Audible Logic Probe with LM339
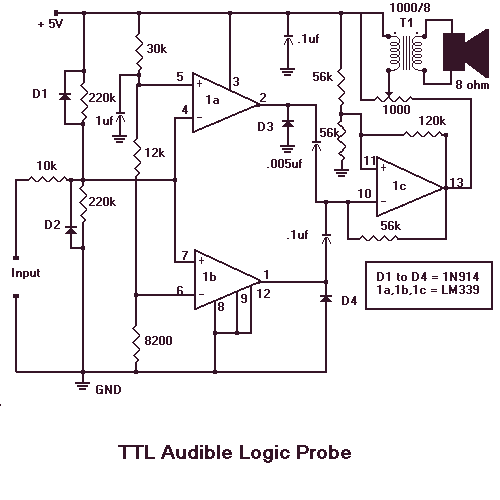
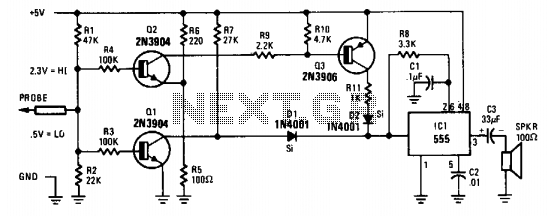
When testing circuits with a logic probe, it is sometimes difficult to watch the LEDs on the probe to determine the logic state. With this probe, the logic states are audible. This probe is designed for TTL circuits only but could be modified for CMOS. The way it works is as follows. The 5-volt power source will be the circuit under test. Clip the ground input of the probe to the ground of the circuit being tested. The other input lead is used to probe the different chips of the circuit being tested. Any input greater than 2 volts will be high and output a high tone through the speaker. Any input less than 0.8 volts will be low and produce a low tone through the speaker.
The audible logic probe operates based on the voltage levels present in TTL (Transistor-Transistor Logic) circuits. The primary components of the probe include a voltage comparator, a tone generator, and an audio output device, typically a small speaker or piezo buzzer.
The voltage comparator is configured to compare the input voltage from the circuit under test against two reference voltages: 2 volts and 0.8 volts. When the probe tip is connected to a point in the circuit, the input voltage is fed into the comparator. If the voltage exceeds 2 volts, the comparator outputs a signal that activates the tone generator to produce a high-frequency tone, indicating a logic high state. Conversely, if the voltage falls below 0.8 volts, the comparator triggers the tone generator to produce a low-frequency tone, indicating a logic low state.
For proper operation, the probe is powered by a 5-volt source, which is typically the same voltage used in TTL circuits. The ground clip must be connected to the circuit's ground to ensure accurate voltage readings. The probe's design can be adapted for CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) circuits by adjusting the reference voltage levels to accommodate the different voltage ranges used in those applications.
In summary, the audible logic probe is a valuable tool for quickly assessing the logic state of various points in a TTL circuit, providing immediate auditory feedback that can enhance the efficiency of circuit testing and troubleshooting.When testing circuits with a logic probe, it is sometimes difficult to watch the LEDS on the probe to determine the logic state. With this probe the logic states are audible. This probe is designed for TTL circuits only but could be modified for CMOS. The way it works is as follows. The 5 volt power source will be the circuit under test. Clip the ground input of the probe to the ground of the circuit being tested. The other input lead is used to probe the different chips of the circuit being tested. Any input greater then 2 volts will be high and output a high tone through the speaker. Any input less then .8 volts will be low and produce a low tone through the speaker. 🔗 External reference
The audible logic probe operates based on the voltage levels present in TTL (Transistor-Transistor Logic) circuits. The primary components of the probe include a voltage comparator, a tone generator, and an audio output device, typically a small speaker or piezo buzzer.
The voltage comparator is configured to compare the input voltage from the circuit under test against two reference voltages: 2 volts and 0.8 volts. When the probe tip is connected to a point in the circuit, the input voltage is fed into the comparator. If the voltage exceeds 2 volts, the comparator outputs a signal that activates the tone generator to produce a high-frequency tone, indicating a logic high state. Conversely, if the voltage falls below 0.8 volts, the comparator triggers the tone generator to produce a low-frequency tone, indicating a logic low state.
For proper operation, the probe is powered by a 5-volt source, which is typically the same voltage used in TTL circuits. The ground clip must be connected to the circuit's ground to ensure accurate voltage readings. The probe's design can be adapted for CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) circuits by adjusting the reference voltage levels to accommodate the different voltage ranges used in those applications.
In summary, the audible logic probe is a valuable tool for quickly assessing the logic state of various points in a TTL circuit, providing immediate auditory feedback that can enhance the efficiency of circuit testing and troubleshooting.When testing circuits with a logic probe, it is sometimes difficult to watch the LEDS on the probe to determine the logic state. With this probe the logic states are audible. This probe is designed for TTL circuits only but could be modified for CMOS. The way it works is as follows. The 5 volt power source will be the circuit under test. Clip the ground input of the probe to the ground of the circuit being tested. The other input lead is used to probe the different chips of the circuit being tested. Any input greater then 2 volts will be high and output a high tone through the speaker. Any input less then .8 volts will be low and produce a low tone through the speaker. 🔗 External reference