Active AM Radio Antenna Amplifier / Preamplifier Circuit
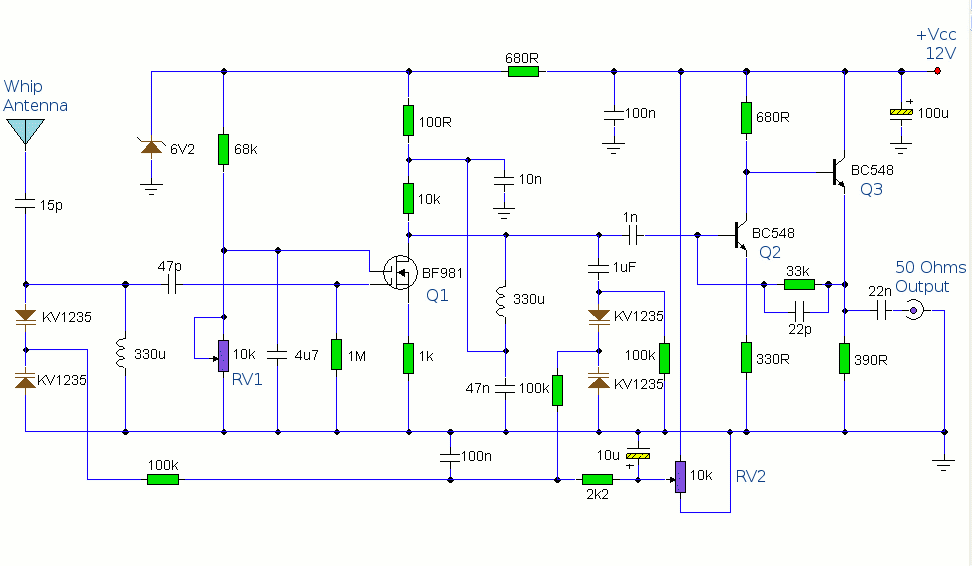
The antenna amplifier circuit comprises approximately 40 components, featuring two NPN transistors (BC548), one MOSFET (BF981), two varicap diodes (KV1235), and a 6.2V zener diode. It includes a 330µH inductor/coil, which can be modified for operation on different frequency bands. Designed for use with a telescopic whip antenna, the amplifier operates within the AM/Medium Wave band of 550 to 1650 kHz, requiring a 12V DC power supply. The circuit includes a gain control feature, allowing for the amplification of weak signals as needed, controlled via RV1. The output impedance of the amplifier circuit is 50 ohms, which is standard for radio receivers, ensuring compatibility with AM receivers. The preamplifier is intended to amplify the input from a telescopic whip antenna, covering the medium waveband from approximately 550 kHz to 1650 kHz. The tuning voltage is supplied through RV2, a 10k potentiometer connected to the 12V power supply. RV1 serves as the gain control, enabling weak signals to be amplified or strong signals to be attenuated. The control voltage is applied to gate 2 of TR1, a dual-gate MOSFET, while the input signal is applied to gate 1. The input signal is double-tuned using the 330µH coil and the two KV1235 varicap diodes at the MOSFET's input and at the BF981 MOSFET's drain terminal. Both tuned circuits provide high selectivity across the entire tuning range. To enhance stability, the MOSFET stage is powered by a 6.2V zener stabilized supply. To drive low impedance (50 ohm) receivers, the medium output impedance of the BF981 stage is improved by a composite amplifier formed by Q2 and Q3. Q2 operates in common emitter mode, boosting voltage levels by just over 2, while Q3 functions as an emitter follower, providing low output impedance. This active antenna can be adapted for use on other bands by changing the values of the 330µH coils. Switches or relays can be employed to modify the coil values for multi-band operation.
The antenna amplifier circuit is designed to enhance the reception capabilities of AM radio receivers by amplifying weak signals from a telescopic whip antenna. The use of two NPN transistors and a MOSFET allows for efficient signal processing, while the varicap diodes enable fine-tuning of the frequency response. The 330µH inductor/coil serves as a critical component for tuning across the medium waveband, providing flexibility for different frequency ranges.
The gain control feature, facilitated by RV1, allows users to adjust the amplification level based on signal strength. This is particularly useful in environments with varying signal conditions, enabling optimal reception without distortion from strong signals. The output impedance of 50 ohms ensures compatibility with standard radio receivers, facilitating straightforward integration into existing systems.
The dual-gate MOSFET configuration not only enhances selectivity but also improves overall performance through its ability to handle varying input signals effectively. The zener diode provides stability to the power supply, ensuring consistent performance of the amplifier circuit. The composite amplifier configuration, utilizing Q2 and Q3, further enhances the circuit's ability to drive low impedance loads, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
For users interested in multi-band operation, the circuit's design allows for easy modification of the inductor values. By incorporating switches or relays, users can quickly adapt the circuit to operate efficiently across different frequency bands, making this antenna amplifier a versatile solution for AM radio applications.The antenna amplifier circuit has a part count of about 40, using the following active parts: 2 NPN transistors (BC548`s), 1 MOSFET (BF981), 2 Varicap diodes (KV1235), as well as a 6v2 zener-diode. there is and a 330uH (micro Henry) inductor / coil, which can be modified for operation on other frequency bands.
Designed to work with a telescopic wh ip antenna, the amplifier circuit operates in the typical AM / MediumWave band of 550 - 1650 kHz (kilohertz), with a power requirement of 12 Volts DC. The circuit also has a gain control feature, so weather signals can be amplifier more, if need be. This amplification alteration is provided via, RV1 The amplifier circuit`s output impedance is 50 Ohms, which is the standard for all of radio receivers, so it ought to work well along with your AM receiver.
This circuit is designed to amplify the input from a telescopic whip antenna. The preamplifier is designed to cover the medium waveband from about 550Khz to 1650Khz. The tuning voltage is supplied via RV2, a 10k potentiometer connected to the 12 Volt power supply. RV1 is the gain control allowing weak signals to be amplified or strong signals to be attenuated. The control voltage is applied to gate 2 of TR1, a dual-gate MOSFET, the signal voltage applied via gate 1; the input signal being double tuned via the 330uH coil and the two KV1235 varicap diodes at the MOSFET`s input and by the same components at the BF981 MOSFET`s drain terminal. Both tuned circuits provide high selectivity across the entire tuning range. To aid stability the MOSFET stage is fed from a 6. 2V zener stabilized supply. To drive low impedance (50 ohm) receivers, the medium output impedance of the BF981 stage is enhanced by the composite amplifier made from Q2 and Q3.
Q2 is operating in common emitter boosting voltage levels by just over 2, Q3 is operating in emitter follower providing the circuit with low output impedance. Finally this active antenna can be used on other bands by changing the values of the 330uH coils. To perform on multiple bands switches or relays can be used to change the value of the coils. 🔗 External reference
The antenna amplifier circuit is designed to enhance the reception capabilities of AM radio receivers by amplifying weak signals from a telescopic whip antenna. The use of two NPN transistors and a MOSFET allows for efficient signal processing, while the varicap diodes enable fine-tuning of the frequency response. The 330µH inductor/coil serves as a critical component for tuning across the medium waveband, providing flexibility for different frequency ranges.
The gain control feature, facilitated by RV1, allows users to adjust the amplification level based on signal strength. This is particularly useful in environments with varying signal conditions, enabling optimal reception without distortion from strong signals. The output impedance of 50 ohms ensures compatibility with standard radio receivers, facilitating straightforward integration into existing systems.
The dual-gate MOSFET configuration not only enhances selectivity but also improves overall performance through its ability to handle varying input signals effectively. The zener diode provides stability to the power supply, ensuring consistent performance of the amplifier circuit. The composite amplifier configuration, utilizing Q2 and Q3, further enhances the circuit's ability to drive low impedance loads, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
For users interested in multi-band operation, the circuit's design allows for easy modification of the inductor values. By incorporating switches or relays, users can quickly adapt the circuit to operate efficiently across different frequency bands, making this antenna amplifier a versatile solution for AM radio applications.The antenna amplifier circuit has a part count of about 40, using the following active parts: 2 NPN transistors (BC548`s), 1 MOSFET (BF981), 2 Varicap diodes (KV1235), as well as a 6v2 zener-diode. there is and a 330uH (micro Henry) inductor / coil, which can be modified for operation on other frequency bands.
Designed to work with a telescopic wh ip antenna, the amplifier circuit operates in the typical AM / MediumWave band of 550 - 1650 kHz (kilohertz), with a power requirement of 12 Volts DC. The circuit also has a gain control feature, so weather signals can be amplifier more, if need be. This amplification alteration is provided via, RV1 The amplifier circuit`s output impedance is 50 Ohms, which is the standard for all of radio receivers, so it ought to work well along with your AM receiver.
This circuit is designed to amplify the input from a telescopic whip antenna. The preamplifier is designed to cover the medium waveband from about 550Khz to 1650Khz. The tuning voltage is supplied via RV2, a 10k potentiometer connected to the 12 Volt power supply. RV1 is the gain control allowing weak signals to be amplified or strong signals to be attenuated. The control voltage is applied to gate 2 of TR1, a dual-gate MOSFET, the signal voltage applied via gate 1; the input signal being double tuned via the 330uH coil and the two KV1235 varicap diodes at the MOSFET`s input and by the same components at the BF981 MOSFET`s drain terminal. Both tuned circuits provide high selectivity across the entire tuning range. To aid stability the MOSFET stage is fed from a 6. 2V zener stabilized supply. To drive low impedance (50 ohm) receivers, the medium output impedance of the BF981 stage is enhanced by the composite amplifier made from Q2 and Q3.
Q2 is operating in common emitter boosting voltage levels by just over 2, Q3 is operating in emitter follower providing the circuit with low output impedance. Finally this active antenna can be used on other bands by changing the values of the 330uH coils. To perform on multiple bands switches or relays can be used to change the value of the coils. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713