Circuit measures currents in dc servo motor
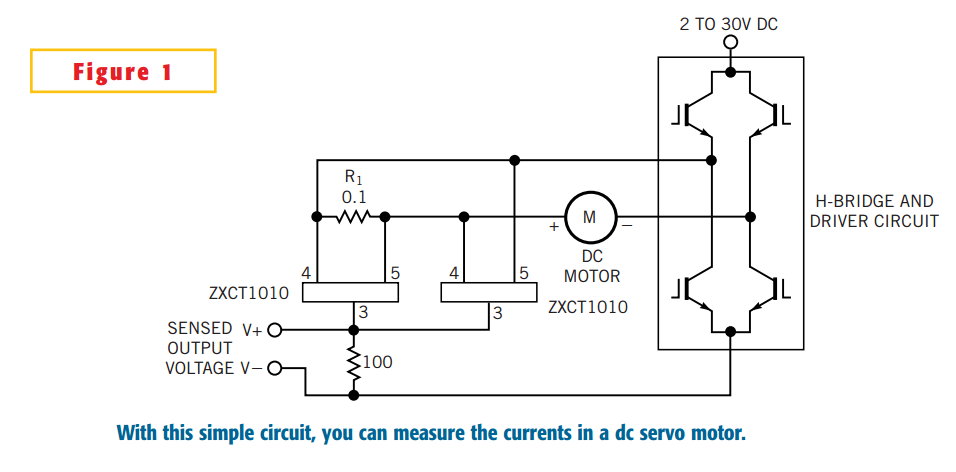
The simple circuit design in Figure 1 lets you measure all components of a current flowing in a dc servo motor. The rectified output of the circuit uses ground as a reference, so you can measure the output by using a single-ended A/D converter. The current-sense resistor, R1, has a value of 0.1. The Zetex ZXCT1010 IC converts the differential signal across R1 to a single-ended signal. Two of these ICs form a signal rectifier. The single-ended signal makes measurement by an A/D converter cost-effective, small, and frugal in power consumption.
The described circuit is designed for precise current measurement in a DC servo motor application. The use of a current-sense resistor, R1, valued at 0.1 ohms, is critical for developing a voltage drop proportional to the current flowing through the motor. This voltage drop is then processed by the Zetex ZXCT1010 integrated circuit, which is specifically designed for current sensing applications.
The ZXCT1010 operates by taking the differential voltage across the current-sense resistor and converting it into a single-ended output. This functionality is essential because it simplifies the interfacing of the circuit with a single-ended Analog-to-Digital (A/D) converter, allowing for easier integration into microcontroller systems or digital signal processors. The dual configuration of the ZXCT1010 ICs serves as a signal rectifier, ensuring that the output signal is suitable for accurate measurement.
The design leverages the ground as a reference point, which is a common practice in electronic measurement systems. This approach minimizes the complexity of the circuit and reduces the number of required components. The overall design is optimized for cost, size, and power efficiency, making it ideal for applications where space and energy resources are limited.
In summary, this circuit design provides a robust solution for measuring current in DC servo motors, utilizing the ZXCT1010 IC for effective signal conversion and ensuring compatibility with single-ended A/D converters. The choice of a low-value current-sense resistor enhances the circuit's sensitivity while maintaining a compact footprint, suitable for various electronic applications.The simple circuit design in Figure 1 lets you measure all components of a current flowing in a dc servo motor. The rectified output of the circuit uses ground as a reference, so you can measure the output by using a single-ended A/D converter.
The current-sense resistor, R1, has a value of 0.1. The Zetex (www.zetex.com) ZXCT1010 IC converts the differential signal across R1 to a single-ended signal. Two of these ICs form a signal rectifier. The single-ended signal makes measurement by an A/D converter cost-effective, small, and frugal in power consumption.
🔗 External reference
The described circuit is designed for precise current measurement in a DC servo motor application. The use of a current-sense resistor, R1, valued at 0.1 ohms, is critical for developing a voltage drop proportional to the current flowing through the motor. This voltage drop is then processed by the Zetex ZXCT1010 integrated circuit, which is specifically designed for current sensing applications.
The ZXCT1010 operates by taking the differential voltage across the current-sense resistor and converting it into a single-ended output. This functionality is essential because it simplifies the interfacing of the circuit with a single-ended Analog-to-Digital (A/D) converter, allowing for easier integration into microcontroller systems or digital signal processors. The dual configuration of the ZXCT1010 ICs serves as a signal rectifier, ensuring that the output signal is suitable for accurate measurement.
The design leverages the ground as a reference point, which is a common practice in electronic measurement systems. This approach minimizes the complexity of the circuit and reduces the number of required components. The overall design is optimized for cost, size, and power efficiency, making it ideal for applications where space and energy resources are limited.
In summary, this circuit design provides a robust solution for measuring current in DC servo motors, utilizing the ZXCT1010 IC for effective signal conversion and ensuring compatibility with single-ended A/D converters. The choice of a low-value current-sense resistor enhances the circuit's sensitivity while maintaining a compact footprint, suitable for various electronic applications.The simple circuit design in Figure 1 lets you measure all components of a current flowing in a dc servo motor. The rectified output of the circuit uses ground as a reference, so you can measure the output by using a single-ended A/D converter.
The current-sense resistor, R1, has a value of 0.1. The Zetex (www.zetex.com) ZXCT1010 IC converts the differential signal across R1 to a single-ended signal. Two of these ICs form a signal rectifier. The single-ended signal makes measurement by an A/D converter cost-effective, small, and frugal in power consumption.
🔗 External reference