Automatic Headlight Dimmer Safe Yourself and Others
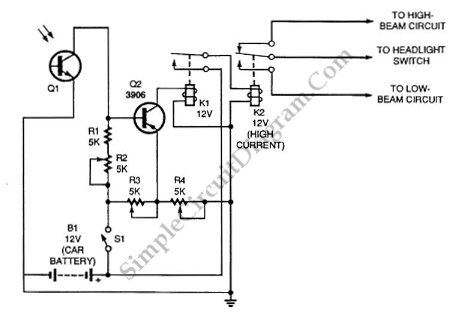
Automatic headlight dimmer circuit diagram for a car's headlight. This circuit ensures maximum brightness for optimal visibility while automatically switching when necessary.
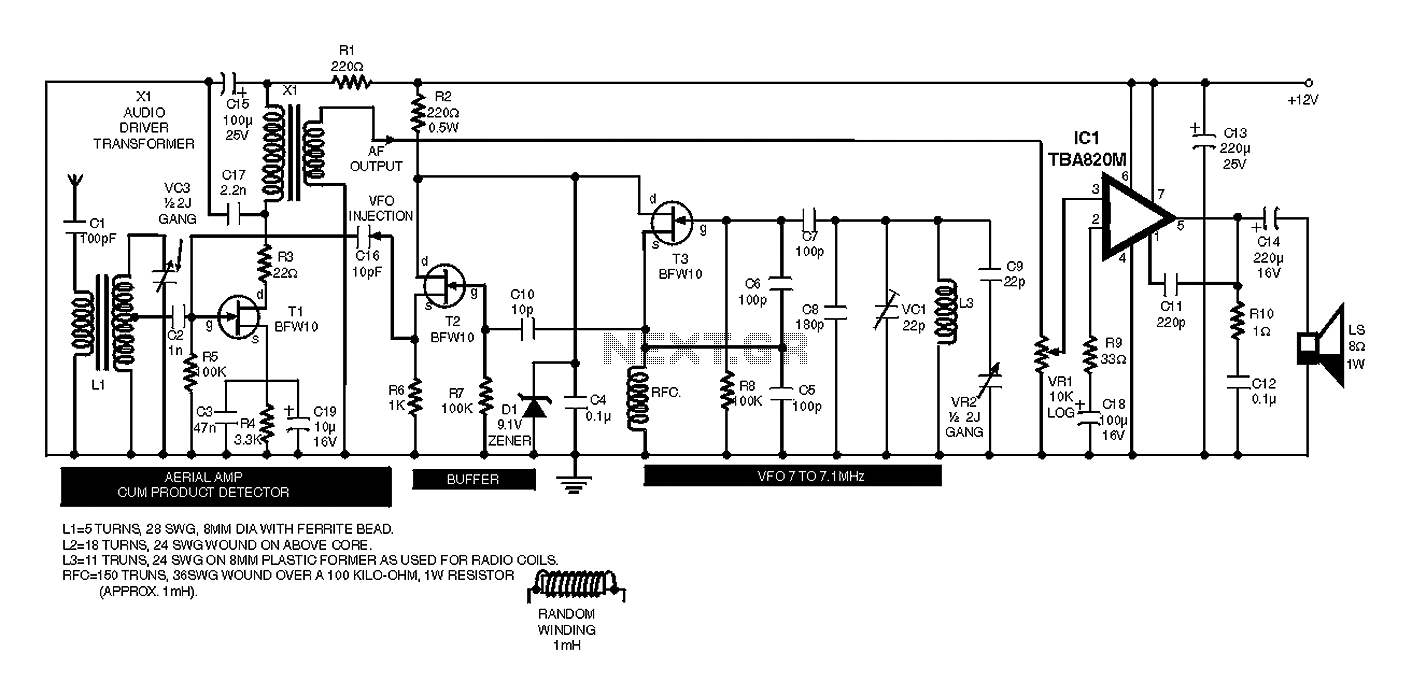
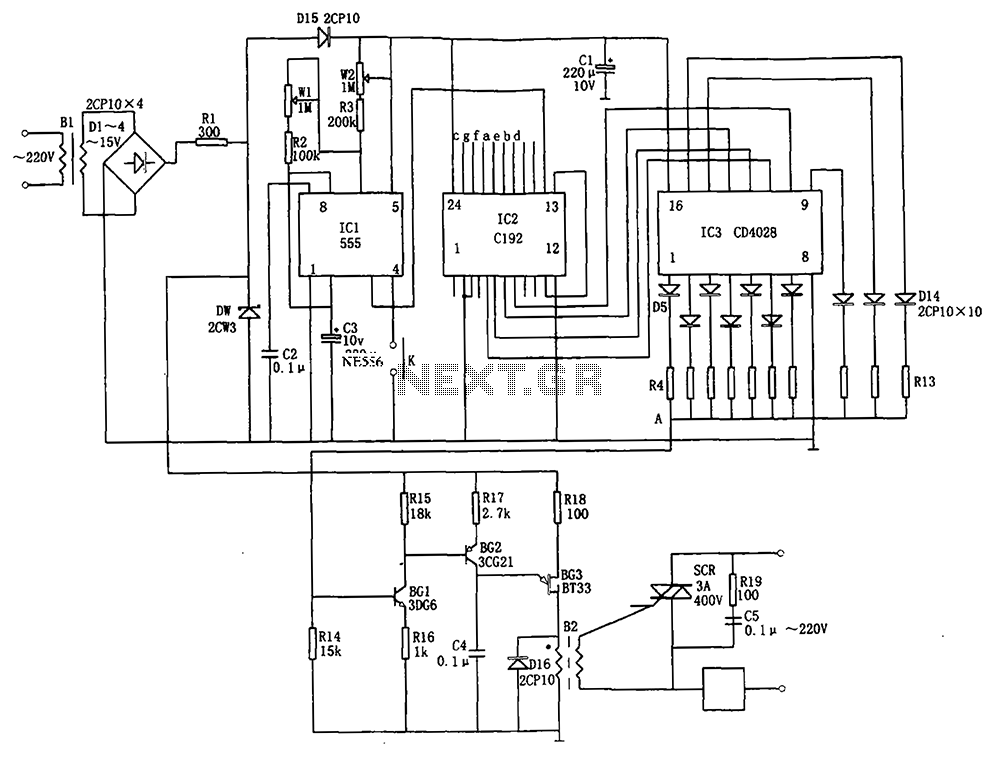
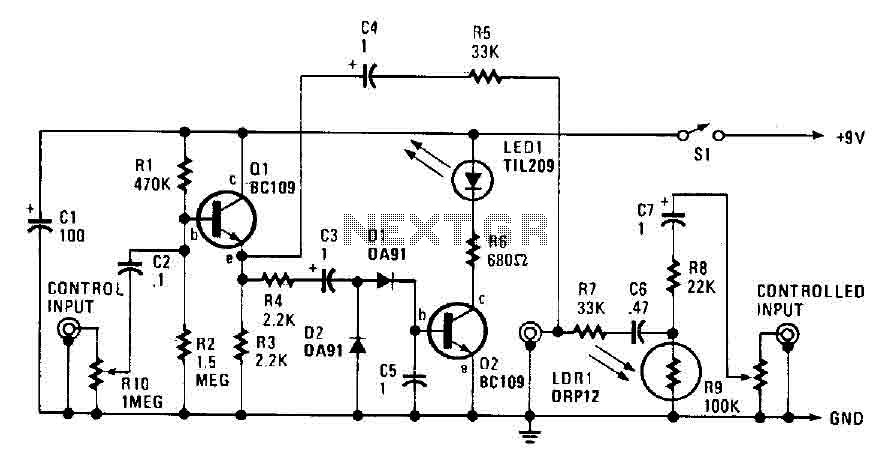
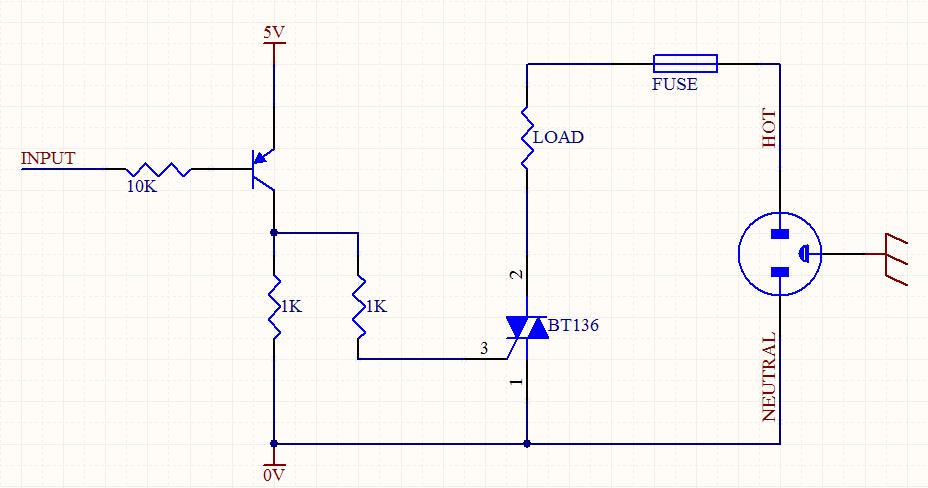
The automatic headlight dimmer circuit is designed to enhance driving safety by adjusting the brightness of the vehicle's headlights based on surrounding light conditions. The primary components of this circuit typically include a light-dependent resistor (LDR), a transistor, a relay, and a diode.
The LDR serves as a sensor that detects ambient light levels. In daylight, the resistance of the LDR is low, which keeps the transistor in a non-conductive state, preventing the relay from activating. As the surrounding light diminishes, the resistance of the LDR increases, allowing the transistor to conduct, which subsequently energizes the relay. This action engages the headlight circuit, switching the headlights to a higher brightness setting.
A diode is included in the circuit to protect against back EMF generated by the relay coil when it is de-energized. This prevents potential damage to the transistor and other components in the circuit. The design may also incorporate adjustable resistors to fine-tune the sensitivity of the LDR, allowing for customization based on user preferences or specific driving conditions.
The schematic typically illustrates the connections between these components, indicating the power supply, ground paths, and signal flow. Proper layout and component selection are crucial to ensure reliable operation and responsiveness of the automatic dimming feature, ultimately contributing to a safer driving experience.Automatic headlight dimmer circuit diagram for your car`s headlight, keep you safe with maximum bright for farthest visibility, but will automatically switch . 🔗 External reference
The automatic headlight dimmer circuit is designed to enhance driving safety by adjusting the brightness of the vehicle's headlights based on surrounding light conditions. The primary components of this circuit typically include a light-dependent resistor (LDR), a transistor, a relay, and a diode.
The LDR serves as a sensor that detects ambient light levels. In daylight, the resistance of the LDR is low, which keeps the transistor in a non-conductive state, preventing the relay from activating. As the surrounding light diminishes, the resistance of the LDR increases, allowing the transistor to conduct, which subsequently energizes the relay. This action engages the headlight circuit, switching the headlights to a higher brightness setting.
A diode is included in the circuit to protect against back EMF generated by the relay coil when it is de-energized. This prevents potential damage to the transistor and other components in the circuit. The design may also incorporate adjustable resistors to fine-tune the sensitivity of the LDR, allowing for customization based on user preferences or specific driving conditions.
The schematic typically illustrates the connections between these components, indicating the power supply, ground paths, and signal flow. Proper layout and component selection are crucial to ensure reliable operation and responsiveness of the automatic dimming feature, ultimately contributing to a safer driving experience.Automatic headlight dimmer circuit diagram for your car`s headlight, keep you safe with maximum bright for farthest visibility, but will automatically switch . 🔗 External reference