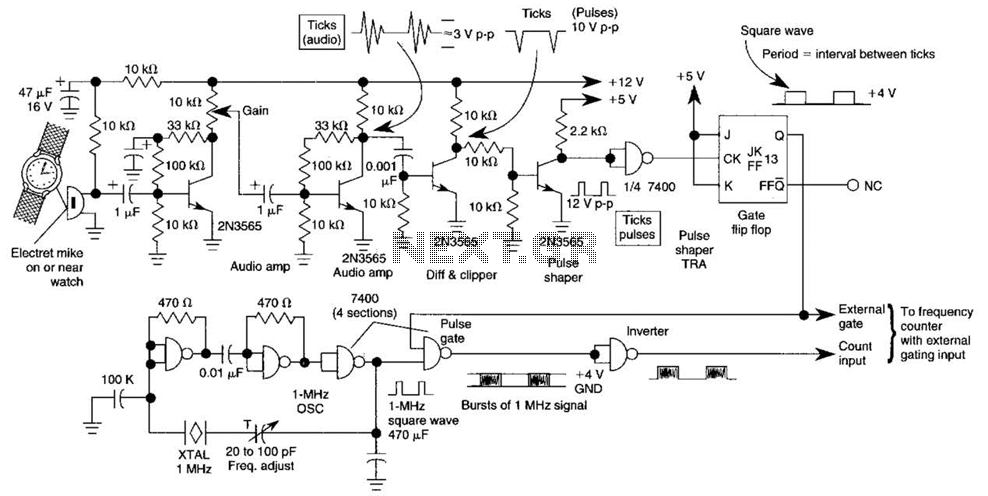
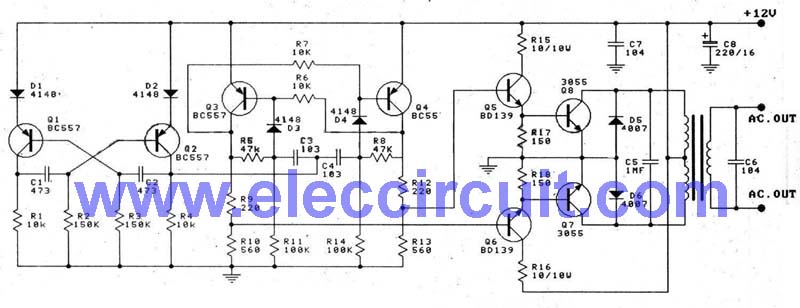
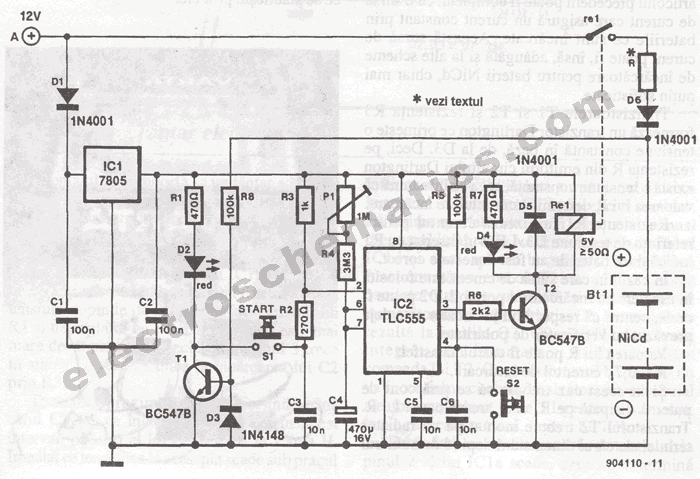
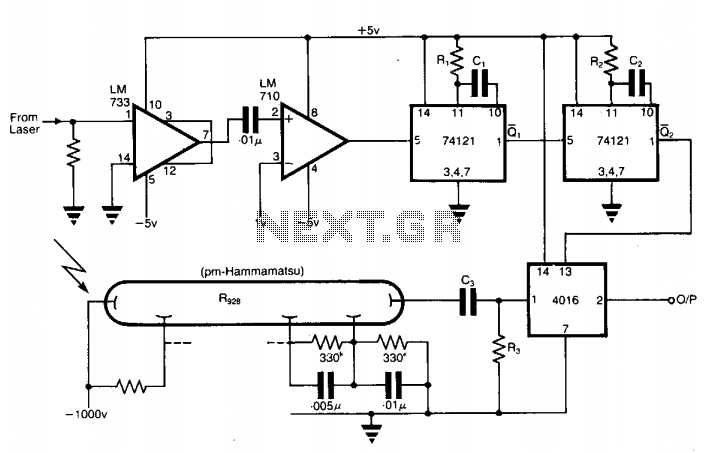
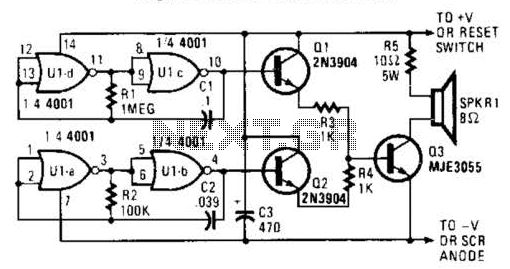
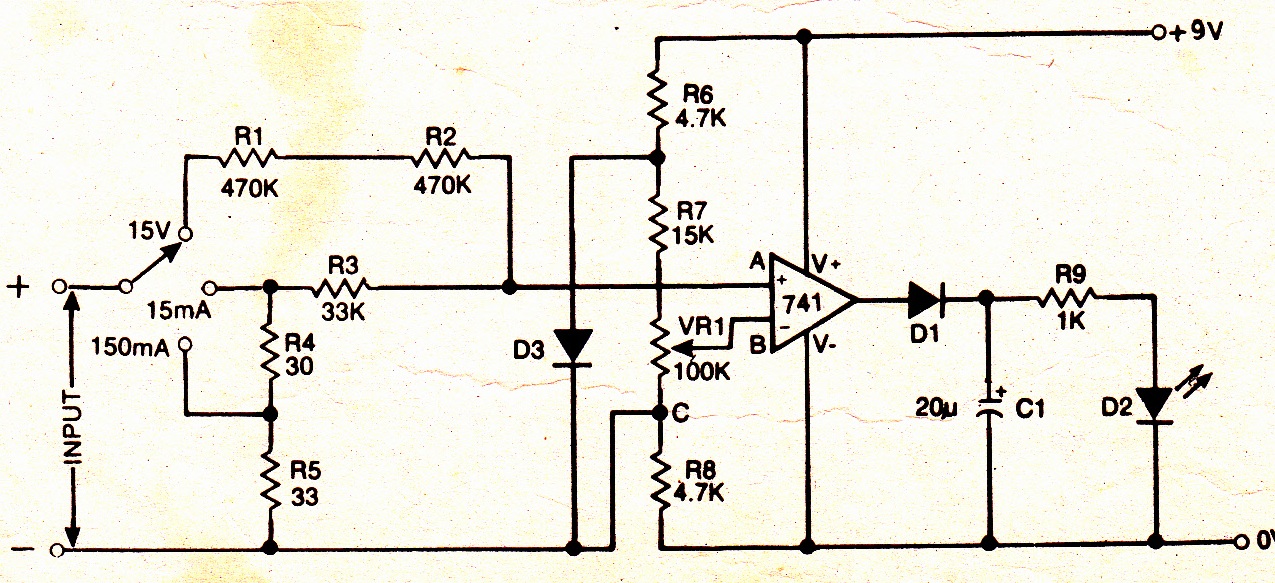
Anti-saturation function delete circuit schematics
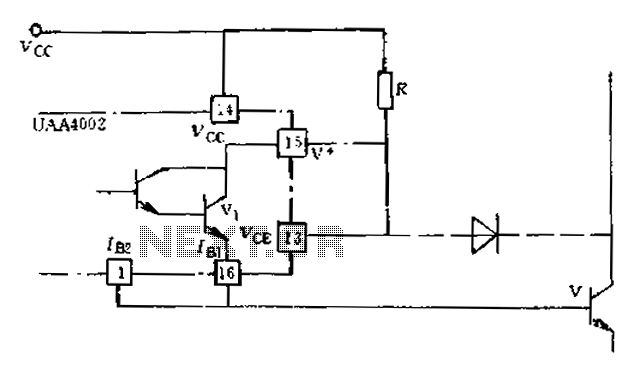
Anti-saturation devices have been removed from the UAA4002 routine applications. The base current of the switching transistor, which is driven by another transistor, is automatically adjusted. This adjustment allows the power transistors to operate in critical saturation. However, when the operating frequency of the driven transistor is very low, the switching losses are negligible, and the main losses are due to low conduction losses. This situation arises from the removal of the anti-saturation network, leading to the power transistor operating in saturation. This objective can be achieved through two methods: First, the CE pin diode of the UAA4002V is driven off the collector of the power transistor and is directly connected to the CE pin and V+ pin via a resistor after picking Vcc (refer to Fig. 12-28). This method effectively addresses the drawbacks encountered by the driving transistor, preventing it from saturating rapidly and providing effective protection.
The UAA4002 integrated circuit is utilized in applications requiring precise control of switching transistors. The removal of anti-saturation devices simplifies the circuit design while maintaining operational efficiency. The automatic adjustment of the base current ensures that the switching transistor can respond dynamically to varying load conditions, which is essential for maintaining optimal performance in power applications.
In this configuration, the CE pin diode plays a critical role in managing the voltage levels across the power transistor. By connecting the CE pin directly to the collector of the power transistor, the circuit minimizes the risk of saturation. The resistor used to connect Vcc to the CE and V+ pins helps to regulate the voltage supplied to the driving circuit, ensuring that the transistor remains in the desired operating region.
The design choice to operate the power transistor in saturation is particularly advantageous at low frequencies, where switching losses are minimal. This approach reduces overall power dissipation and enhances the efficiency of the system. The low conduction losses that arise from this configuration can be attributed to the inherent characteristics of the power transistor when it operates in the saturation region.
Overall, this circuit design demonstrates a sophisticated approach to managing transistor operation in power electronics, emphasizing efficiency and reliability while addressing potential saturation issues through careful component selection and configuration.Anti-saturation devices deleted: UAA4002 routine applications, switching transistor transistor (switching transistor driven) base current is adjusted automatically, driven powe r transistors in the critical saturation, but driven transistor operating frequency when the rate is very low, the switching losses were insignificant, then the losses are mainly low conduction losses due to artificially remove and anti-saturation network, that has been driven through the power transistor operating in saturation. Way to achieve this purpose is twofold: First, the UAA4002V CE pin diode is driven off the power transistor collector, and directly to the y CE pin and V + pin is connected through a resistor after the pick vcc (see Fig.
12-28), such an approach is that the drawbacks encountered by the driving transistor can not be saturated after the rapid and effective protection,
The UAA4002 integrated circuit is utilized in applications requiring precise control of switching transistors. The removal of anti-saturation devices simplifies the circuit design while maintaining operational efficiency. The automatic adjustment of the base current ensures that the switching transistor can respond dynamically to varying load conditions, which is essential for maintaining optimal performance in power applications.
In this configuration, the CE pin diode plays a critical role in managing the voltage levels across the power transistor. By connecting the CE pin directly to the collector of the power transistor, the circuit minimizes the risk of saturation. The resistor used to connect Vcc to the CE and V+ pins helps to regulate the voltage supplied to the driving circuit, ensuring that the transistor remains in the desired operating region.
The design choice to operate the power transistor in saturation is particularly advantageous at low frequencies, where switching losses are minimal. This approach reduces overall power dissipation and enhances the efficiency of the system. The low conduction losses that arise from this configuration can be attributed to the inherent characteristics of the power transistor when it operates in the saturation region.
Overall, this circuit design demonstrates a sophisticated approach to managing transistor operation in power electronics, emphasizing efficiency and reliability while addressing potential saturation issues through careful component selection and configuration.Anti-saturation devices deleted: UAA4002 routine applications, switching transistor transistor (switching transistor driven) base current is adjusted automatically, driven powe r transistors in the critical saturation, but driven transistor operating frequency when the rate is very low, the switching losses were insignificant, then the losses are mainly low conduction losses due to artificially remove and anti-saturation network, that has been driven through the power transistor operating in saturation. Way to achieve this purpose is twofold: First, the UAA4002V CE pin diode is driven off the power transistor collector, and directly to the y CE pin and V + pin is connected through a resistor after the pick vcc (see Fig.
12-28), such an approach is that the drawbacks encountered by the driving transistor can not be saturated after the rapid and effective protection,