Varactor or varicap Diode
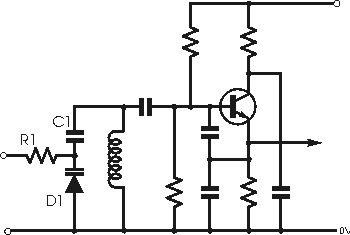
A summary of the varactor or varicap diode used in many radio frequency circuits to provide an electronically variable capacitance.
Varactor diodes, also known as varicap diodes, are semiconductor devices that exploit the voltage-dependent capacitance of a reverse-biased p-n junction. These diodes are widely utilized in radio frequency (RF) applications, particularly in tuning circuits, frequency modulation, and phase-locked loops. The capacitance of a varactor diode varies inversely with the applied reverse voltage, allowing for precise control of resonant frequencies in oscillators and filters.
In RF circuits, varactor diodes are often employed in conjunction with inductors to form LC resonant circuits. By adjusting the reverse bias voltage applied to the varactor, the effective capacitance can be altered, thereby tuning the frequency of the oscillator or filter. This capability is particularly advantageous in applications such as voltage-controlled oscillators (VCOs), where the frequency needs to be varied dynamically in response to control signals.
The performance characteristics of varactor diodes, including their capacitance range, quality factor (Q), and series resistance, are critical in determining their suitability for specific applications. The choice of material, such as silicon or gallium arsenide, as well as the diode's physical structure, influences these parameters. Additionally, varactor diodes are characterized by their non-linear capacitance-voltage relationship, which must be considered in the design of circuits to ensure linearity and minimize distortion.
Overall, varactor diodes play a crucial role in modern RF circuit design, enabling the development of compact and efficient tuning mechanisms essential for a wide range of communication and signal processing applications.A summary of the varactor or varicap diode used in many radio frequency circuits to provide an electronically variable capacitance 🔗 External reference
Varactor diodes, also known as varicap diodes, are semiconductor devices that exploit the voltage-dependent capacitance of a reverse-biased p-n junction. These diodes are widely utilized in radio frequency (RF) applications, particularly in tuning circuits, frequency modulation, and phase-locked loops. The capacitance of a varactor diode varies inversely with the applied reverse voltage, allowing for precise control of resonant frequencies in oscillators and filters.
In RF circuits, varactor diodes are often employed in conjunction with inductors to form LC resonant circuits. By adjusting the reverse bias voltage applied to the varactor, the effective capacitance can be altered, thereby tuning the frequency of the oscillator or filter. This capability is particularly advantageous in applications such as voltage-controlled oscillators (VCOs), where the frequency needs to be varied dynamically in response to control signals.
The performance characteristics of varactor diodes, including their capacitance range, quality factor (Q), and series resistance, are critical in determining their suitability for specific applications. The choice of material, such as silicon or gallium arsenide, as well as the diode's physical structure, influences these parameters. Additionally, varactor diodes are characterized by their non-linear capacitance-voltage relationship, which must be considered in the design of circuits to ensure linearity and minimize distortion.
Overall, varactor diodes play a crucial role in modern RF circuit design, enabling the development of compact and efficient tuning mechanisms essential for a wide range of communication and signal processing applications.A summary of the varactor or varicap diode used in many radio frequency circuits to provide an electronically variable capacitance 🔗 External reference