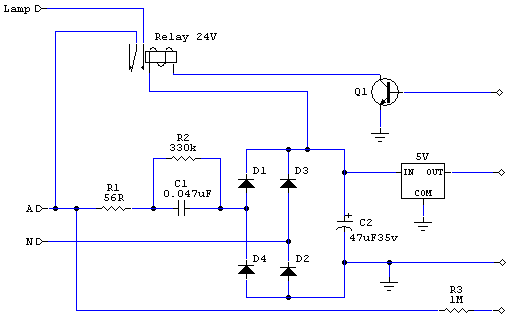
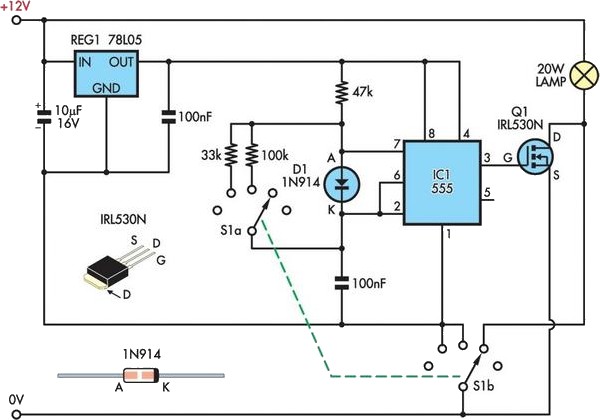
automatic 12v lead acid battery charger

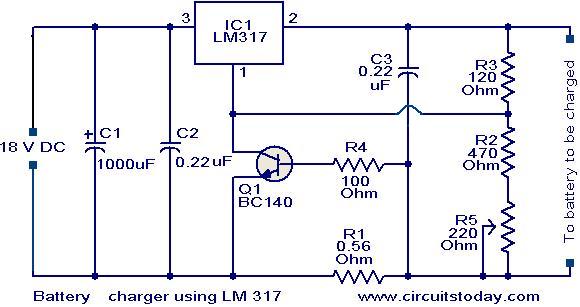
This design is for a charger circuit suitable for lead-acid batteries, including flooded, gel, and AGM types. The circuit features a simple design. The automatic function means that this charger will stop charging automatically when the battery voltage reaches a certain point, indicating that the battery has been fully charged. Charging will restart if the battery voltage falls below that threshold. An LED indicator is provided to show when the battery is fully charged. This automatic battery charger can be left connected to a battery indefinitely to maintain a full charge safely. R2 is used to adjust the final voltage at which the charger should stop charging. For flooded and gel types, the batteries are usually charged to 13.8V. For cycling the battery (AGM or gel), a voltage range of 14.5V to 14.9V is typically recommended by battery manufacturers. The R2 potentiometer should be set to midpoint, the charger turned on, and a battery connected to its output. The charge should be monitored with a voltmeter until the battery reaches the proper end voltage, then the potentiometer should be adjusted until the LED glows steadily. To charge different types of batteries, the potentiometer can be mounted on the front of the case with markings indicating the ending voltage for each battery type. A proper heat sink should be installed for Q1, and a small fan may be necessary, which can generally be powered directly from the output of D1 if the circuit is mounted in a case. If the circuit is powered off, the battery should be disconnected, as the circuit will slowly drain the battery, which could damage it if the voltage falls below approximately 10V.
The charger circuit operates by employing a voltage regulation mechanism to ensure that the charging voltage remains within the specified limits for different types of lead-acid batteries. The use of a potentiometer (R2) allows for fine-tuning of the cut-off voltage, which is critical for maintaining battery health and longevity. The design incorporates an automatic shut-off feature that is activated once the battery reaches the predetermined voltage, preventing overcharging. This is essential for lead-acid batteries, as overcharging can lead to gassing and damage.
The LED indicator serves a dual purpose: it provides a visual confirmation of the charging status and indicates when the battery is fully charged. This feature enhances user convenience and safety, allowing users to monitor the charging process without needing to check the voltage manually.
The inclusion of a heat sink for the transistor (Q1) is crucial, as charging processes can generate significant heat, especially under high load conditions. The option to add a fan powered by the output of the rectifier (D1) ensures that the circuit remains within safe operating temperatures, thereby enhancing reliability and performance.
Finally, the recommendation to disconnect the battery when the circuit is powered off is a critical safety measure. This prevents the risk of slow discharge, which can lead to battery damage if the voltage drops below the safe threshold. Properly implementing these design considerations will result in a robust and efficient charger circuit for various lead-acid battery types.This is design for charger circuit that is suitable for lead-acid battery, including flooded, gel, and AGM types. This circuit is simple design. This is the figure of the circuit. The automatic term means that this charger will stop charging automatically when the battery voltage reach a certain pint, indicating that the battery has been fully cha
rged, and charging will be restarted if the battery voltage falls below that threshold. A LED indicator is provided to show you when the battery is fully charged. This automatic battery charger can be left connected to a battery indefinitely to maintain full charge safely. 1. R2 is used to adjust the final voltage when the charger should stop charging. For flooded and gel type, the batteries are usually charged to 13. 8V. For cycling the battery (AGM or gel), 14. 5V to 14. 9V is usually recommended by battery manufacturers. Set the R2 pot to midpoint, turn on the charger and connect a battery to its output. Monitor the charge with a voltmeter until the battery reaches the proper end voltage, then adjust the pot until the LED glows constantly.
To charge different types of batteries, you can mount the pot on the front of the case and mark each position of every battery types ending voltage. 2. Install proper heat sink for Q1. A small fan might be necessary and can generally be powered right off the output of D1 If the circuit is mounted in a case.
4. If the circuit is powered off, you should disconnect the battery because the circuit will drain the battery slowly, and this could damage your battery if the battery is drained while it`s voltage falls below about 10V. 🔗 External reference
The charger circuit operates by employing a voltage regulation mechanism to ensure that the charging voltage remains within the specified limits for different types of lead-acid batteries. The use of a potentiometer (R2) allows for fine-tuning of the cut-off voltage, which is critical for maintaining battery health and longevity. The design incorporates an automatic shut-off feature that is activated once the battery reaches the predetermined voltage, preventing overcharging. This is essential for lead-acid batteries, as overcharging can lead to gassing and damage.
The LED indicator serves a dual purpose: it provides a visual confirmation of the charging status and indicates when the battery is fully charged. This feature enhances user convenience and safety, allowing users to monitor the charging process without needing to check the voltage manually.
The inclusion of a heat sink for the transistor (Q1) is crucial, as charging processes can generate significant heat, especially under high load conditions. The option to add a fan powered by the output of the rectifier (D1) ensures that the circuit remains within safe operating temperatures, thereby enhancing reliability and performance.
Finally, the recommendation to disconnect the battery when the circuit is powered off is a critical safety measure. This prevents the risk of slow discharge, which can lead to battery damage if the voltage drops below the safe threshold. Properly implementing these design considerations will result in a robust and efficient charger circuit for various lead-acid battery types.This is design for charger circuit that is suitable for lead-acid battery, including flooded, gel, and AGM types. This circuit is simple design. This is the figure of the circuit. The automatic term means that this charger will stop charging automatically when the battery voltage reach a certain pint, indicating that the battery has been fully cha
rged, and charging will be restarted if the battery voltage falls below that threshold. A LED indicator is provided to show you when the battery is fully charged. This automatic battery charger can be left connected to a battery indefinitely to maintain full charge safely. 1. R2 is used to adjust the final voltage when the charger should stop charging. For flooded and gel type, the batteries are usually charged to 13. 8V. For cycling the battery (AGM or gel), 14. 5V to 14. 9V is usually recommended by battery manufacturers. Set the R2 pot to midpoint, turn on the charger and connect a battery to its output. Monitor the charge with a voltmeter until the battery reaches the proper end voltage, then adjust the pot until the LED glows constantly.
To charge different types of batteries, you can mount the pot on the front of the case and mark each position of every battery types ending voltage. 2. Install proper heat sink for Q1. A small fan might be necessary and can generally be powered right off the output of D1 If the circuit is mounted in a case.
4. If the circuit is powered off, you should disconnect the battery because the circuit will drain the battery slowly, and this could damage your battery if the battery is drained while it`s voltage falls below about 10V. 🔗 External reference