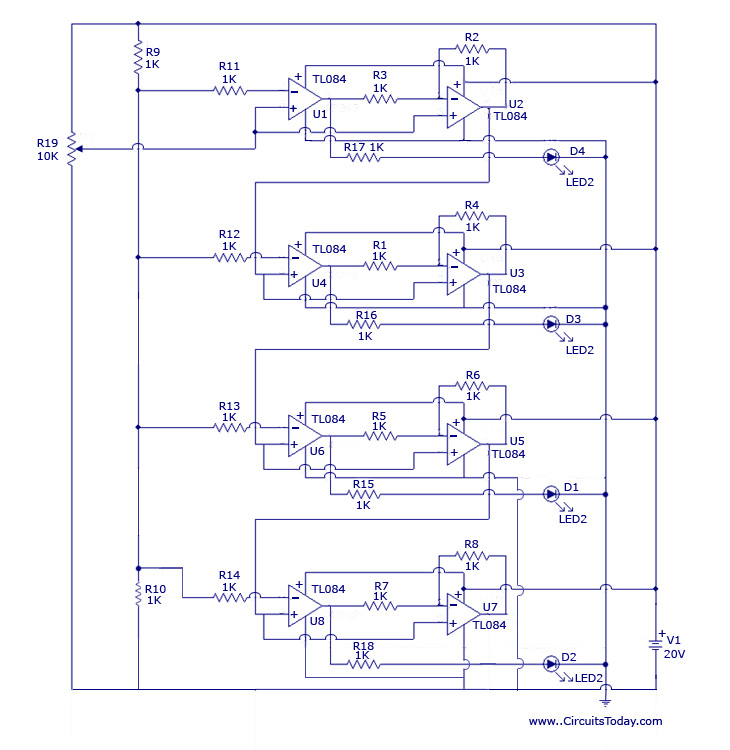
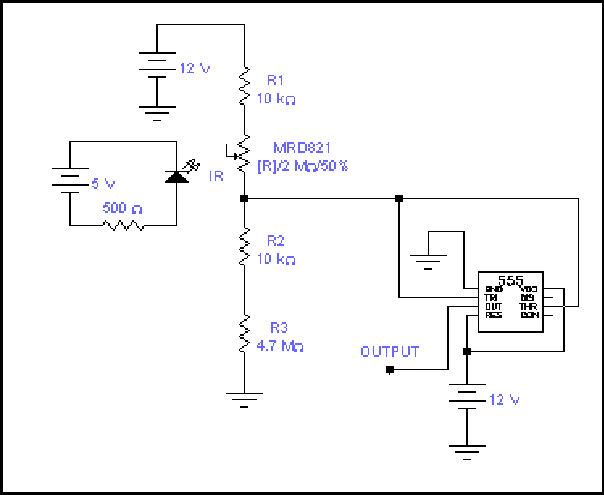
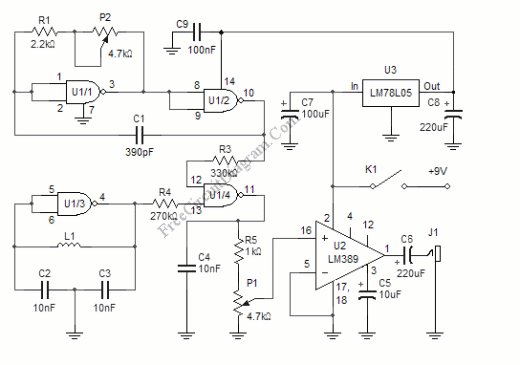
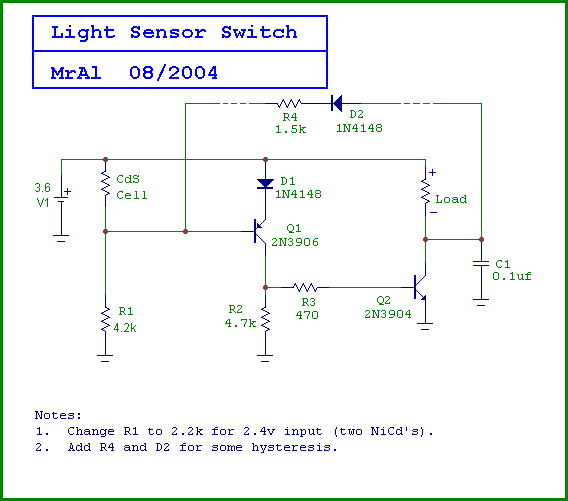
AM Broadcast Detector
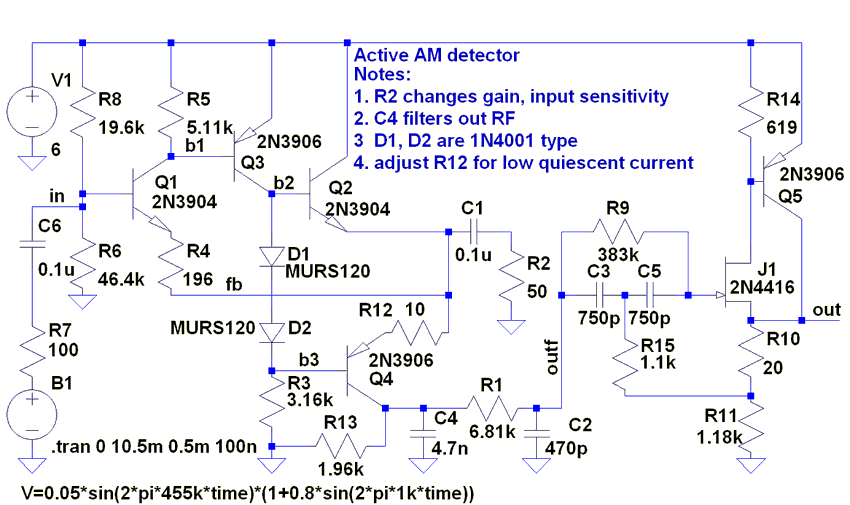
The following circuit illustrates an AM Broadcast Detector Circuit Diagram. Features include a 10 kHz notch filter, which is suitable for low voltage single supply applications.
The AM Broadcast Detector Circuit is designed to demodulate amplitude modulated (AM) signals, allowing for the extraction of audio information from the RF carrier wave. The circuit typically consists of a diode, which serves as the demodulating element, and additional components such as resistors and capacitors that form the notch filter.
The inclusion of a 10 kHz notch filter is crucial in this design as it effectively attenuates unwanted frequencies around 10 kHz, which may arise from interference or noise in the transmission environment. This helps to enhance the clarity of the received audio signal. The circuit may utilize a low voltage single supply, making it suitable for battery-operated devices or applications where power efficiency is a priority.
In detail, the diode's forward bias allows it to conduct during the positive half-cycles of the AM signal, while blocking the negative half-cycles. This results in a pulsating DC output that corresponds to the audio envelope of the modulated signal. The output is then smoothed using a capacitor, which helps to filter out high-frequency components and provides a more stable audio signal.
The notch filter can be implemented using an R-C (resistor-capacitor) network, strategically designed to create a frequency response that minimizes gain at 10 kHz while allowing other frequencies to pass through. This is particularly beneficial in environments with multiple overlapping AM signals, as it helps to isolate the desired station.
Overall, this AM Broadcast Detector Circuit is an essential tool for receiving AM signals, particularly in low-power applications, and its design can be adapted for various frequencies and environmental conditions to optimize performance.The following circuit shows about AM Broadcast Detector Circuit Diagram. Features: with 10KHz notch filter, fits well with a low voltage single .. 🔗 External reference
The AM Broadcast Detector Circuit is designed to demodulate amplitude modulated (AM) signals, allowing for the extraction of audio information from the RF carrier wave. The circuit typically consists of a diode, which serves as the demodulating element, and additional components such as resistors and capacitors that form the notch filter.
The inclusion of a 10 kHz notch filter is crucial in this design as it effectively attenuates unwanted frequencies around 10 kHz, which may arise from interference or noise in the transmission environment. This helps to enhance the clarity of the received audio signal. The circuit may utilize a low voltage single supply, making it suitable for battery-operated devices or applications where power efficiency is a priority.
In detail, the diode's forward bias allows it to conduct during the positive half-cycles of the AM signal, while blocking the negative half-cycles. This results in a pulsating DC output that corresponds to the audio envelope of the modulated signal. The output is then smoothed using a capacitor, which helps to filter out high-frequency components and provides a more stable audio signal.
The notch filter can be implemented using an R-C (resistor-capacitor) network, strategically designed to create a frequency response that minimizes gain at 10 kHz while allowing other frequencies to pass through. This is particularly beneficial in environments with multiple overlapping AM signals, as it helps to isolate the desired station.
Overall, this AM Broadcast Detector Circuit is an essential tool for receiving AM signals, particularly in low-power applications, and its design can be adapted for various frequencies and environmental conditions to optimize performance.The following circuit shows about AM Broadcast Detector Circuit Diagram. Features: with 10KHz notch filter, fits well with a low voltage single .. 🔗 External reference