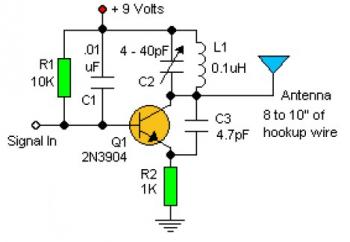
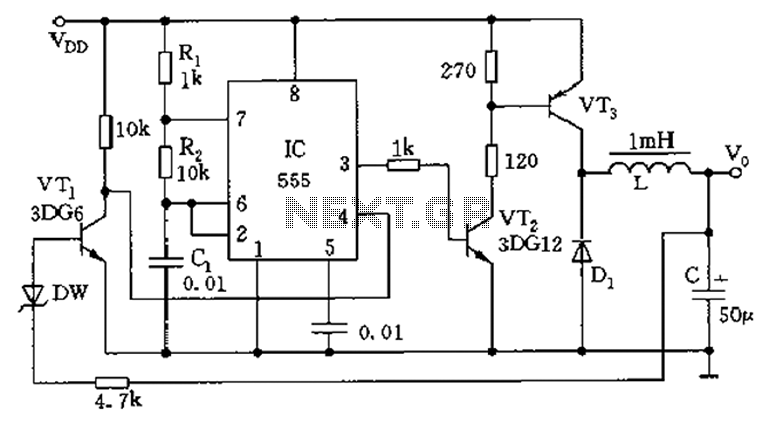
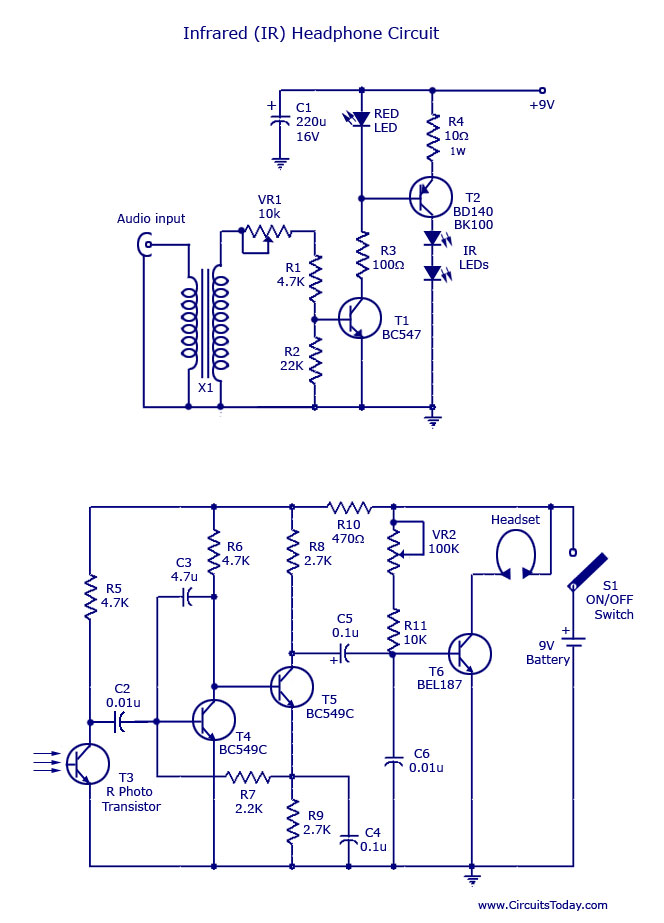
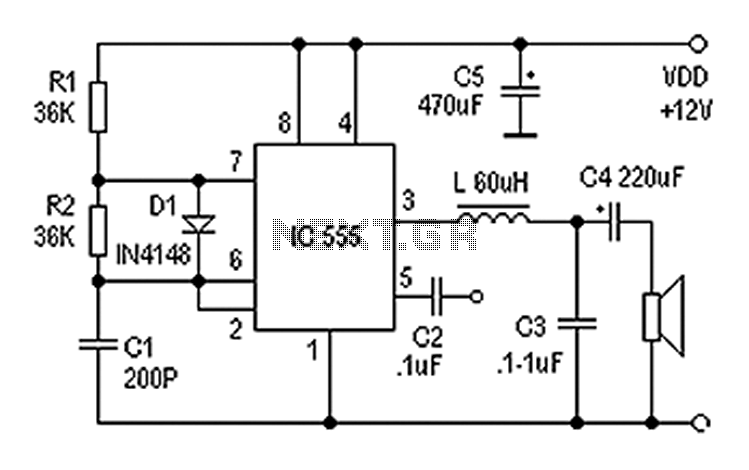
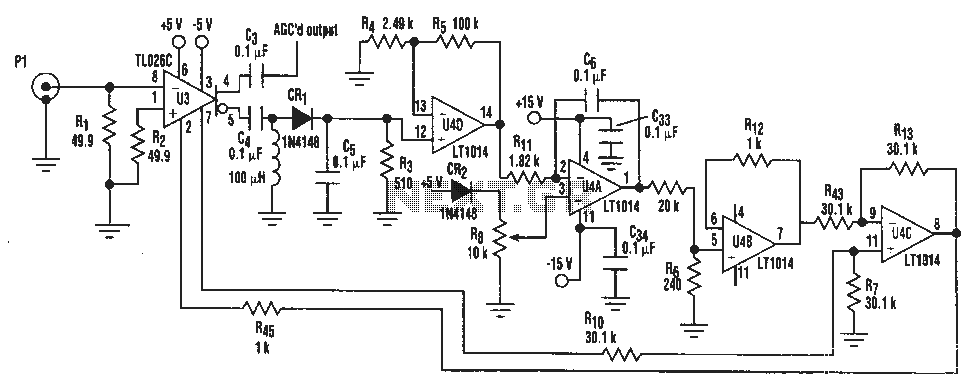
Boss GE-7 Equalizer guitar pedal schematic diagram

The Boss GE-7 Equalizer pedal modifies the harmonic content of an instrument across 7 distinct frequency bands, spanning from 100Hz to 6.4kHz, with a boost or cut of up to 15dB for each band. An additional Level control knob allows for adjustment of volume levels between normal and effect sounds, or enables the pedal to function solely as a gain booster.
The Boss GE-7 Equalizer pedal features a versatile design that allows musicians to shape their sound precisely. Each of the seven frequency bands is carefully selected to cover the critical range of human hearing, ensuring that users can enhance or attenuate specific tonal qualities of their instrument. The frequency bands include: 100Hz, 200Hz, 400Hz, 800Hz, 1.6kHz, 3.2kHz, and 6.4kHz, enabling fine-tuning of bass, midrange, and treble frequencies.
The ability to boost or cut each band by 15dB provides significant control over the tonal characteristics of the instrument. This feature is particularly useful for live performances or studio recordings, where achieving the desired sound is essential. The Level control knob adds an extra layer of functionality, allowing the player to adjust the overall output level of the pedal. This can be particularly beneficial when switching between different sound settings, ensuring a consistent volume level regardless of the EQ adjustments made.
The pedal's design typically includes LED indicators to show when the effect is engaged, and the rugged construction ensures durability in various performance environments. The GE-7 is compatible with a standard 9V power supply, making it easy to integrate into existing pedalboards. Overall, the Boss GE-7 Equalizer pedal is a powerful tool for musicians seeking to refine their sound, offering both flexibility and precision in tonal adjustment.The Boss GE-7 Equalizer pedal adjusts the harmonic contents of an instrument in 7 separate bands ranging from 100Hz to 6. 4kHz, with a boost/cut 15dB per band. The additional Level control knob helps you to set a different volume for normal and effect sound (or to use the pedal only as a gain booster).
🔗 External reference
The Boss GE-7 Equalizer pedal features a versatile design that allows musicians to shape their sound precisely. Each of the seven frequency bands is carefully selected to cover the critical range of human hearing, ensuring that users can enhance or attenuate specific tonal qualities of their instrument. The frequency bands include: 100Hz, 200Hz, 400Hz, 800Hz, 1.6kHz, 3.2kHz, and 6.4kHz, enabling fine-tuning of bass, midrange, and treble frequencies.
The ability to boost or cut each band by 15dB provides significant control over the tonal characteristics of the instrument. This feature is particularly useful for live performances or studio recordings, where achieving the desired sound is essential. The Level control knob adds an extra layer of functionality, allowing the player to adjust the overall output level of the pedal. This can be particularly beneficial when switching between different sound settings, ensuring a consistent volume level regardless of the EQ adjustments made.
The pedal's design typically includes LED indicators to show when the effect is engaged, and the rugged construction ensures durability in various performance environments. The GE-7 is compatible with a standard 9V power supply, making it easy to integrate into existing pedalboards. Overall, the Boss GE-7 Equalizer pedal is a powerful tool for musicians seeking to refine their sound, offering both flexibility and precision in tonal adjustment.The Boss GE-7 Equalizer pedal adjusts the harmonic contents of an instrument in 7 separate bands ranging from 100Hz to 6. 4kHz, with a boost/cut 15dB per band. The additional Level control knob helps you to set a different volume for normal and effect sound (or to use the pedal only as a gain booster).
🔗 External reference