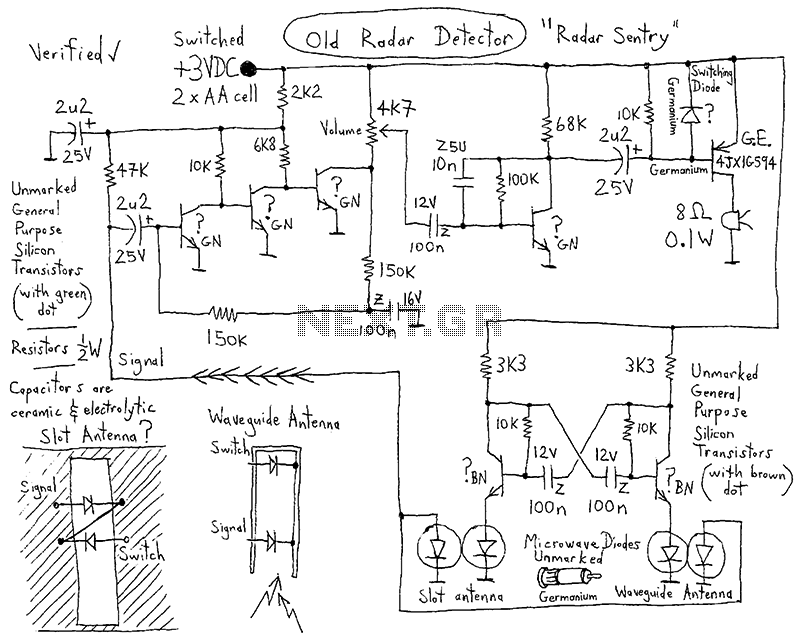
Tone probe for testing digital ics
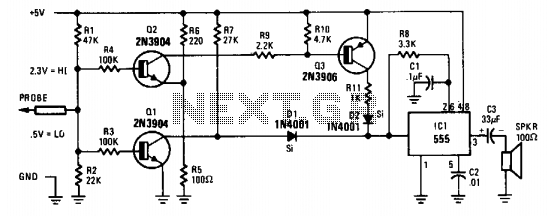
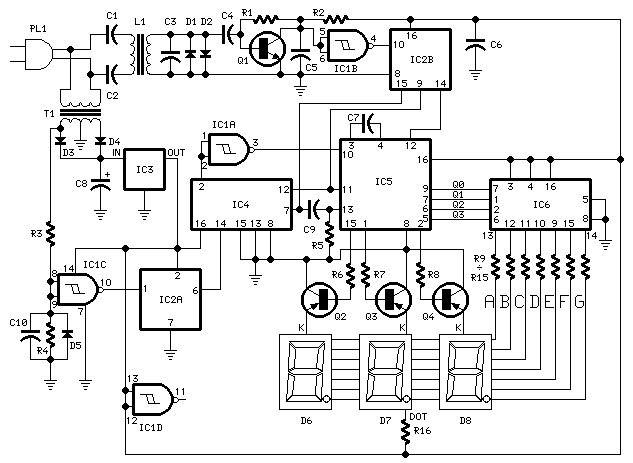
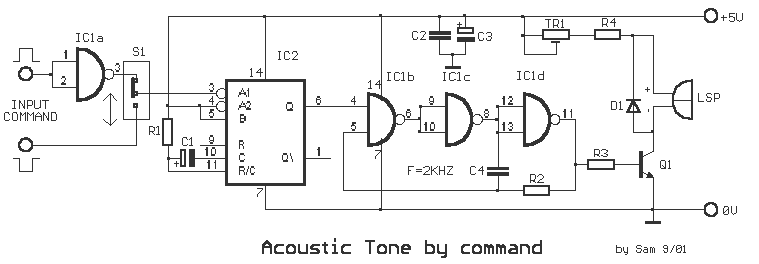
The probe's input circuit detects the signal condition and generates a low-pitched tone for low-level signals (below 0.8 V) or a high-pitched tone for high-level signals (above 2 V). The tone probe employs sound to indicate the status of the signal being measured.
The probe's input circuit is designed to monitor electrical signals and provide auditory feedback regarding their levels. It operates by utilizing a comparator circuit that evaluates the input voltage against predefined thresholds. When the input voltage falls below 0.8 V, the circuit activates a low-frequency oscillator, producing a low-pitched tone. Conversely, when the signal exceeds 2 V, the circuit switches to a high-frequency oscillator, generating a high-pitched tone.
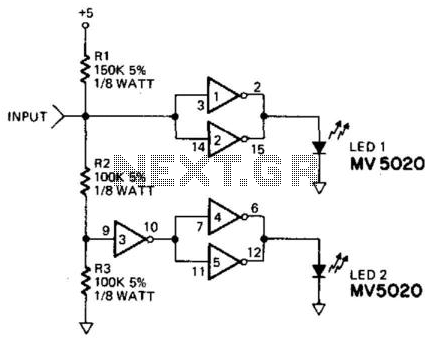
The circuit typically consists of several key components: a voltage divider to scale the input signal, an operational amplifier configured as a comparator, and a piezoelectric speaker or buzzer for sound output. The voltage divider ensures that the input signal is within the operational range of the comparator, while the operational amplifier provides the necessary gain and switching capability.
Additionally, the design may include a microcontroller to enhance functionality, allowing for adjustable thresholds, signal processing, and possibly visual indicators, such as LEDs, to accompany the audible tones. This combination of sound and visual feedback aids in the effective monitoring of signal conditions in various electronic applications, such as troubleshooting and maintenance tasks. The tone probe serves as a valuable tool for engineers and technicians, providing immediate and intuitive feedback on signal status. The probe's input circuit senses the condition of the signal and produces either a low-pitched tone for low-level signals (less than 0.8 V) or a high-pitched tone for high-level signals (greater than 2 V). The tone probe uses sound to tell the status of the signal being probed. 🔗 External reference
The probe's input circuit is designed to monitor electrical signals and provide auditory feedback regarding their levels. It operates by utilizing a comparator circuit that evaluates the input voltage against predefined thresholds. When the input voltage falls below 0.8 V, the circuit activates a low-frequency oscillator, producing a low-pitched tone. Conversely, when the signal exceeds 2 V, the circuit switches to a high-frequency oscillator, generating a high-pitched tone.
The circuit typically consists of several key components: a voltage divider to scale the input signal, an operational amplifier configured as a comparator, and a piezoelectric speaker or buzzer for sound output. The voltage divider ensures that the input signal is within the operational range of the comparator, while the operational amplifier provides the necessary gain and switching capability.
Additionally, the design may include a microcontroller to enhance functionality, allowing for adjustable thresholds, signal processing, and possibly visual indicators, such as LEDs, to accompany the audible tones. This combination of sound and visual feedback aids in the effective monitoring of signal conditions in various electronic applications, such as troubleshooting and maintenance tasks. The tone probe serves as a valuable tool for engineers and technicians, providing immediate and intuitive feedback on signal status. The probe's input circuit senses the condition of the signal and produces either a low-pitched tone for low-level signals (less than 0.8 V) or a high-pitched tone for high-level signals (greater than 2 V). The tone probe uses sound to tell the status of the signal being probed. 🔗 External reference