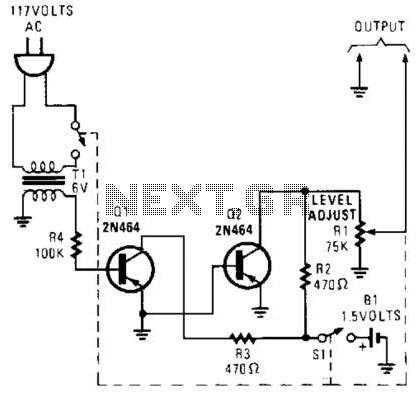
sine wave oscillator
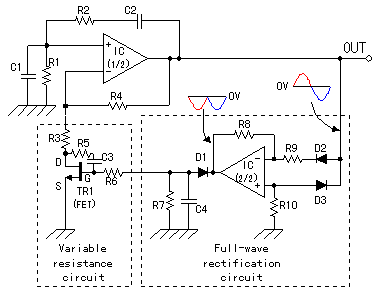
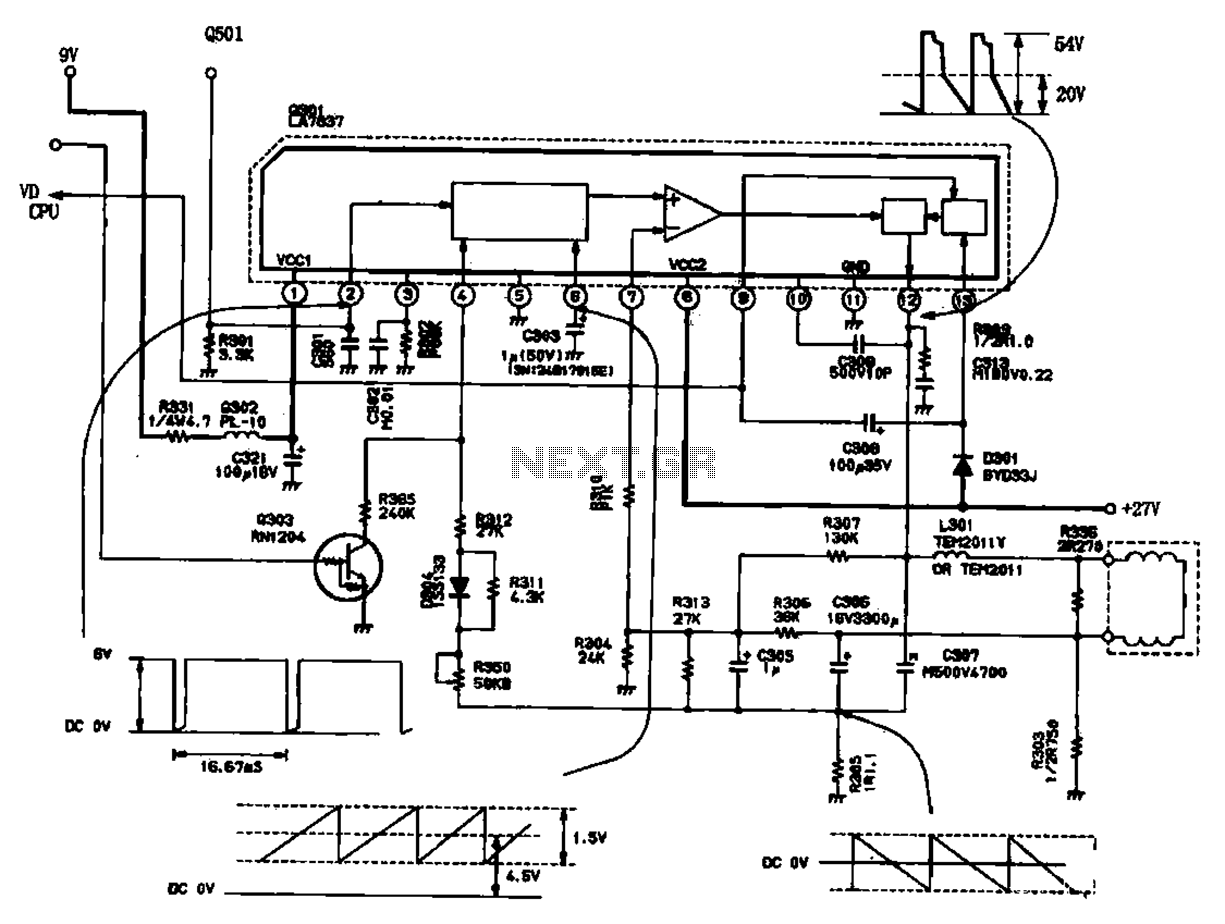
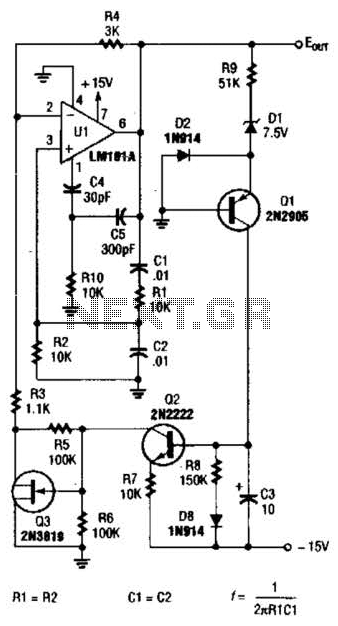
In Japan, the household electricity operates at either 50 Hz or 60 Hz. For a frequency of 50 Hz, one complete sine wave occurs 50 times in one second, while at 60 Hz, it occurs 60 times. Lissajous figures can be used to visualize the relationship between sine waves and circles. When a sine wave is undistorted, the Lissajous figure appears as a perfect circle. An amplifier reaches a saturation state when the feedback signal returned to it is excessively large, resulting in distortion of the output signal. The phase refers to the position of the signal, and in electronic circuits, the phase of both the input and output is influenced by capacitors, inductors, and the amplifier itself. If the input signal's phase is not properly adjusted, oscillation will not occur. The components C1, C2, R1, and R2 form a positive feedback circuit for the operational amplifier, enabling it to oscillate. The oscillation frequency is determined by the time constant of the CR circuit. The oscillator begins to oscillate when the gain factor (mu) is equal to or greater than 3; below this threshold, it does not oscillate. When the mu factor exceeds 3, the output may become saturated, distorting the signal. A low-pass filter allows low-frequency signals to pass while blocking high-frequency signals, causing the output voltage to decrease as frequency increases due to the influence of C1. Conversely, a high-pass filter permits high-frequency signals and blocks low-frequency signals, as the signal passing through C2 diminishes at lower frequencies. When these two filters are combined, they create a band-pass filter, allowing signals within a specific overlapping frequency range to pass. The circuit in question adjusts the resistance of a Field Effect Transistor (FET) using the direct current voltage rectified from the oscillation output in full wave. Current flows from the drain terminal of the N-channel semiconductor to the source terminal, while a P-channel semiconductor is utilized for the gate. When a negative voltage is applied to the gate terminal, electrons in the N-channel are repelled, creating a depletion region at the junction with the P-channel. As there are no electrons in this region, current flow is halted. If the gate voltage is low, the depletion region is small, allowing some drain current to flow. Control is achieved solely through gate voltage, eliminating the need for power (current multiplied by voltage) in the control process. This operation is analogous to that of a tube well. When the oscillator's output voltage is positive, the signal propagates through the negative input terminal of IC(2/2) via D2, while D3 prevents signal flow at the positive input terminal. Conversely, when the oscillator's output voltage is negative, the signal flows through the positive input terminal of IC(2/2) via D3, with D2 blocking the negative input terminal. The negative voltage at the gate of TR1 increases when the output signal of IC(1/2) rises, causing the resistance between the drain and source of TR1 to increase. This increase in resistance raises the effective resistance of R3 and TR1 in series, reducing the mu factor of IC(1/2) and subsequently restraining its output.
The described circuit integrates several key components and functions, including oscillators, filters, and feedback mechanisms, to manage signal processing effectively. The operational amplifier's behavior is crucial for generating oscillations, while the interaction between the FET and gate voltage allows for precise control of current flow without the necessity for direct power input. The use of Lissajous figures aids in visualizing the waveforms, thereby enhancing understanding of the circuit's operation. The combination of low-pass and high-pass filters into a band-pass filter effectively narrows the frequency range of interest, ensuring that only desired signals are processed. Overall, this circuit exemplifies the principles of analog signal processing, demonstrating the interplay between frequency, phase, and feedback in achieving stable oscillations and controlled signal output.In case of Japan, the electricity to be using in the home is 50 Hz or 60 Hz. In case of 50 Hz, the 1-cycle sine wave occurs the 50 times for the 1 second. 60 Hz are the 60 times. There is a way of making make the Lissajous as the way of understanding that the sine wave relates to the circle. In case of the sine wave which doesn`t have the distorti on, the Lissajous becomes the true circle. The amplifier becomes the saturation state when the signal which returns to the amplifier through the feedback circuit is too big and the beautiful signal doesn`t come out. The phase means the position of the signal. At the electronic circuits, phase of the input and the output depends on capacitors, the coils, the amplifier itself.
Because it is, it doesn`t oscillate when not adjusting the phase of the input signal. The part which is composed of C1, C2, R1, R2 becomes the positive feedback circuit of the operational amplifier. With it, the operational amplifier works in the oscillation. Also, the circuit sets the oscillation frequency in the damping time constant of the CR. This oscillator begins the oscillation when it makes the mu factor equal to or more than 3. At less than 3, it doesn`t oscillate. The beautiful signal doesn`t come out by output`s being saturated when the mu factor is more than 3. The low pass filter make pass the low frequency signal and blocks the high frequency signal. The signal flows through the grounding with C1 and the output voltage becomes low when the frequency becomes high.
Oppositely, the high pass filter make pass the high frequency signal and blocks the low frequency signal. It is because the signal which passes C2 becomes little when the frequency becomes low. When combining these two, the signal in the area that the characteristic is the overlapping frequency gets to pass.
Such a filter is called the band pass filter. The circuit to be using this time changes the resistance value of the Field Effect-type Transistor(FET) at the d. c. voltage which rectified the oscillation output in the full wave. The electric current of the controlled circuit flows from the drain terminal of the semiconductor on the N-channel to the source terminal.
The semiconductor on the P channel is used for the gate. When the negative voltage is gained by the gate terminal, the electron on the N-channel(it has the negative electric charge) repels and can make the depletion region to be the junction part with the P channel. Because the electron doesn`t exist in the depletion region, the electric current doesn`t flow. When the voltage which is gained by the gate isn`t high, the depletion region is small and the flow of the drain electric current isn`t too much influenced.
It is possible to control only at the voltage of the gate. The electric power(current X voltage) isn`t necessary in spite of the control. This operation resembles the operation of the tube well. When the output voltage of the oscillator is the positive voltage, the signal spreads through the negative input terminal of IC(2/2) through D2. At the positive input terminal, it is prevented by D3 and the signal doesn`t spread. Next, when the output voltage of the oscillator is the negative voltage, the signal spreads through the positive input terminal of IC(2/2) through D3.
At the negative input terminal, it is prevented by D2 and the signal doesn`t spread. The negative voltage which is gained by the gate of TR1 becomes high when the output signal of IC(1/2) becomes big. Then, the resistance value between the drain and the source of TR1, too, becomes high. The mu factor of IC(1/2) falls when the resistance value of R3 and TR1 which is stored in series becomes high.
The output of IC(1/2) is restrained by it. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit integrates several key components and functions, including oscillators, filters, and feedback mechanisms, to manage signal processing effectively. The operational amplifier's behavior is crucial for generating oscillations, while the interaction between the FET and gate voltage allows for precise control of current flow without the necessity for direct power input. The use of Lissajous figures aids in visualizing the waveforms, thereby enhancing understanding of the circuit's operation. The combination of low-pass and high-pass filters into a band-pass filter effectively narrows the frequency range of interest, ensuring that only desired signals are processed. Overall, this circuit exemplifies the principles of analog signal processing, demonstrating the interplay between frequency, phase, and feedback in achieving stable oscillations and controlled signal output.In case of Japan, the electricity to be using in the home is 50 Hz or 60 Hz. In case of 50 Hz, the 1-cycle sine wave occurs the 50 times for the 1 second. 60 Hz are the 60 times. There is a way of making make the Lissajous as the way of understanding that the sine wave relates to the circle. In case of the sine wave which doesn`t have the distorti on, the Lissajous becomes the true circle. The amplifier becomes the saturation state when the signal which returns to the amplifier through the feedback circuit is too big and the beautiful signal doesn`t come out. The phase means the position of the signal. At the electronic circuits, phase of the input and the output depends on capacitors, the coils, the amplifier itself.
Because it is, it doesn`t oscillate when not adjusting the phase of the input signal. The part which is composed of C1, C2, R1, R2 becomes the positive feedback circuit of the operational amplifier. With it, the operational amplifier works in the oscillation. Also, the circuit sets the oscillation frequency in the damping time constant of the CR. This oscillator begins the oscillation when it makes the mu factor equal to or more than 3. At less than 3, it doesn`t oscillate. The beautiful signal doesn`t come out by output`s being saturated when the mu factor is more than 3. The low pass filter make pass the low frequency signal and blocks the high frequency signal. The signal flows through the grounding with C1 and the output voltage becomes low when the frequency becomes high.
Oppositely, the high pass filter make pass the high frequency signal and blocks the low frequency signal. It is because the signal which passes C2 becomes little when the frequency becomes low. When combining these two, the signal in the area that the characteristic is the overlapping frequency gets to pass.
Such a filter is called the band pass filter. The circuit to be using this time changes the resistance value of the Field Effect-type Transistor(FET) at the d. c. voltage which rectified the oscillation output in the full wave. The electric current of the controlled circuit flows from the drain terminal of the semiconductor on the N-channel to the source terminal.
The semiconductor on the P channel is used for the gate. When the negative voltage is gained by the gate terminal, the electron on the N-channel(it has the negative electric charge) repels and can make the depletion region to be the junction part with the P channel. Because the electron doesn`t exist in the depletion region, the electric current doesn`t flow. When the voltage which is gained by the gate isn`t high, the depletion region is small and the flow of the drain electric current isn`t too much influenced.
It is possible to control only at the voltage of the gate. The electric power(current X voltage) isn`t necessary in spite of the control. This operation resembles the operation of the tube well. When the output voltage of the oscillator is the positive voltage, the signal spreads through the negative input terminal of IC(2/2) through D2. At the positive input terminal, it is prevented by D3 and the signal doesn`t spread. Next, when the output voltage of the oscillator is the negative voltage, the signal spreads through the positive input terminal of IC(2/2) through D3.
At the negative input terminal, it is prevented by D2 and the signal doesn`t spread. The negative voltage which is gained by the gate of TR1 becomes high when the output signal of IC(1/2) becomes big. Then, the resistance value between the drain and the source of TR1, too, becomes high. The mu factor of IC(1/2) falls when the resistance value of R3 and TR1 which is stored in series becomes high.
The output of IC(1/2) is restrained by it. 🔗 External reference