h bridge circuit
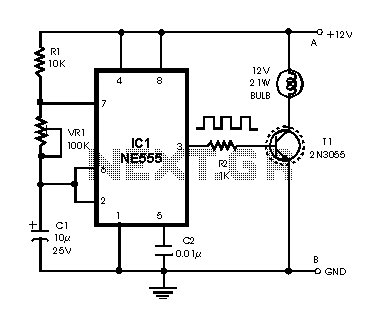
An H-bridge is a type of circuit utilized for controlling the direction (and occasionally the speed) of an electric motor by employing a single polarity voltage. The circuit functions by reversing the current flow to change the motor's rotation direction. It consists of four transistors configured as ON/OFF switches. Two signal lines are used to drive the motor in one direction, and when the signals are reversed, the motor operates in the opposite direction. While the design is simple to implement, caution is advised when using larger motors, as the higher currents can damage the components.
An H-bridge circuit is essential in applications requiring bidirectional control of DC motors. The configuration typically includes four switching elements, which can be either bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) or field-effect transistors (FETs). The arrangement of these transistors allows for two complementary paths for current to flow through the motor, enabling it to rotate in either direction based on the control signals applied to the gates or bases of the transistors.
The H-bridge operates by activating two diagonally opposite transistors while keeping the other two off, allowing current to flow through the motor in one direction. To reverse the motor's direction, the control signals are switched to turn off the first pair of transistors and turn on the other pair. This method of control provides a straightforward solution for applications such as robotics, where precise motor direction control is necessary.
It is crucial to select appropriate transistors that can handle the maximum current the motor may draw during operation. For small motors, standard transistors may suffice; however, for larger motors, higher-rated components or additional protective measures, such as heat sinks, may be required to prevent thermal damage. Additionally, implementing flyback diodes across the transistors can protect the circuit from voltage spikes generated when the motor is turned off, thus enhancing reliability.
In summary, the H-bridge circuit is a fundamental building block in motor control systems, providing an efficient means to manage motor direction with minimal complexity while requiring careful consideration of component ratings to ensure safe and reliable operation.An H bridge is a kind of circuit you use to control the direction (and sometimes speed) of an electric motor, using only a single polarity voltage (you need to reverse the way current flows in order to reverse the way the motor rolls). You have 4 transistors, wired as ON OFF switches. Two signal lines allow you to run the motor in one direction, w hen reversed, the motor runs in the other direction. It`s very straightforward to use and build, but be careful to use only small motors, as the currents drawn from the bigger types can burn your components. 🔗 External reference
An H-bridge circuit is essential in applications requiring bidirectional control of DC motors. The configuration typically includes four switching elements, which can be either bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) or field-effect transistors (FETs). The arrangement of these transistors allows for two complementary paths for current to flow through the motor, enabling it to rotate in either direction based on the control signals applied to the gates or bases of the transistors.
The H-bridge operates by activating two diagonally opposite transistors while keeping the other two off, allowing current to flow through the motor in one direction. To reverse the motor's direction, the control signals are switched to turn off the first pair of transistors and turn on the other pair. This method of control provides a straightforward solution for applications such as robotics, where precise motor direction control is necessary.
It is crucial to select appropriate transistors that can handle the maximum current the motor may draw during operation. For small motors, standard transistors may suffice; however, for larger motors, higher-rated components or additional protective measures, such as heat sinks, may be required to prevent thermal damage. Additionally, implementing flyback diodes across the transistors can protect the circuit from voltage spikes generated when the motor is turned off, thus enhancing reliability.
In summary, the H-bridge circuit is a fundamental building block in motor control systems, providing an efficient means to manage motor direction with minimal complexity while requiring careful consideration of component ratings to ensure safe and reliable operation.An H bridge is a kind of circuit you use to control the direction (and sometimes speed) of an electric motor, using only a single polarity voltage (you need to reverse the way current flows in order to reverse the way the motor rolls). You have 4 transistors, wired as ON OFF switches. Two signal lines allow you to run the motor in one direction, w hen reversed, the motor runs in the other direction. It`s very straightforward to use and build, but be careful to use only small motors, as the currents drawn from the bigger types can burn your components. 🔗 External reference