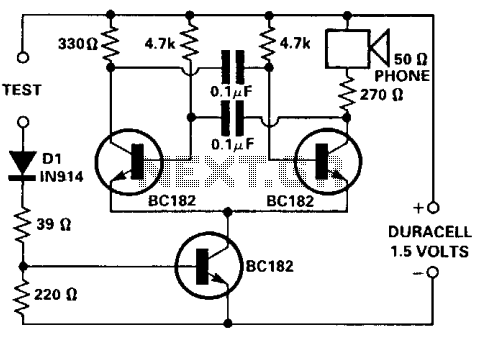
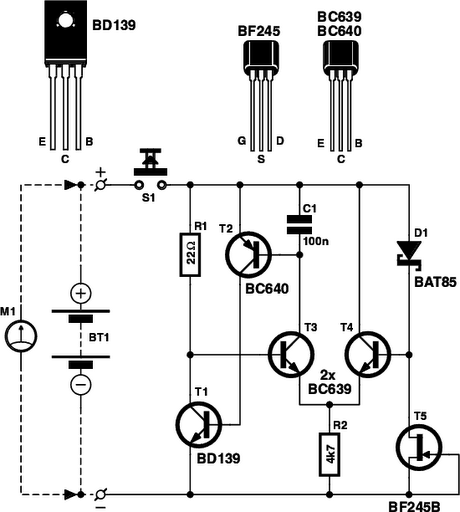
battery tester circuit schematic
Is the battery depleted, or is there an issue with the device? This question often arises when a battery-operated device, such as a Walkman, fails to power on. Before seeking professional repair services, it is advisable to first test the battery or batteries. This requires a dependable battery tester, which allows for minimizing potential costs to just the price of a new battery or two, along with the initial investment of time and resources to create an appropriate tester.
A battery tester is an essential tool for diagnosing battery health and functionality in various electronic devices. The basic design of a battery tester typically includes a simple circuit that can measure voltage and, in some cases, load testing capabilities to assess the battery's performance under operational conditions.
The schematic for a basic battery tester may consist of the following components:
1. **Power Supply**: A small power source, such as a 9V battery, to power the tester circuit itself.
2. **Voltage Divider**: A resistor network that scales down the voltage of the battery being tested to a level that can be safely measured.
3. **Microcontroller or Analog Meter**: A microcontroller can be used to interpret the voltage readings and display them on an LCD screen, while a simpler analog meter can provide a direct voltage readout.
4. **Load Resistor**: This component is used to apply a known load to the battery, allowing for a more accurate assessment of its ability to deliver current.
5. **Switch**: A toggle switch to select between testing modes, such as voltage measurement and load testing.
6. **Output Display**: LEDs or an LCD screen to indicate the battery status, such as "Good," "Weak," or "Replace."
When constructing a battery tester, it is important to ensure that the components are rated appropriately for the maximum voltage and current that may be encountered. The circuit should be housed in a durable enclosure to protect it from physical damage and ensure longevity. Additionally, proper labeling and clear instructions should accompany the device to guide users in its operation.
In summary, a battery tester is a valuable tool that can save time and money by diagnosing battery issues before resorting to professional repair services. The design and construction of such a device can be straightforward, making it accessible for those with basic electronics knowledge.Is the battery empty, or is there something wrong with the device? That s always a difficult question when your walkman or some other battery-powered device appears to be dead when you switch it on. Before you take it to the shop for servicing, the first thing you should do is to test the battery or batteries.
Of course, this means you need a reliable battery tester, but it also means you can limit the damage to the cost of a battery or two and a one-time investment of time and money in building a suitable tester.. 🔗 External reference
A battery tester is an essential tool for diagnosing battery health and functionality in various electronic devices. The basic design of a battery tester typically includes a simple circuit that can measure voltage and, in some cases, load testing capabilities to assess the battery's performance under operational conditions.
The schematic for a basic battery tester may consist of the following components:
1. **Power Supply**: A small power source, such as a 9V battery, to power the tester circuit itself.
2. **Voltage Divider**: A resistor network that scales down the voltage of the battery being tested to a level that can be safely measured.
3. **Microcontroller or Analog Meter**: A microcontroller can be used to interpret the voltage readings and display them on an LCD screen, while a simpler analog meter can provide a direct voltage readout.
4. **Load Resistor**: This component is used to apply a known load to the battery, allowing for a more accurate assessment of its ability to deliver current.
5. **Switch**: A toggle switch to select between testing modes, such as voltage measurement and load testing.
6. **Output Display**: LEDs or an LCD screen to indicate the battery status, such as "Good," "Weak," or "Replace."
When constructing a battery tester, it is important to ensure that the components are rated appropriately for the maximum voltage and current that may be encountered. The circuit should be housed in a durable enclosure to protect it from physical damage and ensure longevity. Additionally, proper labeling and clear instructions should accompany the device to guide users in its operation.
In summary, a battery tester is a valuable tool that can save time and money by diagnosing battery issues before resorting to professional repair services. The design and construction of such a device can be straightforward, making it accessible for those with basic electronics knowledge.Is the battery empty, or is there something wrong with the device? That s always a difficult question when your walkman or some other battery-powered device appears to be dead when you switch it on. Before you take it to the shop for servicing, the first thing you should do is to test the battery or batteries.
Of course, this means you need a reliable battery tester, but it also means you can limit the damage to the cost of a battery or two and a one-time investment of time and money in building a suitable tester.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713