automatic gain control
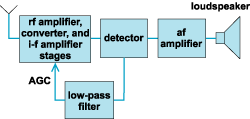
Automatic gain control. A control circuit that automatically changes the gain (amplification) of a receiver.
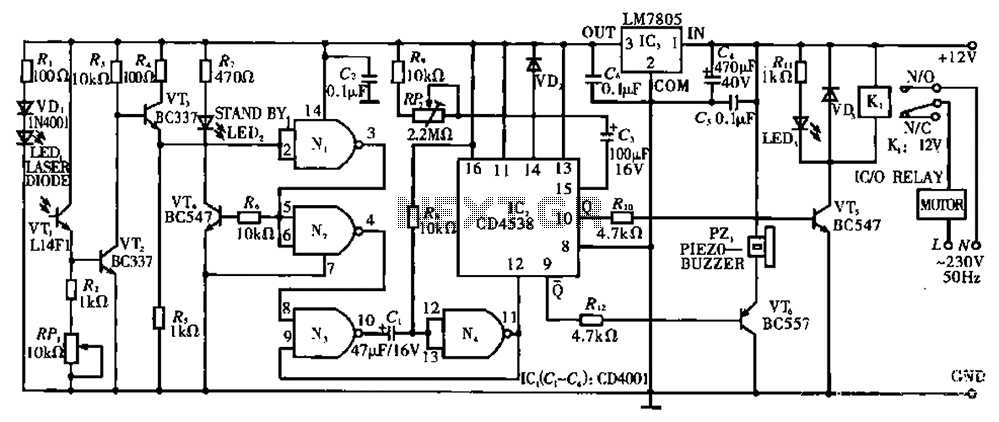
Automatic Gain Control (AGC) is a crucial circuit used in various electronic devices to maintain a consistent output level despite variations in input signal strength. The primary function of AGC is to adjust the gain of an amplifier or receiver dynamically. This adjustment ensures that the output signal remains within a desired range, preventing distortion or clipping that can occur when the input signal is too strong, while also amplifying weaker signals for better clarity.
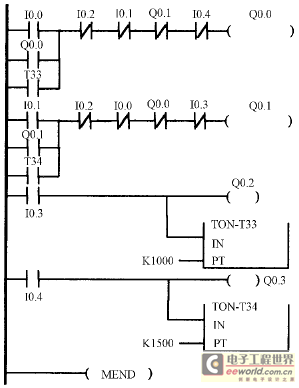
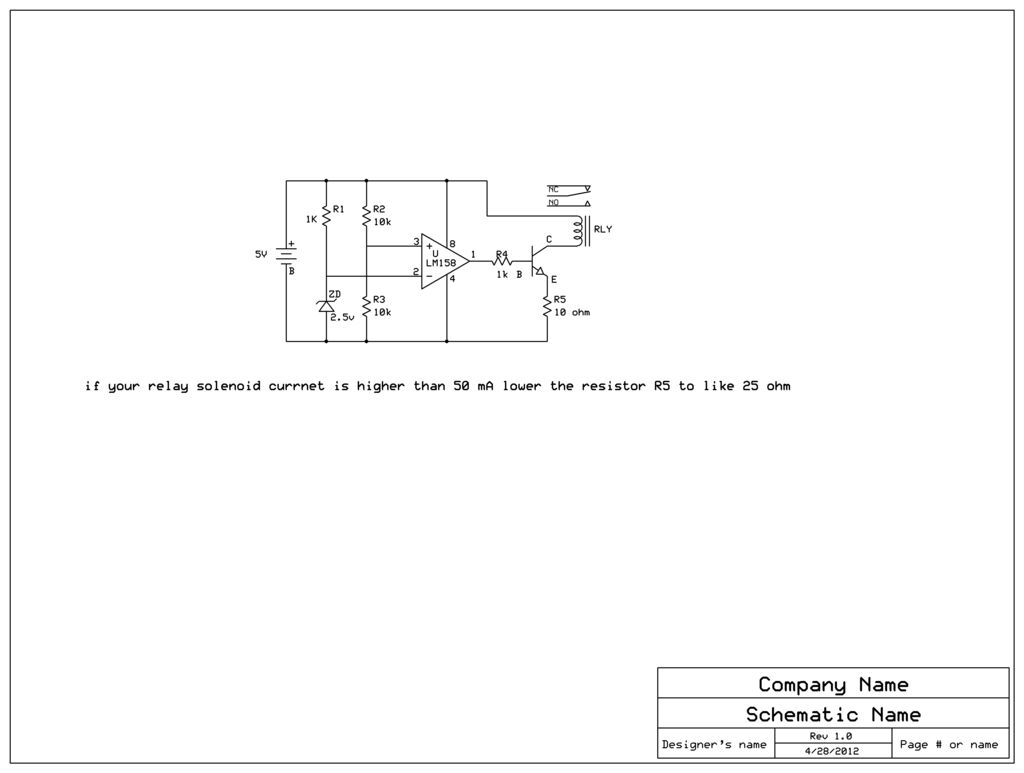
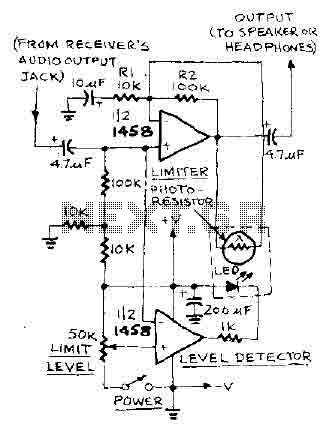
The AGC circuit typically employs a feedback mechanism to monitor the output signal level. When the output exceeds a predefined threshold, the circuit reduces the gain to prevent saturation. Conversely, if the output level falls below the threshold, the gain is increased to enhance the signal. This feedback loop is often implemented using operational amplifiers, diodes, and capacitors, which work together to create a responsive and stable gain adjustment.
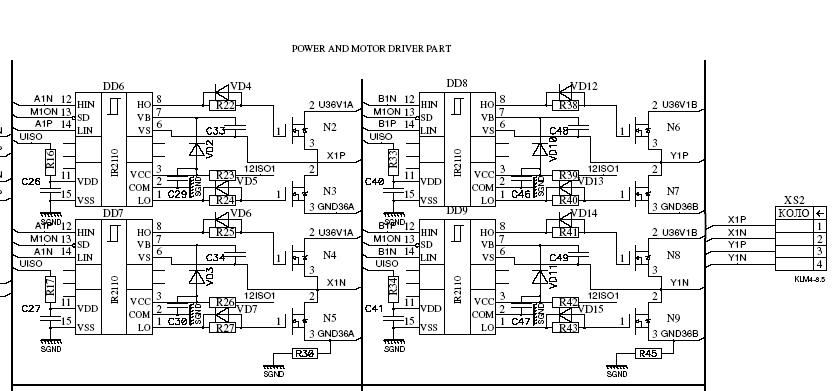
In practical applications, AGC is widely used in radio receivers, audio processing equipment, and communication systems. In radio receivers, AGC helps in managing the variability of signal strength due to distance from the transmitter or interference from other signals. In audio systems, it ensures that sound levels remain consistent, improving user experience and clarity of sound.
The design of an AGC circuit can vary depending on the specific requirements of the application. Key parameters such as attack time, release time, and gain range must be carefully selected to achieve optimal performance. Attack time refers to how quickly the circuit responds to an increase in signal level, while release time indicates how fast it returns to normal gain after the signal level decreases. A well-designed AGC circuit enhances the overall performance and reliability of electronic systems by ensuring consistent signal quality across varying conditions.automatic gain control. A control circuit that automatically changes the gain (amplification) of a receiver.. 🔗 External reference
Automatic Gain Control (AGC) is a crucial circuit used in various electronic devices to maintain a consistent output level despite variations in input signal strength. The primary function of AGC is to adjust the gain of an amplifier or receiver dynamically. This adjustment ensures that the output signal remains within a desired range, preventing distortion or clipping that can occur when the input signal is too strong, while also amplifying weaker signals for better clarity.
The AGC circuit typically employs a feedback mechanism to monitor the output signal level. When the output exceeds a predefined threshold, the circuit reduces the gain to prevent saturation. Conversely, if the output level falls below the threshold, the gain is increased to enhance the signal. This feedback loop is often implemented using operational amplifiers, diodes, and capacitors, which work together to create a responsive and stable gain adjustment.
In practical applications, AGC is widely used in radio receivers, audio processing equipment, and communication systems. In radio receivers, AGC helps in managing the variability of signal strength due to distance from the transmitter or interference from other signals. In audio systems, it ensures that sound levels remain consistent, improving user experience and clarity of sound.
The design of an AGC circuit can vary depending on the specific requirements of the application. Key parameters such as attack time, release time, and gain range must be carefully selected to achieve optimal performance. Attack time refers to how quickly the circuit responds to an increase in signal level, while release time indicates how fast it returns to normal gain after the signal level decreases. A well-designed AGC circuit enhances the overall performance and reliability of electronic systems by ensuring consistent signal quality across varying conditions.automatic gain control. A control circuit that automatically changes the gain (amplification) of a receiver.. 🔗 External reference