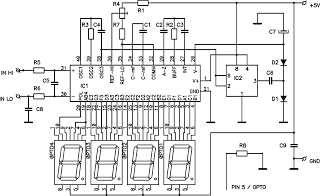
ATmega8 based RPM Meter
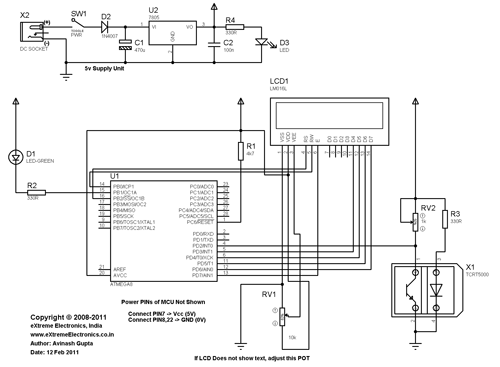
This document outlines the procedure for creating a simple RPM meter using the AVR ATmega8 microcontroller. The RPM meter designed will operate in a contactless manner.
The RPM meter circuit utilizes the AVR ATmega8 microcontroller, which is a popular 8-bit microcontroller known for its versatility and efficiency in handling various applications. The contactless feature of the RPM meter allows it to measure the rotational speed of a shaft or wheel without the need for physical contact, which minimizes wear and tear on both the sensor and the measured object.
The circuit typically includes a light source, such as an infrared LED, and a photodetector, like a phototransistor or photodiode. The infrared LED emits a beam that reflects off a reflective surface on the rotating object. As the object rotates, the reflective surface interrupts the beam, which is detected by the photodetector. The microcontroller processes the incoming signals from the photodetector to calculate the RPM based on the frequency of the interruptions.
The ATmega8 is programmed using embedded C or assembly language to interpret the signals and calculate the RPM. The program can be designed to display the RPM value on an LCD or send it to a computer for further analysis. Key considerations in the design include the selection of suitable components, calibration of the system for accurate measurements, and the implementation of noise filtering techniques to ensure reliable operation in various environmental conditions.
Power supply considerations should also be addressed, with the circuit typically powered by a regulated DC source to ensure stable operation of the microcontroller and peripheral components. Proper grounding and layout techniques are essential to minimize electromagnetic interference and ensure accurate readings.Hello All, Today I will show you how you can make a simple RPM Meter using AVR ATmega8. The RPM meter we will be making is a contact less type. 🔗 External reference
The RPM meter circuit utilizes the AVR ATmega8 microcontroller, which is a popular 8-bit microcontroller known for its versatility and efficiency in handling various applications. The contactless feature of the RPM meter allows it to measure the rotational speed of a shaft or wheel without the need for physical contact, which minimizes wear and tear on both the sensor and the measured object.
The circuit typically includes a light source, such as an infrared LED, and a photodetector, like a phototransistor or photodiode. The infrared LED emits a beam that reflects off a reflective surface on the rotating object. As the object rotates, the reflective surface interrupts the beam, which is detected by the photodetector. The microcontroller processes the incoming signals from the photodetector to calculate the RPM based on the frequency of the interruptions.
The ATmega8 is programmed using embedded C or assembly language to interpret the signals and calculate the RPM. The program can be designed to display the RPM value on an LCD or send it to a computer for further analysis. Key considerations in the design include the selection of suitable components, calibration of the system for accurate measurements, and the implementation of noise filtering techniques to ensure reliable operation in various environmental conditions.
Power supply considerations should also be addressed, with the circuit typically powered by a regulated DC source to ensure stable operation of the microcontroller and peripheral components. Proper grounding and layout techniques are essential to minimize electromagnetic interference and ensure accurate readings.Hello All, Today I will show you how you can make a simple RPM Meter using AVR ATmega8. The RPM meter we will be making is a contact less type. 🔗 External reference