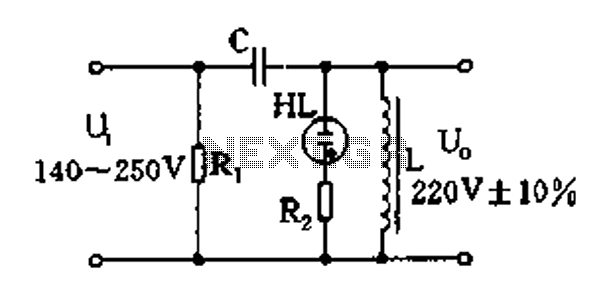
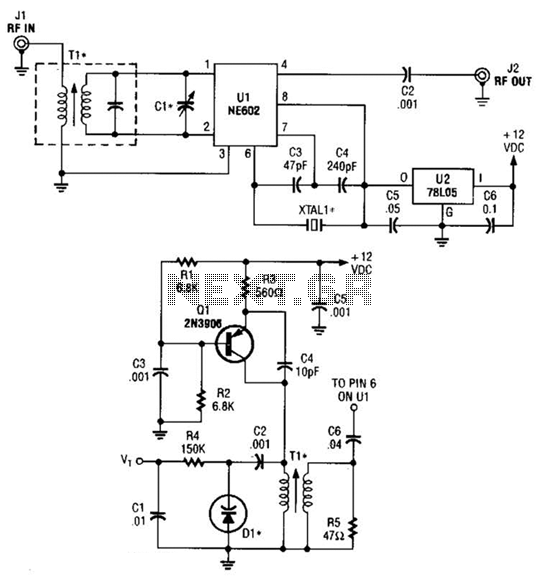
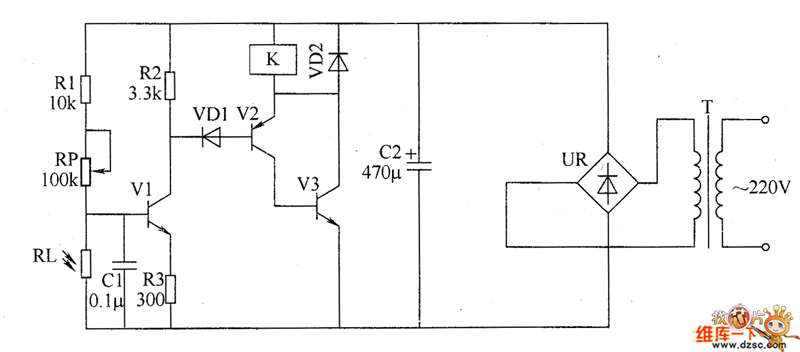
CMOS and PMOS cross interface circuit b
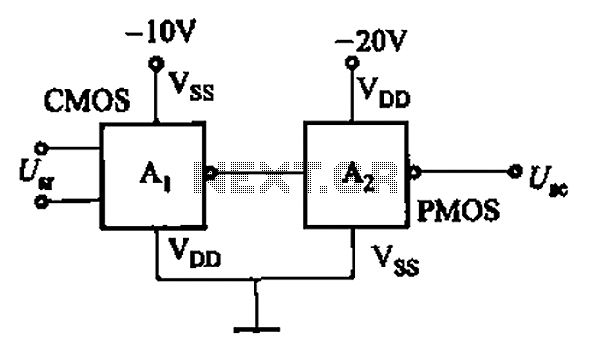
CMOS and PMOS cross interface circuit with PMOS integrated circuit providing high input impedance, allowing the input current to be negligible. The CMOS and PMOS interface circuit is illustrated in the accompanying figure.
The CMOS and PMOS cross interface circuit is designed to facilitate seamless communication between CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) and PMOS (P-channel Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) technologies. The primary advantage of utilizing PMOS in this configuration is its high input impedance, which results in minimal loading on preceding stages of the circuit. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in applications where signal integrity is paramount, as it ensures that the input current can be effectively ignored, thereby preserving the original signal characteristics.
In the schematic representation of the circuit, the PMOS transistors are typically arranged in a manner that allows them to interface effectively with CMOS logic levels. The circuit may incorporate level-shifting mechanisms to accommodate the different voltage levels inherent in CMOS and PMOS technologies. This ensures compatibility and reliable operation across various parts of the system.
The design may also include pull-up or pull-down resistors to maintain the desired logic levels during transitions. Additionally, capacitive coupling may be employed to filter out noise and stabilize the input signals. The careful selection of component values is crucial to achieve the desired performance metrics, including switching speed, power consumption, and thermal stability.
Overall, the CMOS and PMOS cross interface circuit is a vital component in mixed-signal applications, enabling efficient signal processing and interfacing between different semiconductor technologies while maintaining high fidelity and low power consumption. CMOS and PMOS cross interface circuit b PMOS integrated circuit high input impedance, input current can be ignored. CMOS and PMOS interface circuit shown in Figure
The CMOS and PMOS cross interface circuit is designed to facilitate seamless communication between CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) and PMOS (P-channel Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) technologies. The primary advantage of utilizing PMOS in this configuration is its high input impedance, which results in minimal loading on preceding stages of the circuit. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in applications where signal integrity is paramount, as it ensures that the input current can be effectively ignored, thereby preserving the original signal characteristics.
In the schematic representation of the circuit, the PMOS transistors are typically arranged in a manner that allows them to interface effectively with CMOS logic levels. The circuit may incorporate level-shifting mechanisms to accommodate the different voltage levels inherent in CMOS and PMOS technologies. This ensures compatibility and reliable operation across various parts of the system.
The design may also include pull-up or pull-down resistors to maintain the desired logic levels during transitions. Additionally, capacitive coupling may be employed to filter out noise and stabilize the input signals. The careful selection of component values is crucial to achieve the desired performance metrics, including switching speed, power consumption, and thermal stability.
Overall, the CMOS and PMOS cross interface circuit is a vital component in mixed-signal applications, enabling efficient signal processing and interfacing between different semiconductor technologies while maintaining high fidelity and low power consumption. CMOS and PMOS cross interface circuit b PMOS integrated circuit high input impedance, input current can be ignored. CMOS and PMOS interface circuit shown in Figure