bistable multivibrator using ic 555
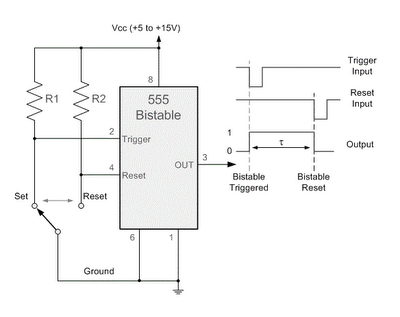
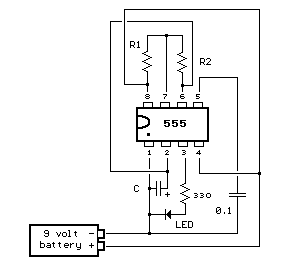
By applying a "LOW" signal to the Trigger input (pin 2) while the switch is in the Set position, the output state changes to "HIGH". Conversely, applying a "LOW" signal to the Reset input (pin 4) while the switch is in the Reset position changes the output to "LOW". This 555 timer circuit can maintain either state indefinitely, thus functioning as a bistable device.
The 555 timer in bistable mode operates as a flip-flop, allowing it to store a binary state. In this configuration, the circuit utilizes two primary inputs: the Trigger and Reset. The Trigger input (pin 2) is activated by a negative edge signal. When this pin receives a "LOW" signal, it causes the output (pin 3) to switch to "HIGH", indicating that the circuit is in the Set state. The Reset input (pin 4) serves a complementary function; when it is pulled "LOW", it resets the output to "LOW", placing the circuit in the Reset state.
The bistable configuration of the 555 timer is particularly useful in applications requiring stable states, such as memory storage, toggle switches, or state retention in digital logic systems. The device remains in its current state until an appropriate input signal is applied, ensuring it does not change states accidentally due to noise or fluctuations in the input signals.
The timing characteristics of the 555 timer in this mode are determined by external components connected to the circuit, such as resistors and capacitors, which can influence the response time and stability of the output states. However, in its basic bistable operation, the 555 timer is capable of maintaining its output state without the need for continuous input signals, making it a reliable choice for various electronic applications.By taking the Trigger input (pin 2) "LOW", switch in Set position, changes the output state into the "HIGH" state and by taking the Reset input (pin 4) "LOW", switch in Reset position, changes the output into the "LOW" state. This 555 timer circuit will remain in either state indefinitely and is therefore bistable. Then the Bistable 555 timer is s table in both states, "HIGH" and "LOW". 🔗 External reference
The 555 timer in bistable mode operates as a flip-flop, allowing it to store a binary state. In this configuration, the circuit utilizes two primary inputs: the Trigger and Reset. The Trigger input (pin 2) is activated by a negative edge signal. When this pin receives a "LOW" signal, it causes the output (pin 3) to switch to "HIGH", indicating that the circuit is in the Set state. The Reset input (pin 4) serves a complementary function; when it is pulled "LOW", it resets the output to "LOW", placing the circuit in the Reset state.
The bistable configuration of the 555 timer is particularly useful in applications requiring stable states, such as memory storage, toggle switches, or state retention in digital logic systems. The device remains in its current state until an appropriate input signal is applied, ensuring it does not change states accidentally due to noise or fluctuations in the input signals.
The timing characteristics of the 555 timer in this mode are determined by external components connected to the circuit, such as resistors and capacitors, which can influence the response time and stability of the output states. However, in its basic bistable operation, the 555 timer is capable of maintaining its output state without the need for continuous input signals, making it a reliable choice for various electronic applications.By taking the Trigger input (pin 2) "LOW", switch in Set position, changes the output state into the "HIGH" state and by taking the Reset input (pin 4) "LOW", switch in Reset position, changes the output into the "LOW" state. This 555 timer circuit will remain in either state indefinitely and is therefore bistable. Then the Bistable 555 timer is s table in both states, "HIGH" and "LOW". 🔗 External reference