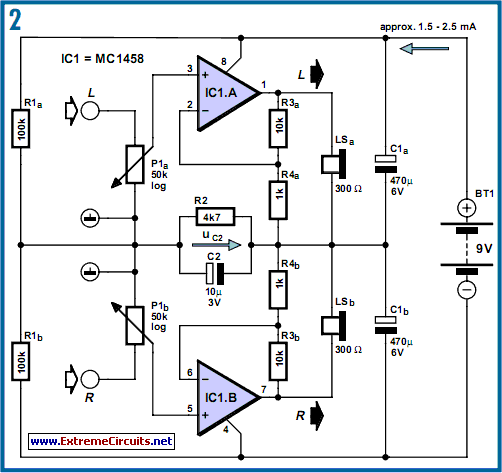
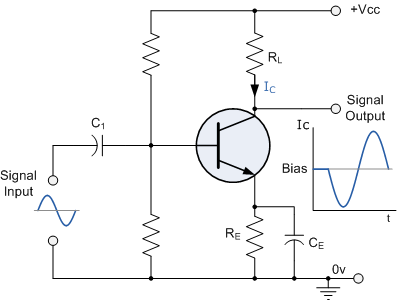
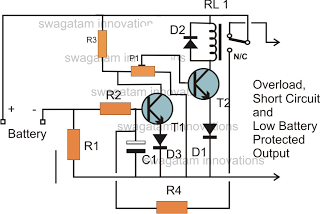
Battery powered buffer amplifier
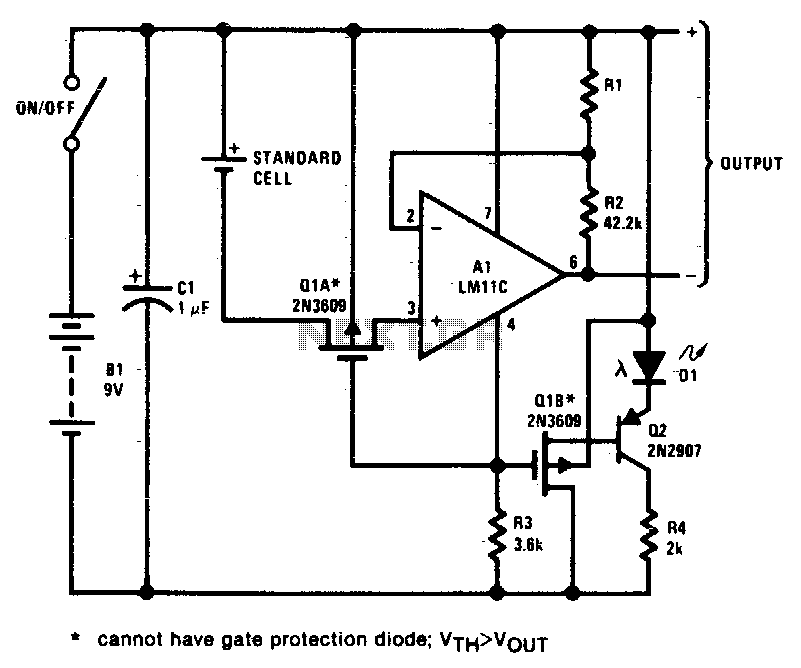
This circuit exhibits negligible loading and disconnects the cell in response to low supply voltage or an overload on the output. Additionally, the indicator diode turns off when the disconnect circuitry is activated.
The circuit design incorporates a voltage monitoring mechanism that continuously assesses the supply voltage levels. When the voltage falls below a predefined threshold, the circuit activates a disconnect feature to safeguard the cell from potential damage due to under-voltage conditions. This is particularly crucial in battery management systems where maintaining the integrity of the cell is paramount.
In the event of an output overload, the circuit also triggers the disconnect functionality. This overload detection is typically implemented using a current sensing resistor in series with the load, allowing the circuit to monitor the current flowing through. If the sensed current exceeds a specified limit, the disconnect circuitry engages, effectively isolating the cell from the load.
The indicator diode serves a dual purpose within the circuit. It provides a visual indication of the circuit's operational status. When the disconnect circuitry is activated, the diode extinguishes, signaling that the cell is no longer connected to the load. This feature is beneficial for user feedback, allowing for immediate recognition of the circuit's state without the need for additional monitoring equipment.
Overall, this circuit design prioritizes the protection of the power source while providing clear operational feedback through the indicator diode, ensuring both reliability and user awareness in various operational scenarios.This circuit has negligible loading and disconnects the cell for low supply voltage or overload on output. The indicator diode extinguishes as disconnect circuitry is activated.
The circuit design incorporates a voltage monitoring mechanism that continuously assesses the supply voltage levels. When the voltage falls below a predefined threshold, the circuit activates a disconnect feature to safeguard the cell from potential damage due to under-voltage conditions. This is particularly crucial in battery management systems where maintaining the integrity of the cell is paramount.
In the event of an output overload, the circuit also triggers the disconnect functionality. This overload detection is typically implemented using a current sensing resistor in series with the load, allowing the circuit to monitor the current flowing through. If the sensed current exceeds a specified limit, the disconnect circuitry engages, effectively isolating the cell from the load.
The indicator diode serves a dual purpose within the circuit. It provides a visual indication of the circuit's operational status. When the disconnect circuitry is activated, the diode extinguishes, signaling that the cell is no longer connected to the load. This feature is beneficial for user feedback, allowing for immediate recognition of the circuit's state without the need for additional monitoring equipment.
Overall, this circuit design prioritizes the protection of the power source while providing clear operational feedback through the indicator diode, ensuring both reliability and user awareness in various operational scenarios.This circuit has negligible loading and disconnects the cell for low supply voltage or overload on output. The indicator diode extinguishes as disconnect circuitry is activated.