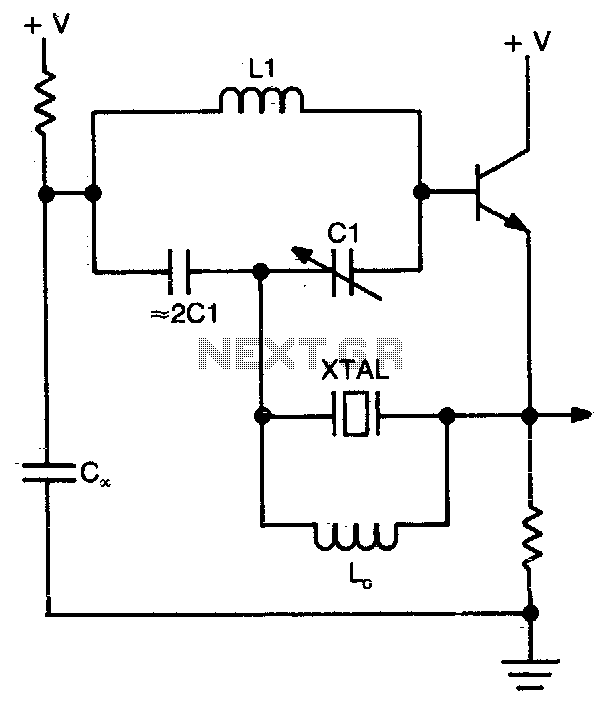
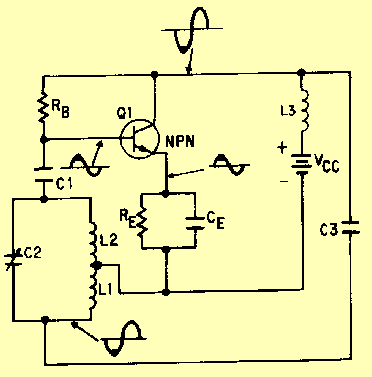
Colpitts harmonic oscillator
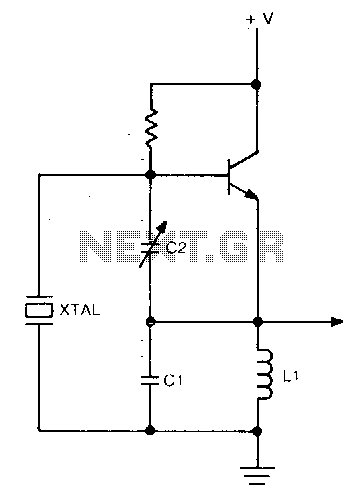
This circuit operates at a frequency range of 30-200 parts per million (ppm) above the series resonance. It is physically simple, yet analytically complex. Additionally, it is cost-effective and exhibits reasonable frequency stability.
The described circuit functions within a specific frequency range, indicating its application in precise frequency modulation or signal generation tasks. Operating at 30-200 ppm above the series resonance suggests that the circuit is likely part of an oscillator or filter design, where maintaining a stable frequency is essential for performance.
The simplicity of the physical design may imply the use of basic components such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors, arranged in a configuration that allows for easy assembly and integration into larger systems. However, the analytical complexity indicates that the behavior of the circuit may involve intricate calculations or simulations to fully understand its performance under various conditions.
Frequency stability is crucial in applications such as communication systems, where signal integrity can be affected by variations in temperature, voltage, and component tolerances. The mention of "fair frequency stability" suggests that while the circuit may not offer the highest precision, it remains adequate for many practical applications, making it a viable choice for cost-sensitive projects.
Overall, this circuit design balances simplicity and performance, making it suitable for a range of electronic applications where moderate frequency stability is acceptable. Further analysis may be required to optimize component values and configurations to meet specific operational requirements.This circuit operates 30-200 ppm above series resonance. Physically simple, but analytically complex It is inexpensive with fair frequency stability. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit functions within a specific frequency range, indicating its application in precise frequency modulation or signal generation tasks. Operating at 30-200 ppm above the series resonance suggests that the circuit is likely part of an oscillator or filter design, where maintaining a stable frequency is essential for performance.
The simplicity of the physical design may imply the use of basic components such as resistors, capacitors, and inductors, arranged in a configuration that allows for easy assembly and integration into larger systems. However, the analytical complexity indicates that the behavior of the circuit may involve intricate calculations or simulations to fully understand its performance under various conditions.
Frequency stability is crucial in applications such as communication systems, where signal integrity can be affected by variations in temperature, voltage, and component tolerances. The mention of "fair frequency stability" suggests that while the circuit may not offer the highest precision, it remains adequate for many practical applications, making it a viable choice for cost-sensitive projects.
Overall, this circuit design balances simplicity and performance, making it suitable for a range of electronic applications where moderate frequency stability is acceptable. Further analysis may be required to optimize component values and configurations to meet specific operational requirements.This circuit operates 30-200 ppm above series resonance. Physically simple, but analytically complex It is inexpensive with fair frequency stability. 🔗 External reference