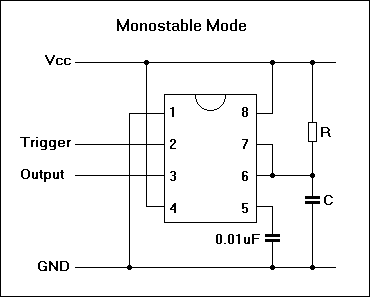
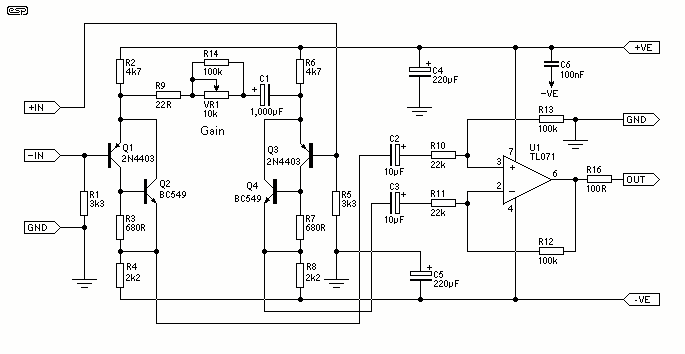
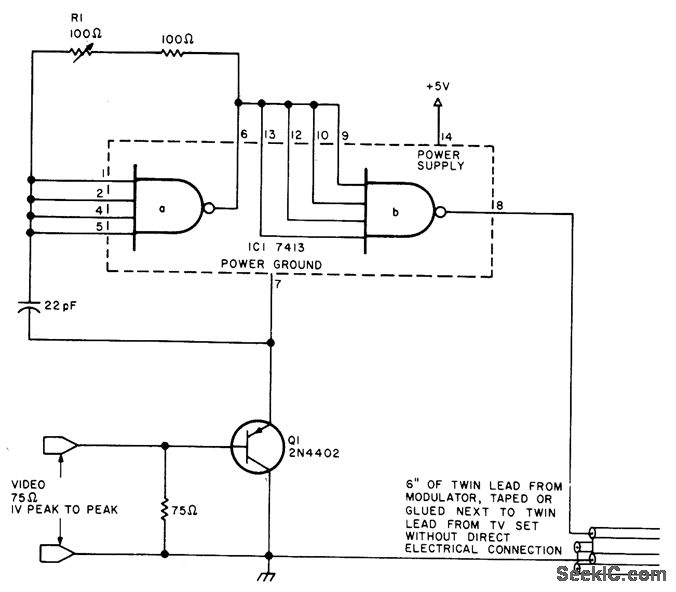
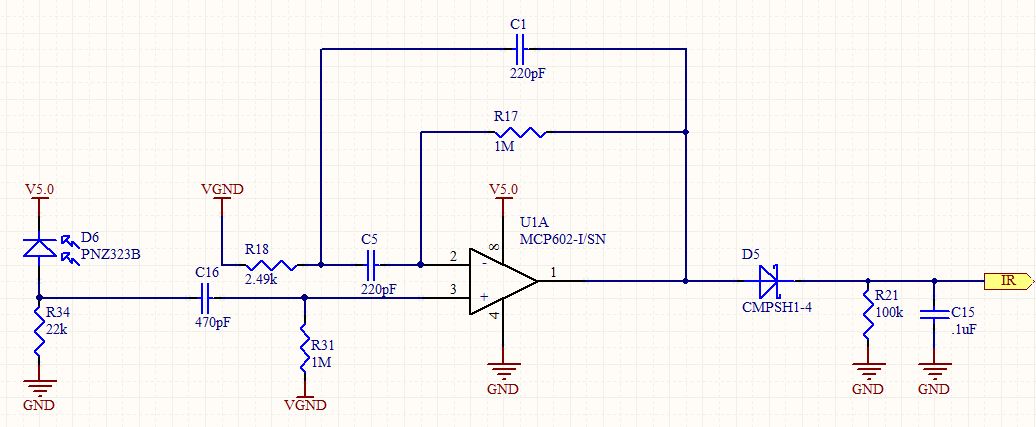
BALANCED MODULATOR FOR ADF
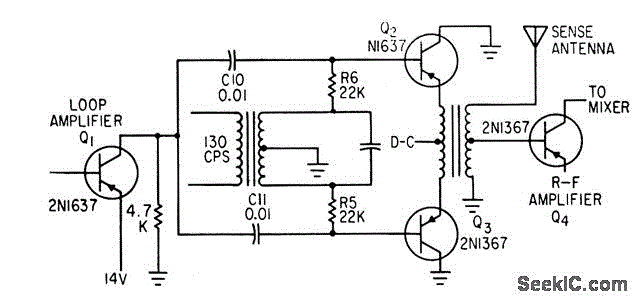
Combines signals from loop and sense antennas of an automatic direction finder to produce a 130-cps output with the correct phase for driving the rotor of a resolver to achieve a null position.
The circuit described is integral to the operation of an automatic direction finder (ADF), which is essential in navigation systems. The primary function is to combine the signals received from loop and sense antennas, allowing for accurate directional information to be extracted.
The loop antenna is designed to pick up signals from a specific direction, while the sense antenna captures signals from all directions. The combination of these signals is crucial for determining the angle of arrival of a radio frequency signal. The output frequency of 130 cycles per second (cps) is significant, as it is tuned to the operational requirements of the resolver, which is a type of rotary electrical transformer used for measuring angular position.
The circuit employs phase manipulation techniques to ensure that the output signal is correctly phased. This is essential for the rotor of the resolver to be driven to the null position, indicating that the ADF is accurately aligned with the incoming signal. By achieving this null position, the system can provide precise directional information, which is vital for navigation and positioning applications.
The implementation of servo filters and gain control within the circuit enhances the performance of the ADF. Servo filters help in stabilizing the output signal by filtering out noise and unwanted frequencies, while gain control adjusts the amplitude of the output signal to ensure optimal performance under varying signal conditions.
Overall, this circuit plays a critical role in the functionality of automatic direction finders, contributing to the accuracy and reliability of navigation systems in various applications, including aviation, maritime, and land-based navigation.Combines signals from loop and sense antennas of automatic direction finder, to give 130-cps output having correct phase for driving rotor of resolver to null position.-P. V.Sparks, Servo Filter and Gain Control lmprove Automatic Direction Finder, Electronics, 34:23, p 110-113..
🔗 External reference
The circuit described is integral to the operation of an automatic direction finder (ADF), which is essential in navigation systems. The primary function is to combine the signals received from loop and sense antennas, allowing for accurate directional information to be extracted.
The loop antenna is designed to pick up signals from a specific direction, while the sense antenna captures signals from all directions. The combination of these signals is crucial for determining the angle of arrival of a radio frequency signal. The output frequency of 130 cycles per second (cps) is significant, as it is tuned to the operational requirements of the resolver, which is a type of rotary electrical transformer used for measuring angular position.
The circuit employs phase manipulation techniques to ensure that the output signal is correctly phased. This is essential for the rotor of the resolver to be driven to the null position, indicating that the ADF is accurately aligned with the incoming signal. By achieving this null position, the system can provide precise directional information, which is vital for navigation and positioning applications.
The implementation of servo filters and gain control within the circuit enhances the performance of the ADF. Servo filters help in stabilizing the output signal by filtering out noise and unwanted frequencies, while gain control adjusts the amplitude of the output signal to ensure optimal performance under varying signal conditions.
Overall, this circuit plays a critical role in the functionality of automatic direction finders, contributing to the accuracy and reliability of navigation systems in various applications, including aviation, maritime, and land-based navigation.Combines signals from loop and sense antennas of automatic direction finder, to give 130-cps output having correct phase for driving rotor of resolver to null position.-P. V.Sparks, Servo Filter and Gain Control lmprove Automatic Direction Finder, Electronics, 34:23, p 110-113..
🔗 External reference