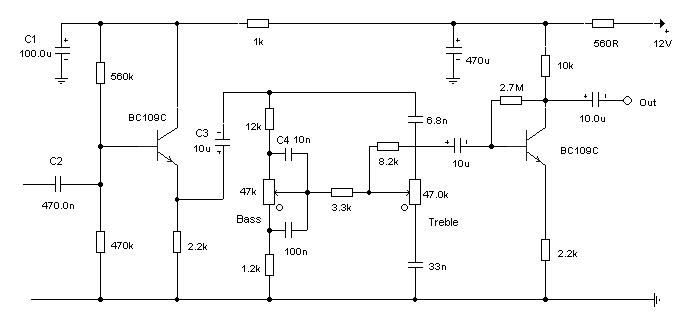
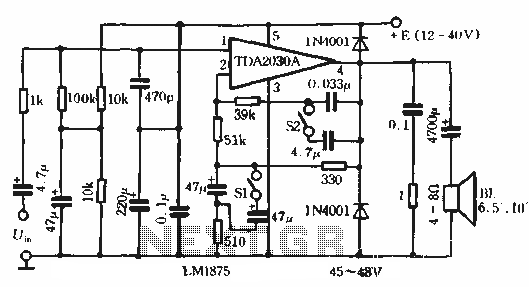
Bass Boost amplifier circuit with compensation
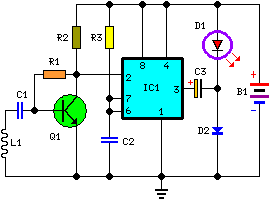
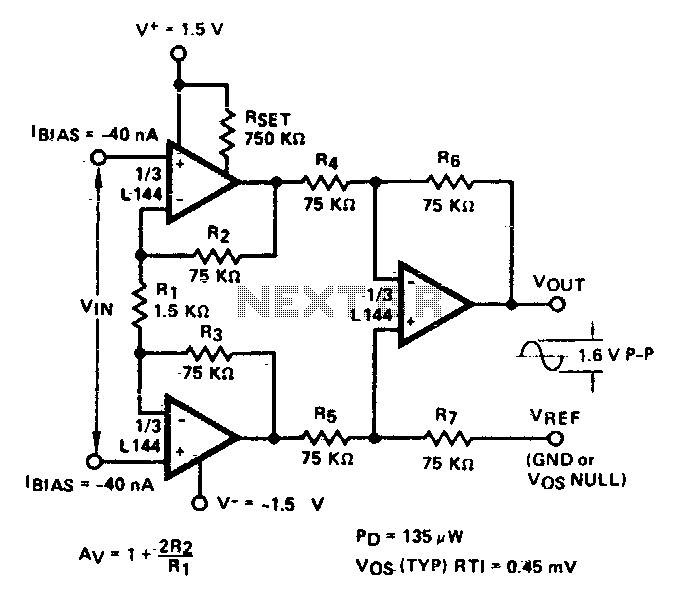
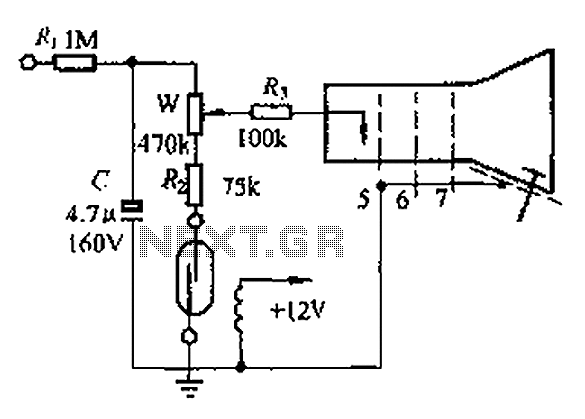
This circuit features bass boost compensation for a practical power amplifier. It is important to adhere to the specified parameters of the amplifier circuit elements. When switches S1 and S2 are disconnected, the bass boost function can be set to enhance audio output at frequencies below 45 Hz, providing a gain increase of approximately 7 to 8 dB relative to 200 Hz. When switch S1 is closed and S2 is disconnected, the amplifier can output audio at frequencies down to 30 Hz, with a gain increase of about 5 to 6 dB relative to 150 Hz. When switch S2 is closed, the amplifier supports a frequency range of 20 Hz to 140 Hz, maintaining a flat frequency response. This configuration is particularly suited for driving subwoofers with sizes of 6 to 5 inches and 10 inches, while the final output can be utilized for signal detection. Real-world listening tests reveal that the bass boost compensation effectively enhances the low-end frequency response, resulting in a clear and impactful sound experience. The 910 bass speaker exhibits flexibility, and the 6.5-inch speaker unit also delivers a noticeable bass impact.
This power amplifier circuit is designed to provide enhanced low-frequency performance through adjustable bass boost features. The circuit utilizes two switches, S1 and S2, to control the bass boost settings, allowing for flexibility in audio output based on the user's preferences and the specific audio environment.
In the configuration where both switches are disconnected, the circuit is optimized for frequencies below 45 Hz, with the ability to increase the gain by 7 to 8 dB relative to a reference frequency of 200 Hz. This adjustment is crucial for applications requiring a pronounced bass response, such as in home theater systems or music playback setups that emphasize low-end frequencies.
When switch S1 is engaged while S2 remains disconnected, the amplifier can effectively output audio frequencies down to 30 Hz. This setting provides a moderate bass boost of 5 to 6 dB relative to 150 Hz, making it suitable for a variety of audio applications where a solid low-end presence is desired without overwhelming the mid-range frequencies.
The configuration with switch S2 closed allows the amplifier to operate within a frequency range of 20 Hz to 140 Hz, offering a flat frequency response that is advantageous for accurate sound reproduction. This setting is particularly effective for subwoofers, enabling them to deliver clear and impactful bass without distortion.
The circuit's design ensures compatibility with various speaker sizes, particularly those measuring 6 to 10 inches. This versatility allows users to tailor their audio systems to their specific needs, whether for casual listening or more critical audio applications. The final output stage of the circuit is designed for signal detection, which can be beneficial in monitoring audio levels and ensuring optimal performance.
Overall, this amplifier circuit with bass boost compensation is engineered to enhance low-frequency audio performance, providing users with a customizable and effective solution for their audio needs. The careful selection of component parameters and the inclusion of adjustable features contribute to a high-quality listening experience.With bass boost compensation for the practical power amplifier circuit. Follow the instructions on the subject of the amplifier circuit element parameters, when the switch Sl, S2 are disconnected, this function can be put under 45Hz canthus audio output gain relative to 200Hz or more, the audio upgrade 7 ~ 8dB;. Sl closed, sz disconnect when the power amplifier can be 30Hz following audio output gain relative to 150Hz .
. [|, Audio upgrade 5 ~ 6dB; and when the switch S2 is closed when the amplifier 20Hz ~ 140Hz with a flat frequency response port obvious front face two output modes suitable for promoting sub-cut woofer 6 + 5 inches and lo inch foam side speaker speaker, and the final output of the flat used as a way for signal detection. Real listening after adoption of the corresponding bass boost compensation amplifier push speaker sound low-end frequency response to improve the situation is very clear.
Speaker released 910 bass very flexible, and 6.5 inches speaker unit has also been released, I could feel the bass from feeling the impact of
This power amplifier circuit is designed to provide enhanced low-frequency performance through adjustable bass boost features. The circuit utilizes two switches, S1 and S2, to control the bass boost settings, allowing for flexibility in audio output based on the user's preferences and the specific audio environment.
In the configuration where both switches are disconnected, the circuit is optimized for frequencies below 45 Hz, with the ability to increase the gain by 7 to 8 dB relative to a reference frequency of 200 Hz. This adjustment is crucial for applications requiring a pronounced bass response, such as in home theater systems or music playback setups that emphasize low-end frequencies.
When switch S1 is engaged while S2 remains disconnected, the amplifier can effectively output audio frequencies down to 30 Hz. This setting provides a moderate bass boost of 5 to 6 dB relative to 150 Hz, making it suitable for a variety of audio applications where a solid low-end presence is desired without overwhelming the mid-range frequencies.
The configuration with switch S2 closed allows the amplifier to operate within a frequency range of 20 Hz to 140 Hz, offering a flat frequency response that is advantageous for accurate sound reproduction. This setting is particularly effective for subwoofers, enabling them to deliver clear and impactful bass without distortion.
The circuit's design ensures compatibility with various speaker sizes, particularly those measuring 6 to 10 inches. This versatility allows users to tailor their audio systems to their specific needs, whether for casual listening or more critical audio applications. The final output stage of the circuit is designed for signal detection, which can be beneficial in monitoring audio levels and ensuring optimal performance.
Overall, this amplifier circuit with bass boost compensation is engineered to enhance low-frequency audio performance, providing users with a customizable and effective solution for their audio needs. The careful selection of component parameters and the inclusion of adjustable features contribute to a high-quality listening experience.With bass boost compensation for the practical power amplifier circuit. Follow the instructions on the subject of the amplifier circuit element parameters, when the switch Sl, S2 are disconnected, this function can be put under 45Hz canthus audio output gain relative to 200Hz or more, the audio upgrade 7 ~ 8dB;. Sl closed, sz disconnect when the power amplifier can be 30Hz following audio output gain relative to 150Hz .
. [|, Audio upgrade 5 ~ 6dB; and when the switch S2 is closed when the amplifier 20Hz ~ 140Hz with a flat frequency response port obvious front face two output modes suitable for promoting sub-cut woofer 6 + 5 inches and lo inch foam side speaker speaker, and the final output of the flat used as a way for signal detection. Real listening after adoption of the corresponding bass boost compensation amplifier push speaker sound low-end frequency response to improve the situation is very clear.
Speaker released 910 bass very flexible, and 6.5 inches speaker unit has also been released, I could feel the bass from feeling the impact of
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713