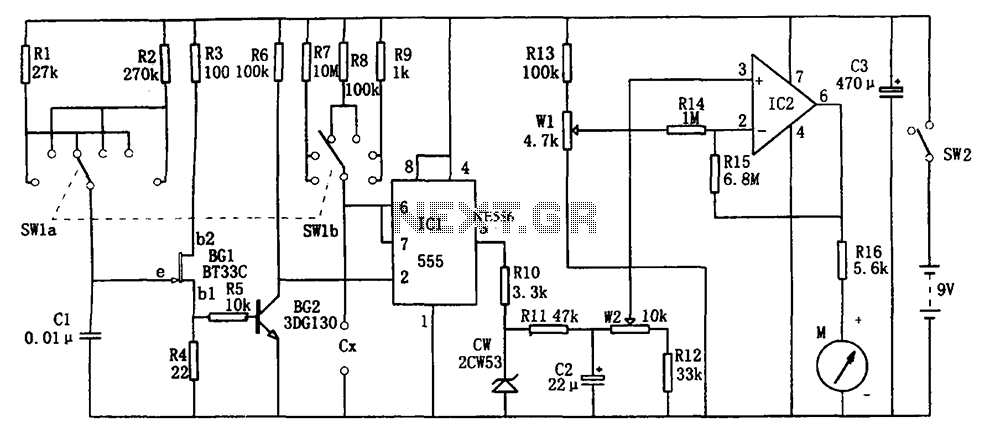
The circuit illustrated in Figure 555 represents a DC capacitor tester. This tester includes a pulse generator, a single-shot circuit, and a head indicating DC amplifier circuit. It is capable of measuring capacitance in the range of nanofarads (nF) and microfarads (μF), specifically from approximately 0 picofarads (pF) to 1 microfarad (μF). The measurement range is segmented into several categories: 0 to 100 pF, 0 to 1 nF, 0 to 10 nF, 0 to 100 nF, 0 to 1 μF, and 0 to 10 μF.
The DC capacitor tester circuit operates by generating a pulse signal through the pulse generator, which is then fed into a single-shot circuit. This circuit is designed to produce a single output pulse in response to the input pulse, effectively allowing for a controlled measurement of the capacitor's characteristics. The head indicating DC amplifier circuit is responsible for amplifying the voltage signal generated by the capacitor under test, enabling accurate readings of its capacitance.
The measurement ranges are defined by the selection of appropriate resistors and capacitors in the circuit, which determine the sensitivity and scale of the measurements. For instance, the lower ranges (0 to 100 pF and 0 to 1 nF) utilize high-precision components to ensure accurate readings of small capacitances, while the higher ranges (0 to 1 μF and 0 to 10 μF) can accommodate larger capacitors, making the tester versatile for various applications.
In practical use, the tester is connected across the terminals of the capacitor to be measured. The resulting voltage signal, once amplified, can be displayed on a digital or analog meter, providing a clear indication of the capacitor's value. This circuit is particularly useful in electronics testing and repair where accurate capacitance measurements are necessary for troubleshooting and component validation. As shown in Figure 555 constituting the DC capacitor tester. The tester from the pulse generator, single-shot, and the head indicating DC amplifier circuit. It measures NpF ~ 1 0 mu F capacitor. Range is divided into 0 ~ 100PF, 0 ~ 1nF, 0 ~ 10nF, 0 ~ 100nF, 0 ~ 1 mu F, 0 ~ 10 mu F.
The DC capacitor tester circuit operates by generating a pulse signal through the pulse generator, which is then fed into a single-shot circuit. This circuit is designed to produce a single output pulse in response to the input pulse, effectively allowing for a controlled measurement of the capacitor's characteristics. The head indicating DC amplifier circuit is responsible for amplifying the voltage signal generated by the capacitor under test, enabling accurate readings of its capacitance.
The measurement ranges are defined by the selection of appropriate resistors and capacitors in the circuit, which determine the sensitivity and scale of the measurements. For instance, the lower ranges (0 to 100 pF and 0 to 1 nF) utilize high-precision components to ensure accurate readings of small capacitances, while the higher ranges (0 to 1 μF and 0 to 10 μF) can accommodate larger capacitors, making the tester versatile for various applications.
In practical use, the tester is connected across the terminals of the capacitor to be measured. The resulting voltage signal, once amplified, can be displayed on a digital or analog meter, providing a clear indication of the capacitor's value. This circuit is particularly useful in electronics testing and repair where accurate capacitance measurements are necessary for troubleshooting and component validation. As shown in Figure 555 constituting the DC capacitor tester. The tester from the pulse generator, single-shot, and the head indicating DC amplifier circuit. It measures NpF ~ 1 0 mu F capacitor. Range is divided into 0 ~ 100PF, 0 ~ 1nF, 0 ~ 10nF, 0 ~ 100nF, 0 ~ 1 mu F, 0 ~ 10 mu F.
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713