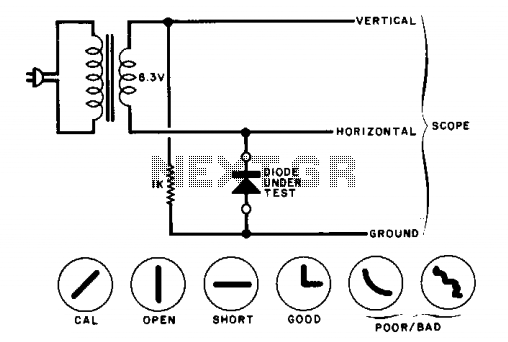
Balanced diode mixer circuit
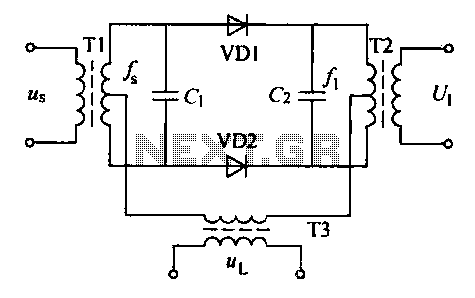
A balanced diode mixer circuit is presented, utilizing two diodes, specifically the 2AP9 model. The circuit operates with a high voltage, causing the diodes to function in an off state, which is also referred to as a diode switch tube balanced mixer.
The balanced diode mixer circuit is designed to efficiently combine two input signals while minimizing unwanted interference and maintaining signal integrity. The use of two diodes, such as the 2AP9, allows for the mixing of high-frequency signals. In this configuration, the diodes are arranged in a balanced manner to achieve a low distortion output.
The operation of the circuit relies on the principle of diode switching. When the input signals are applied, the diodes switch between conducting and non-conducting states based on the amplitude of the signals. This switching action allows for the generation of sum and difference frequencies at the output, which are essential in applications such as radio frequency (RF) communications and signal processing.
The balanced design helps to cancel out common-mode signals and enhances the performance of the mixer by providing better isolation between the input and output. This results in improved linearity and reduced intermodulation distortion, which is crucial for maintaining the quality of the mixed signals.
In summary, the balanced diode mixer circuit employing the 2AP9 diodes operates effectively under high voltage conditions, utilizing the switching characteristics of the diodes to achieve optimal signal mixing while minimizing distortion and interference. The circuit is particularly valuable in RF applications where signal integrity is paramount.Balanced diode mixer circuit is shown. Diode 2AP9 2. Due to the use of two diodes and the voltage is large, the diode operates in the off state, it is also known diode switch tube balanced mixer.
The balanced diode mixer circuit is designed to efficiently combine two input signals while minimizing unwanted interference and maintaining signal integrity. The use of two diodes, such as the 2AP9, allows for the mixing of high-frequency signals. In this configuration, the diodes are arranged in a balanced manner to achieve a low distortion output.
The operation of the circuit relies on the principle of diode switching. When the input signals are applied, the diodes switch between conducting and non-conducting states based on the amplitude of the signals. This switching action allows for the generation of sum and difference frequencies at the output, which are essential in applications such as radio frequency (RF) communications and signal processing.
The balanced design helps to cancel out common-mode signals and enhances the performance of the mixer by providing better isolation between the input and output. This results in improved linearity and reduced intermodulation distortion, which is crucial for maintaining the quality of the mixed signals.
In summary, the balanced diode mixer circuit employing the 2AP9 diodes operates effectively under high voltage conditions, utilizing the switching characteristics of the diodes to achieve optimal signal mixing while minimizing distortion and interference. The circuit is particularly valuable in RF applications where signal integrity is paramount.Balanced diode mixer circuit is shown. Diode 2AP9 2. Due to the use of two diodes and the voltage is large, the diode operates in the off state, it is also known diode switch tube balanced mixer.