555 tone generator 8 ohm speaker
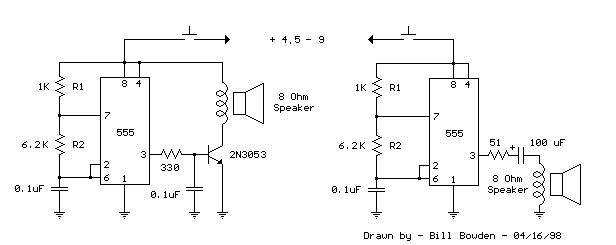
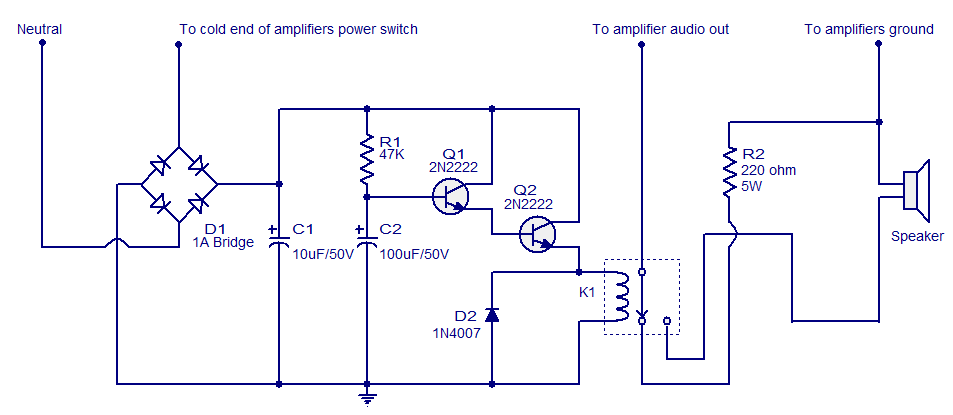
This is a basic 555 square wave oscillator designed to generate a 1 kHz tone for an 8-ohm speaker. In the circuit, the speaker is isolated from the oscillator by an NPN medium power transistor, which supplies more current than the 555 timer can deliver directly (limit = 200 mA). A small capacitor is included at the transistor base to slow the switching times, thereby reducing the inductive voltage generated by the speaker.
The circuit utilizes the 555 timer in astable mode to create a square wave output at a frequency of 1 kHz. The frequency is primarily determined by the values of two resistors (R1 and R2) and a capacitor (C1) connected to the 555 timer. The output from the 555 timer is fed into the base of the NPN transistor, which acts as a switch to drive the speaker.
The use of the NPN transistor is crucial as it allows the circuit to handle higher currents, making it suitable for driving the 8-ohm speaker without exceeding the current limitations of the 555 timer. The small capacitor connected to the base of the transistor serves to filter out high-frequency noise and smooths the switching transitions, which helps to minimize the inductive kickback voltage produced when the speaker is turned off.
This configuration ensures that the speaker receives a clean and stable 1 kHz tone while protecting the 555 timer from potential damage due to excess current draw. Overall, this simple oscillator circuit is effective for generating audio tones and can be used in various applications such as alarms, sound effects, or educational projects in electronics.This is a basic 555 squarewave oscillator used to produce a 1 Khz tone from an 8 ohm speaker. In the circuit on the left, the speaker is isolated from the oscillator by the NPN medium power transistor which also provides more current than can be obtained directly from the 555 (limit = 200 mA). A small capacitor is used at the transistor base to slow the switching times which reduces the inductive voltage produced by the speaker..
🔗 External reference
The circuit utilizes the 555 timer in astable mode to create a square wave output at a frequency of 1 kHz. The frequency is primarily determined by the values of two resistors (R1 and R2) and a capacitor (C1) connected to the 555 timer. The output from the 555 timer is fed into the base of the NPN transistor, which acts as a switch to drive the speaker.
The use of the NPN transistor is crucial as it allows the circuit to handle higher currents, making it suitable for driving the 8-ohm speaker without exceeding the current limitations of the 555 timer. The small capacitor connected to the base of the transistor serves to filter out high-frequency noise and smooths the switching transitions, which helps to minimize the inductive kickback voltage produced when the speaker is turned off.
This configuration ensures that the speaker receives a clean and stable 1 kHz tone while protecting the 555 timer from potential damage due to excess current draw. Overall, this simple oscillator circuit is effective for generating audio tones and can be used in various applications such as alarms, sound effects, or educational projects in electronics.This is a basic 555 squarewave oscillator used to produce a 1 Khz tone from an 8 ohm speaker. In the circuit on the left, the speaker is isolated from the oscillator by the NPN medium power transistor which also provides more current than can be obtained directly from the 555 (limit = 200 mA). A small capacitor is used at the transistor base to slow the switching times which reduces the inductive voltage produced by the speaker..
🔗 External reference