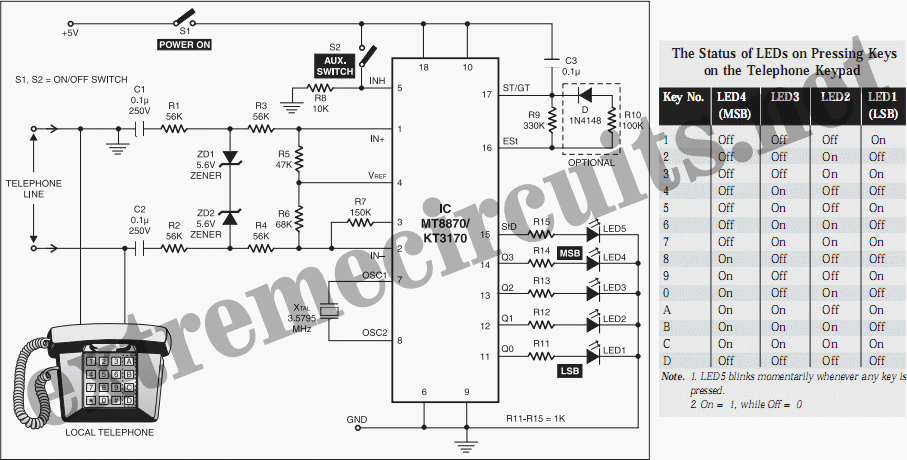
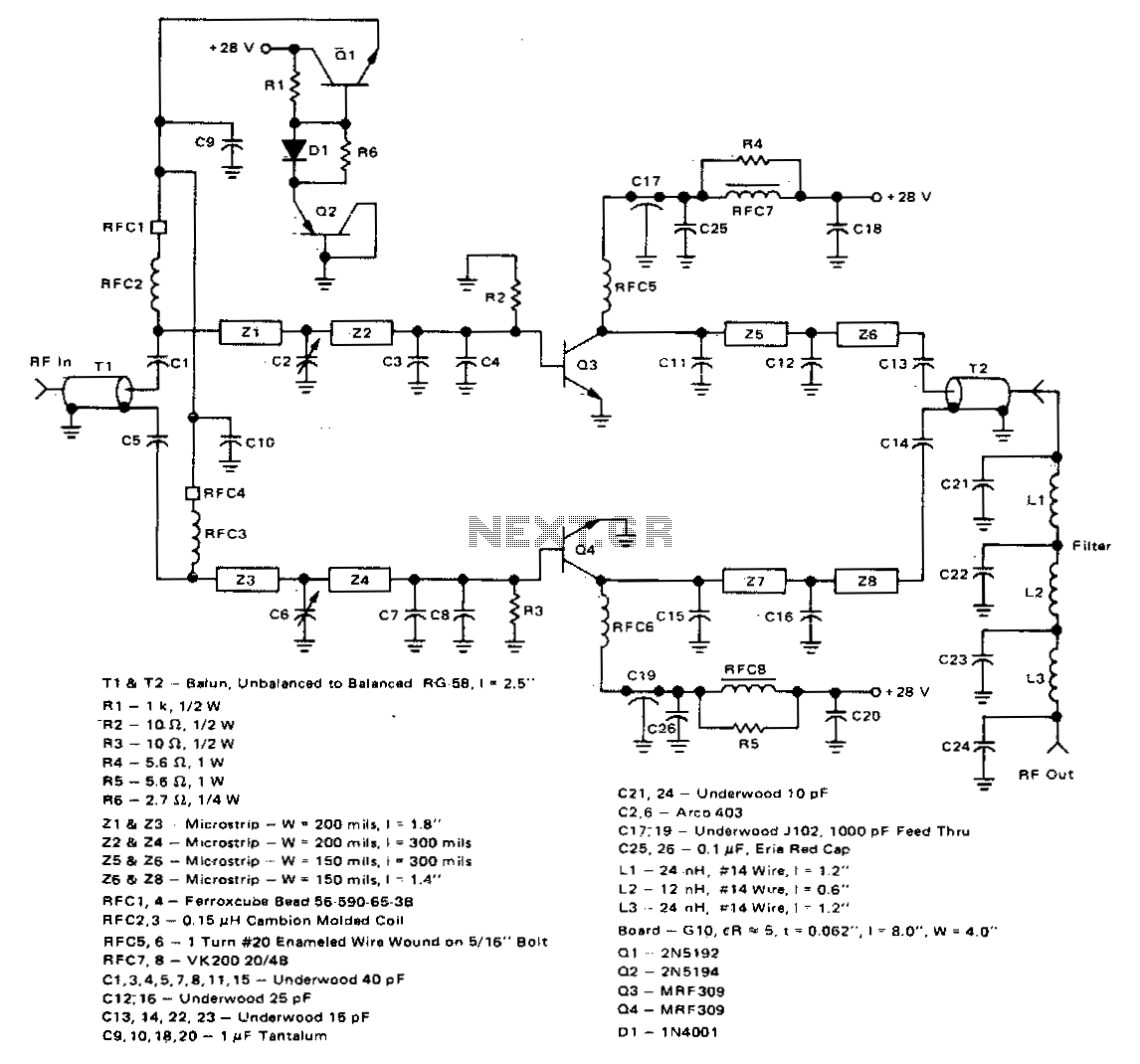
Cmos line receiver
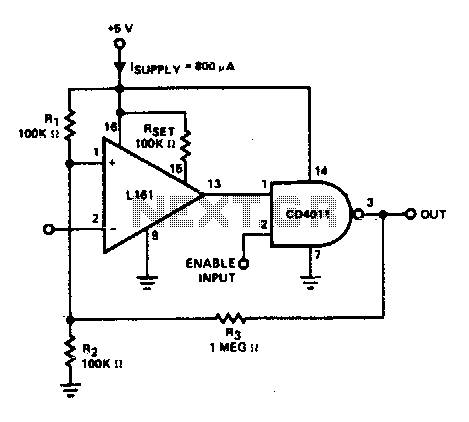
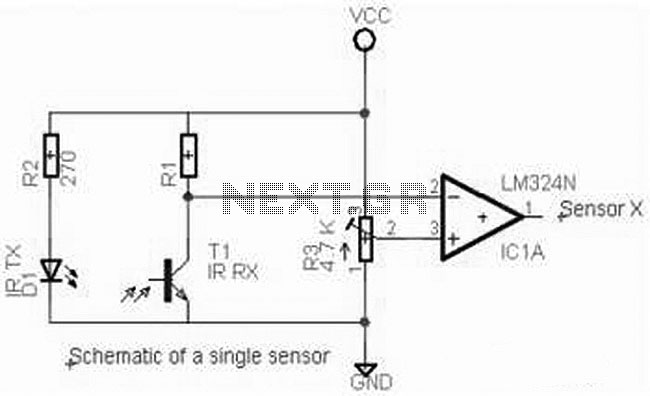
The trip point is set halfway between the supplies by R1 and R2; R3 provides over 200 mV of hysteresis to increase noise immunity. The maximum frequency of operation is about 300 kHz. If response to TTL levels is desired, change R2 to 39 kΩ. The trip point is now centered at 1 V.
The circuit operates as a comparator with a defined trip point, which is established by the resistors R1 and R2. This configuration allows the trip point to be positioned at the midpoint between the positive and negative supply voltages, ensuring balanced operation. The inclusion of resistor R3 introduces hysteresis into the system, effectively providing over 200 mV of feedback that enhances the circuit's noise immunity. This feature is crucial in applications where signal integrity is paramount, as it prevents false triggering due to minor fluctuations or noise in the input signal.
The maximum operational frequency of this circuit is approximately 300 kHz, which indicates its suitability for high-speed applications. For instances where TTL (Transistor-Transistor Logic) level compatibility is required, a modification can be made by replacing R2 with a 39 kΩ resistor. This adjustment alters the trip point, centering it at 1 V, which is optimal for interfacing with TTL logic levels.
In practical applications, this configuration can be utilized in various scenarios, such as signal conditioning, level detection, and pulse-width modulation systems. The circuit's design allows for flexibility in tuning the trip point and hysteresis, making it adaptable to different electronic systems and requirements. By carefully selecting resistor values, one can achieve the desired performance characteristics while maintaining stability and reliability in operation.The trip point is set half way between the supplies by Rl and R2; R3 provides over 200 mV of hysteresis to increase noise immunity. Maximum frequency of operation is about 300 kHz. If response to TTL levels is desired, change R2 to 39 K The trip point is now centered at 1 V.
The circuit operates as a comparator with a defined trip point, which is established by the resistors R1 and R2. This configuration allows the trip point to be positioned at the midpoint between the positive and negative supply voltages, ensuring balanced operation. The inclusion of resistor R3 introduces hysteresis into the system, effectively providing over 200 mV of feedback that enhances the circuit's noise immunity. This feature is crucial in applications where signal integrity is paramount, as it prevents false triggering due to minor fluctuations or noise in the input signal.
The maximum operational frequency of this circuit is approximately 300 kHz, which indicates its suitability for high-speed applications. For instances where TTL (Transistor-Transistor Logic) level compatibility is required, a modification can be made by replacing R2 with a 39 kΩ resistor. This adjustment alters the trip point, centering it at 1 V, which is optimal for interfacing with TTL logic levels.
In practical applications, this configuration can be utilized in various scenarios, such as signal conditioning, level detection, and pulse-width modulation systems. The circuit's design allows for flexibility in tuning the trip point and hysteresis, making it adaptable to different electronic systems and requirements. By carefully selecting resistor values, one can achieve the desired performance characteristics while maintaining stability and reliability in operation.The trip point is set half way between the supplies by Rl and R2; R3 provides over 200 mV of hysteresis to increase noise immunity. Maximum frequency of operation is about 300 kHz. If response to TTL levels is desired, change R2 to 39 K The trip point is now centered at 1 V.