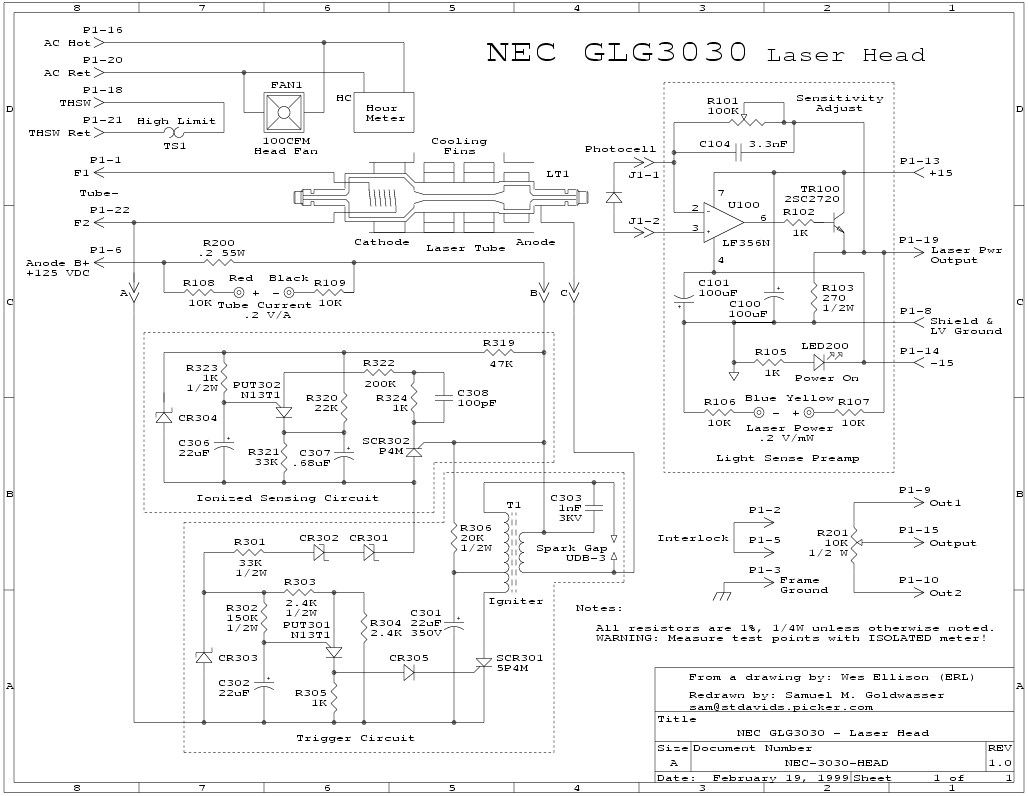
5v dual power supply
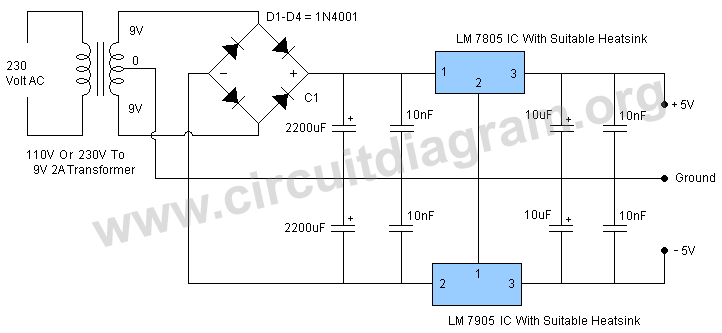
The circuit employs a center-tapped transformer that steps down 230V AC or 110V AC to 9V-0-9V. Four 1N4001 diodes are utilized for the rectification of the AC voltage to DC. A 2200μF / 25V electrolytic capacitor is included to filter the voltage from the diodes, along with additional capacitors used for decoupling purposes.
The circuit design begins with a center-tapped transformer that is capable of handling either 230V AC or 110V AC input voltages, providing a secondary output of 9V-0-9V. The center tap allows for a dual output, which can be beneficial for applications requiring both positive and negative voltages relative to the center tap.
Following the transformer, the AC voltage is routed to a bridge rectifier composed of four 1N4001 diodes. Each diode is rated for a maximum reverse voltage of 50V and a forward current of 1A, making them suitable for this application. The diodes are arranged in a bridge configuration to convert the alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). This configuration allows for full-wave rectification, which improves the efficiency of the power conversion process by utilizing both halves of the AC waveform.
After rectification, the output voltage is still pulsating DC, which requires smoothing to provide a stable DC voltage. A 2200μF electrolytic capacitor rated at 25V is employed to filter the rectified output. This large capacitance value helps to reduce voltage ripple, providing a more constant DC voltage level. The capacitor charges during the peaks of the rectified voltage and discharges during the troughs, thereby smoothing out the fluctuations.
In addition to the primary filtering capacitor, several smaller decoupling capacitors are strategically placed throughout the circuit. These capacitors serve to filter high-frequency noise and transients that may be present in the power supply, ensuring stable operation of the connected load. The selection of these decoupling capacitors is critical for maintaining the integrity of the power supply, especially in sensitive electronic applications.
Overall, the described circuit effectively converts high-voltage AC mains power into a stable low-voltage DC output suitable for various electronic applications, ensuring reliable performance through careful component selection and arrangement.The circuit is using a 230V AC OR 110V AC to 9V-0-9V step down center tapped transformer to step down the mains voltages. Four 1N4001 diodes are used for rectification of the AC voltage to DC. A 2200uF / 25V electrolytic capacitor is used the filter the voltage coming from the diodes and other capacitors are used for decoupling.
🔗 External reference
The circuit design begins with a center-tapped transformer that is capable of handling either 230V AC or 110V AC input voltages, providing a secondary output of 9V-0-9V. The center tap allows for a dual output, which can be beneficial for applications requiring both positive and negative voltages relative to the center tap.
Following the transformer, the AC voltage is routed to a bridge rectifier composed of four 1N4001 diodes. Each diode is rated for a maximum reverse voltage of 50V and a forward current of 1A, making them suitable for this application. The diodes are arranged in a bridge configuration to convert the alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). This configuration allows for full-wave rectification, which improves the efficiency of the power conversion process by utilizing both halves of the AC waveform.
After rectification, the output voltage is still pulsating DC, which requires smoothing to provide a stable DC voltage. A 2200μF electrolytic capacitor rated at 25V is employed to filter the rectified output. This large capacitance value helps to reduce voltage ripple, providing a more constant DC voltage level. The capacitor charges during the peaks of the rectified voltage and discharges during the troughs, thereby smoothing out the fluctuations.
In addition to the primary filtering capacitor, several smaller decoupling capacitors are strategically placed throughout the circuit. These capacitors serve to filter high-frequency noise and transients that may be present in the power supply, ensuring stable operation of the connected load. The selection of these decoupling capacitors is critical for maintaining the integrity of the power supply, especially in sensitive electronic applications.
Overall, the described circuit effectively converts high-voltage AC mains power into a stable low-voltage DC output suitable for various electronic applications, ensuring reliable performance through careful component selection and arrangement.The circuit is using a 230V AC OR 110V AC to 9V-0-9V step down center tapped transformer to step down the mains voltages. Four 1N4001 diodes are used for rectification of the AC voltage to DC. A 2200uF / 25V electrolytic capacitor is used the filter the voltage coming from the diodes and other capacitors are used for decoupling.
🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713