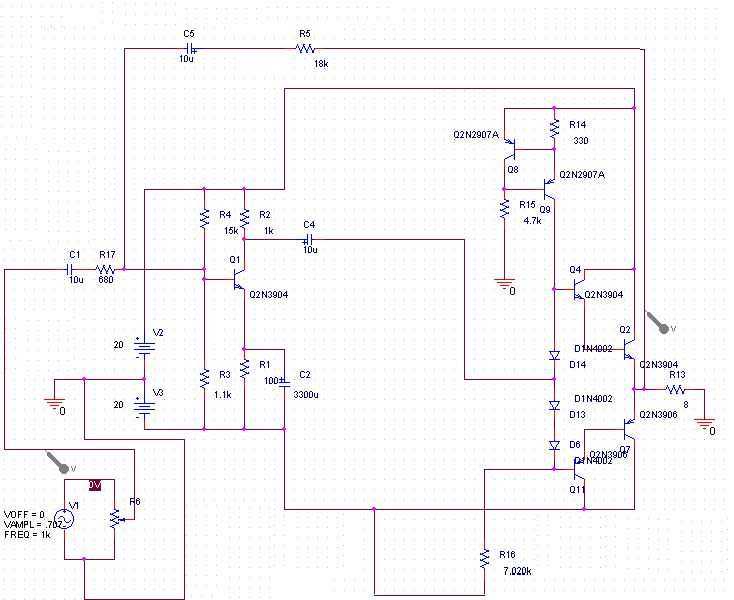
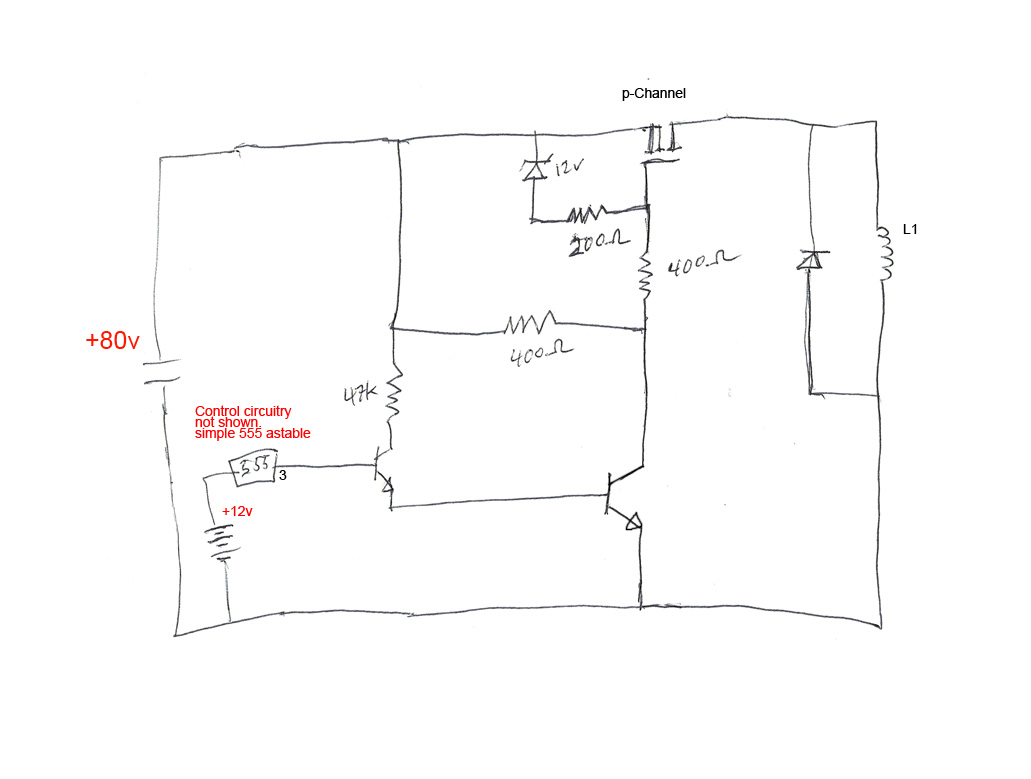
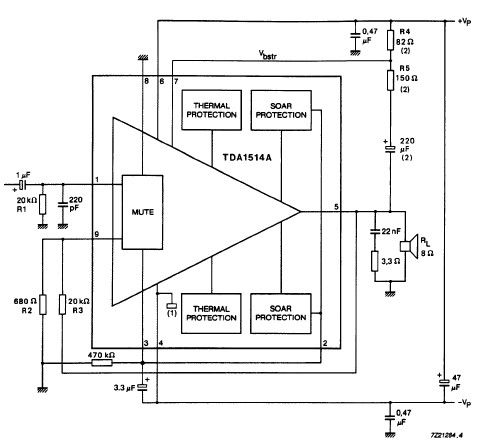
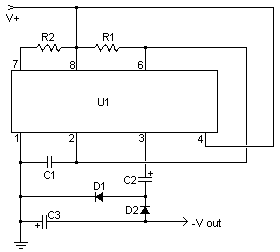
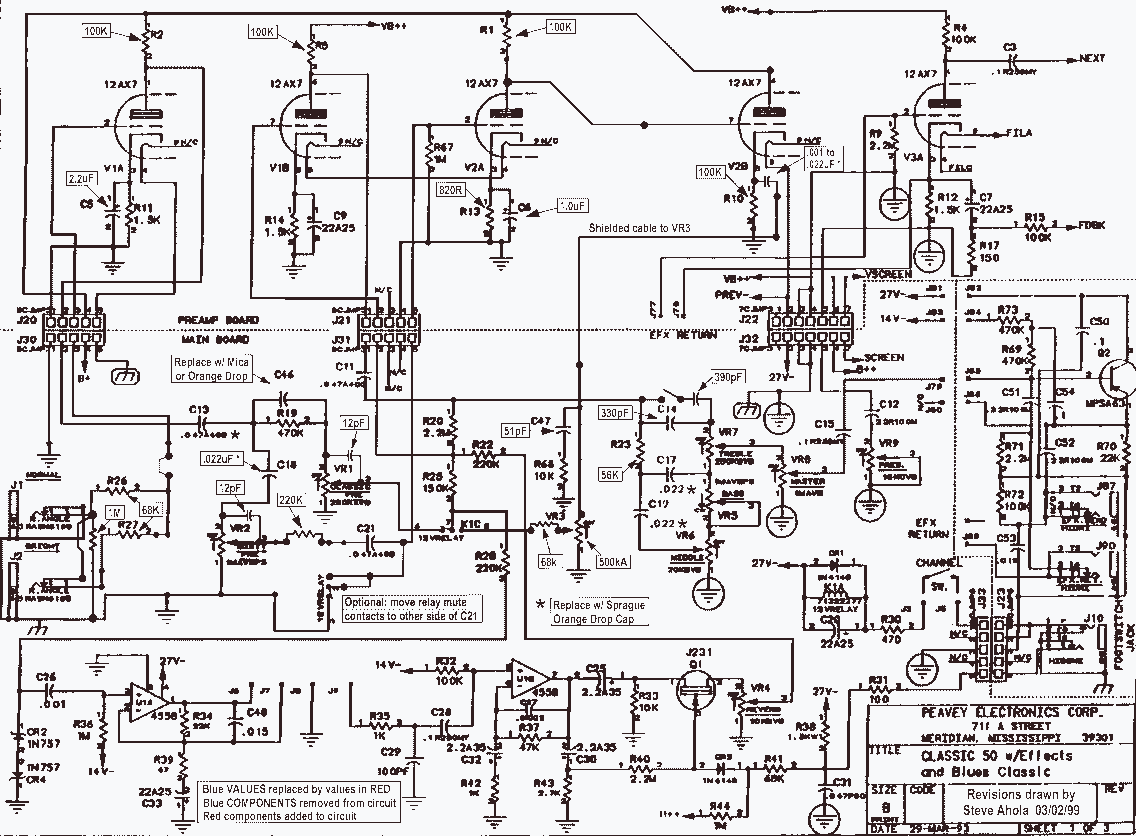
Voltage controlled amplifier
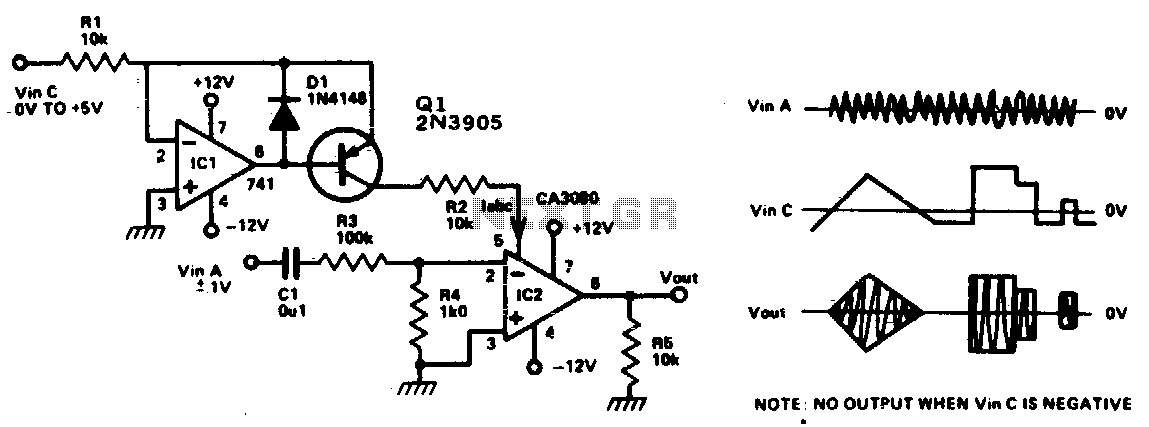
This circuit is essentially an operational amplifier (op-amp) with a differential input voltage of ±10 mV between pins 2 and 3, along with an additional input at pin 5. A current (Iabc) is injected to control the current at pin 5, which influences the input level and subsequently controls the gain of the output signal at pin 6 in a linear manner. Furthermore, an audio signal can be introduced into the circuit.
The operational amplifier circuit described operates as a differential amplifier, where the input signals are applied to the inverting (pin 2) and non-inverting (pin 3) terminals. The differential voltage of ±10 mV indicates that the circuit is designed for high precision, allowing it to amplify small voltage differences effectively. The additional input at pin 5 serves as a control mechanism, where the injected current (Iabc) modulates the gain of the amplifier. This feature is particularly useful in applications requiring dynamic adjustment of gain based on varying input conditions.
The output signal at pin 6 is a function of the differential input voltage and the gain set by the current at pin 5. This relationship can be expressed mathematically as V_out = Gain × V_diff, where V_diff is the voltage difference between pins 2 and 3. The linear control of gain ensures that the output signal remains proportional to the input, which is crucial for maintaining signal integrity, especially in audio applications.
Inserting an audio signal into this circuit allows for the amplification of audio frequencies, making it suitable for various applications such as audio processing, signal conditioning, and other electronic systems where precise signal amplification is required. The design ensures minimal distortion and high fidelity in the output, which is essential for high-quality audio performance.This circuit is basically an op amp with an nal (±10 mV) between pin 2 and 3 and by extra input at pin 5. A current Iabc is injected controlling the current on pin 5, the level of the into this input and this controls the gain of the signal output (pin 6) is controlled, device linerly
Thus by inserting an audio sig-. 🔗 External reference
The operational amplifier circuit described operates as a differential amplifier, where the input signals are applied to the inverting (pin 2) and non-inverting (pin 3) terminals. The differential voltage of ±10 mV indicates that the circuit is designed for high precision, allowing it to amplify small voltage differences effectively. The additional input at pin 5 serves as a control mechanism, where the injected current (Iabc) modulates the gain of the amplifier. This feature is particularly useful in applications requiring dynamic adjustment of gain based on varying input conditions.
The output signal at pin 6 is a function of the differential input voltage and the gain set by the current at pin 5. This relationship can be expressed mathematically as V_out = Gain × V_diff, where V_diff is the voltage difference between pins 2 and 3. The linear control of gain ensures that the output signal remains proportional to the input, which is crucial for maintaining signal integrity, especially in audio applications.
Inserting an audio signal into this circuit allows for the amplification of audio frequencies, making it suitable for various applications such as audio processing, signal conditioning, and other electronic systems where precise signal amplification is required. The design ensures minimal distortion and high fidelity in the output, which is essential for high-quality audio performance.This circuit is basically an op amp with an nal (±10 mV) between pin 2 and 3 and by extra input at pin 5. A current Iabc is injected controlling the current on pin 5, the level of the into this input and this controls the gain of the signal output (pin 6) is controlled, device linerly
Thus by inserting an audio sig-. 🔗 External reference