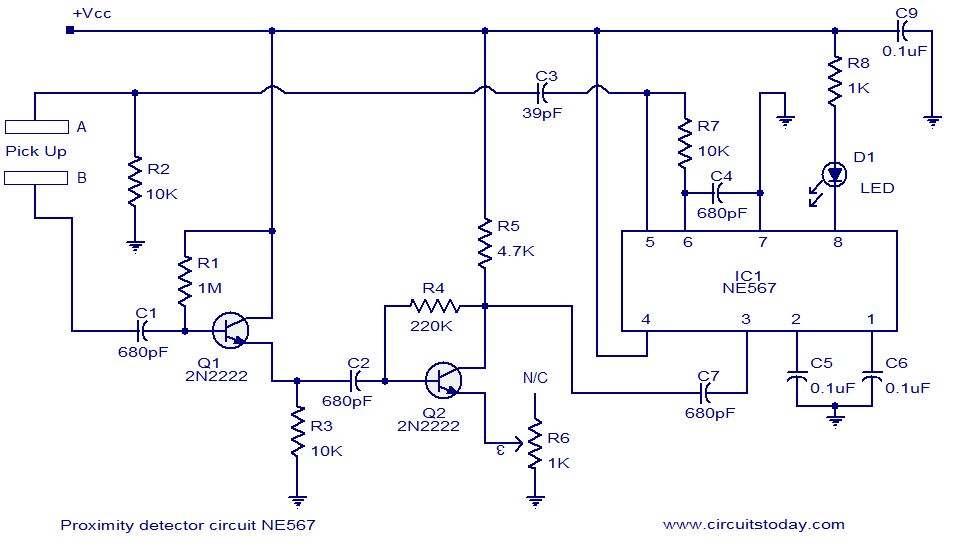
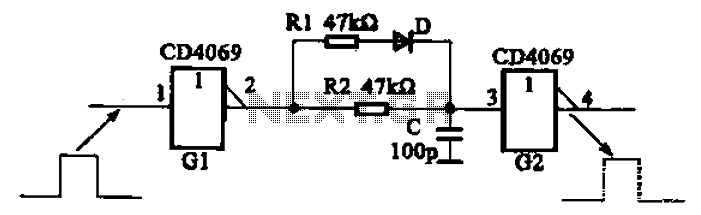
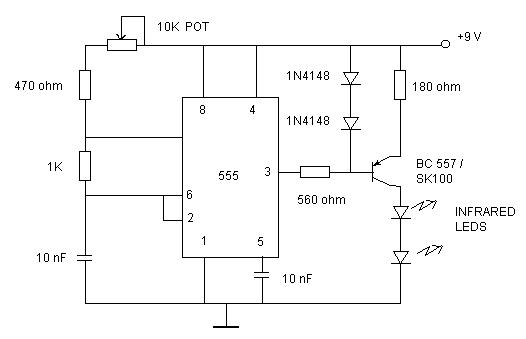
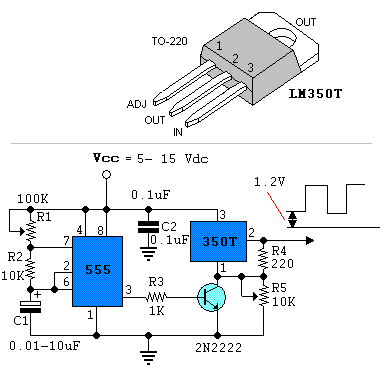
Analog switches carrier suppression amplitude modulation circuit
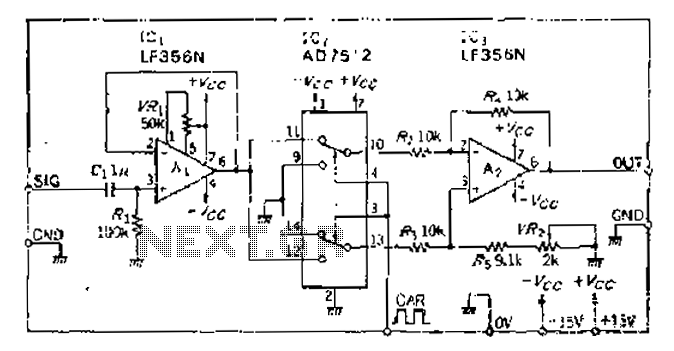
An analog switch (double loop, double-break) and a differential modulation amplifier are used in this circuit. The carrier control switch operates by switching contacts at specific times, inverting the input modulation wave. When the next carrier signal is applied to the inverting input, it enables anti-phase operation, facilitating limited amplitude modulation. The carrier signal will not exhibit distortion or interruption, but rather will experience polarity reversal. It is essential for analog switches to maintain the carrier frequency, as they cannot be utilized at high frequencies. The modulated output is a square wave, which contains high-frequency components. To achieve the desired sine wave signal, a band-pass filter is implemented to modify the output accordingly.
The circuit employs an analog switch configured as a double loop, double-break mechanism, which allows for precise control over the modulation process. The differential modulation amplifier serves to amplify the input modulation wave while ensuring that the signal remains within the desired amplitude limits. This configuration is critical for applications requiring high fidelity in signal transmission.
The carrier control switch is responsible for managing the timing of the modulation. It is designed to switch between different states, ensuring that the modulation wave is inverted at the appropriate intervals. This inversion is crucial for achieving the desired amplitude modulation characteristics, where the carrier signal's polarity is reversed without introducing distortion.
The circuit's operation is contingent upon maintaining a stable carrier frequency. Analog switches, while effective for low-frequency applications, are limited in their performance at high frequencies. Therefore, careful consideration must be given to the selection of components to ensure that the analog switch can handle the required frequency range without degradation of the signal quality.
The output of the modulation process is a square wave, which inherently contains high-frequency harmonics. To refine this output into a more desirable sine wave form, a band-pass filter is integrated into the circuit. This filter is tailored to allow only the desired frequency components to pass through while attenuating unwanted high-frequency noise, thereby enhancing the overall signal integrity.
In summary, this circuit design effectively combines an analog switch and a differential modulation amplifier to achieve controlled amplitude modulation. The incorporation of a band-pass filter further ensures that the output signal meets the required specifications for sine wave characteristics, making this configuration suitable for various electronic applications.Analog switch (double loop, double-break) and differential modulation amplifier complete the work. The carrier control switch, switch contacts in the time, from the inverting i nput Chi input modulation wave is inverted. Back when the next carrier-inverting input, so that the anti- re going, to achieve the limit amplitude modulation, the carrier will not braid week and intermittent, but the polarity reversal. Analog switches must keep the carrier frequency, at high frequencies can not use. The modulated output is crossing the square, containing high frequency changed as needed to increase the band-pass filter, to obtain a sine wave signal.
The circuit employs an analog switch configured as a double loop, double-break mechanism, which allows for precise control over the modulation process. The differential modulation amplifier serves to amplify the input modulation wave while ensuring that the signal remains within the desired amplitude limits. This configuration is critical for applications requiring high fidelity in signal transmission.
The carrier control switch is responsible for managing the timing of the modulation. It is designed to switch between different states, ensuring that the modulation wave is inverted at the appropriate intervals. This inversion is crucial for achieving the desired amplitude modulation characteristics, where the carrier signal's polarity is reversed without introducing distortion.
The circuit's operation is contingent upon maintaining a stable carrier frequency. Analog switches, while effective for low-frequency applications, are limited in their performance at high frequencies. Therefore, careful consideration must be given to the selection of components to ensure that the analog switch can handle the required frequency range without degradation of the signal quality.
The output of the modulation process is a square wave, which inherently contains high-frequency harmonics. To refine this output into a more desirable sine wave form, a band-pass filter is integrated into the circuit. This filter is tailored to allow only the desired frequency components to pass through while attenuating unwanted high-frequency noise, thereby enhancing the overall signal integrity.
In summary, this circuit design effectively combines an analog switch and a differential modulation amplifier to achieve controlled amplitude modulation. The incorporation of a band-pass filter further ensures that the output signal meets the required specifications for sine wave characteristics, making this configuration suitable for various electronic applications.Analog switch (double loop, double-break) and differential modulation amplifier complete the work. The carrier control switch, switch contacts in the time, from the inverting i nput Chi input modulation wave is inverted. Back when the next carrier-inverting input, so that the anti- re going, to achieve the limit amplitude modulation, the carrier will not braid week and intermittent, but the polarity reversal. Analog switches must keep the carrier frequency, at high frequencies can not use. The modulated output is crossing the square, containing high frequency changed as needed to increase the band-pass filter, to obtain a sine wave signal.
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713