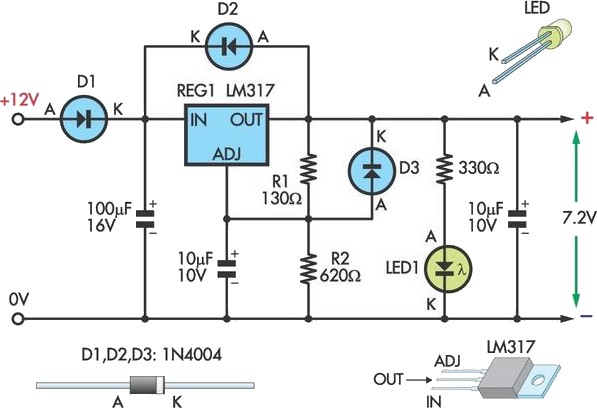
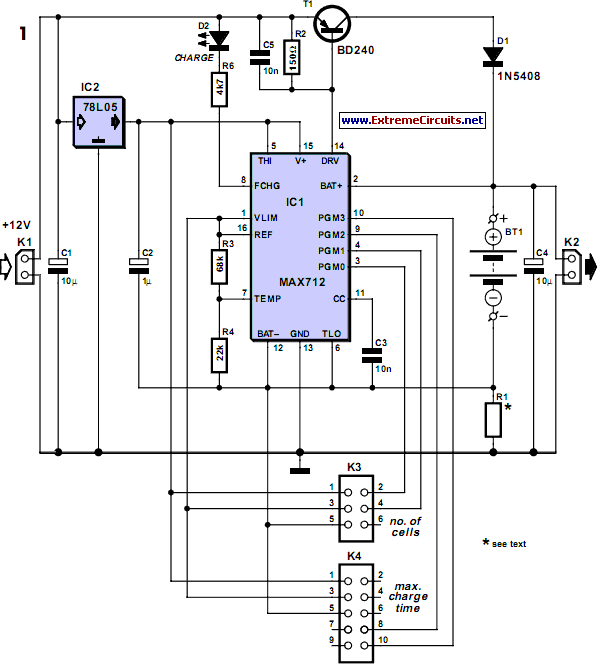
9V NiCd battery charger
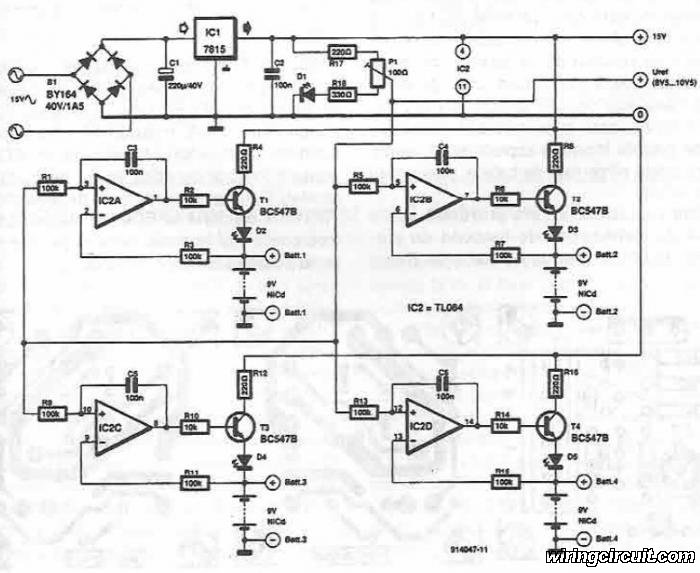
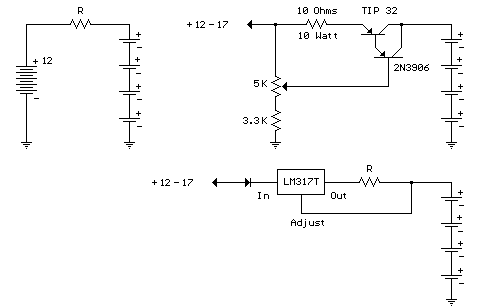
This electronic circuit diagram facilitates the design of a straightforward charging circuit for NiCd batteries. The charger is capable of simultaneously charging four 9V NiCd batteries, with the voltage being adjustable via a potentiometer labeled P1.
The described circuit operates by utilizing a basic charging topology suitable for NiCd batteries, which are known for their robustness and ability to deliver high discharge rates. The circuit includes a power supply unit that provides the necessary voltage and current to charge the batteries. The four battery slots are connected in parallel, allowing them to be charged simultaneously while ensuring that each battery receives the appropriate voltage.
The potentiometer P1 serves as a variable resistor, enabling the user to adjust the output voltage to match the specific requirements of the NiCd batteries being charged. This feature is critical, as charging voltages must be carefully controlled to prevent overcharging, which can lead to reduced battery life or even damage.
In addition to the charging mechanism, the circuit may incorporate various safety features, such as overcurrent protection, thermal cutoff, and possibly a LED indicator to signal when charging is in progress. These enhancements improve the reliability and safety of the charging process, making it suitable for both personal and professional applications.
Overall, the circuit diagram provides a clear and effective solution for charging multiple NiCd batteries, ensuring that they are charged efficiently and safely.Using this electronic circuit diagram can be designed a very simple charging circuit for NiCd batteries. This electronic charger allows simultaneous charge of four NiCd batteries of 9 V, cursor of P1potentiometer set voltage that will used..
🔗 External reference
The described circuit operates by utilizing a basic charging topology suitable for NiCd batteries, which are known for their robustness and ability to deliver high discharge rates. The circuit includes a power supply unit that provides the necessary voltage and current to charge the batteries. The four battery slots are connected in parallel, allowing them to be charged simultaneously while ensuring that each battery receives the appropriate voltage.
The potentiometer P1 serves as a variable resistor, enabling the user to adjust the output voltage to match the specific requirements of the NiCd batteries being charged. This feature is critical, as charging voltages must be carefully controlled to prevent overcharging, which can lead to reduced battery life or even damage.
In addition to the charging mechanism, the circuit may incorporate various safety features, such as overcurrent protection, thermal cutoff, and possibly a LED indicator to signal when charging is in progress. These enhancements improve the reliability and safety of the charging process, making it suitable for both personal and professional applications.
Overall, the circuit diagram provides a clear and effective solution for charging multiple NiCd batteries, ensuring that they are charged efficiently and safely.Using this electronic circuit diagram can be designed a very simple charging circuit for NiCd batteries. This electronic charger allows simultaneous charge of four NiCd batteries of 9 V, cursor of P1potentiometer set voltage that will used..
🔗 External reference