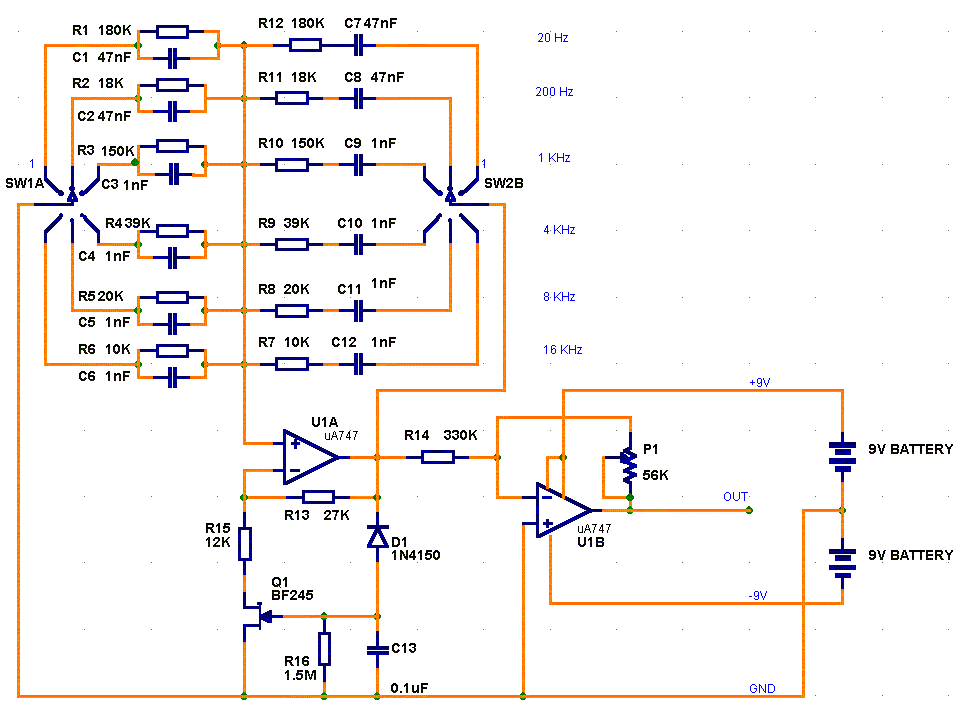
Four-decade variable oscillator
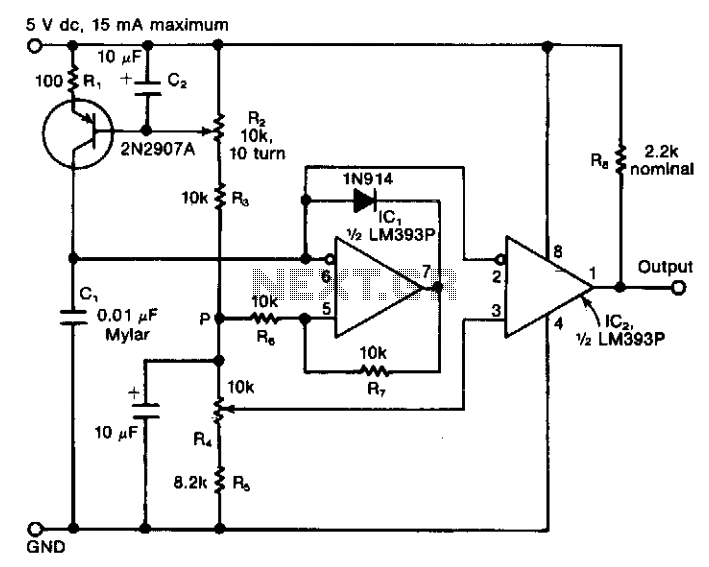
The circuit features a variable current source that charges a capacitor, which is rapidly discharged by a Schmitt-trigger comparator. The resulting sawtooth waveform is provided to another comparator with a variable switching level. The output from this second comparator generates a pulse train with independently adjustable frequency and duty cycle. The variable-frequency ramp generator includes capacitor C1, charged by a variable and nonlinear current source. This current source consists of a 2N2907A PNP transistor, along with resistor R1 and potentiometer R2. Capacitor C2 is used to filter out any ripple or noise at the base of the transistor, preventing frequency jitter in the output.
The described circuit operates as a variable-frequency pulse generator, utilizing a combination of capacitive charging and comparator switching to produce a precise output waveform. The first stage involves the charging of capacitor C1 by a nonlinear current source, which is controlled by the 2N2907A PNP transistor. The transistor's base current is influenced by resistor R1 and the adjustable potentiometer R2, allowing for fine-tuning of the charging rate and, consequently, the frequency of the generated sawtooth waveform.
The Schmitt-trigger comparator plays a crucial role in ensuring that the capacitor discharges rapidly, creating sharp transitions in the voltage across C1. This rapid discharge leads to the generation of a sawtooth waveform, which is characterized by a linear rise followed by a quick drop, suitable for pulse-width modulation applications.
The second comparator receives the sawtooth waveform and compares it against a variable reference voltage, which is set by the user. This variable switching level allows the output pulse train's duty cycle to be adjusted independently of its frequency. The output of the second comparator is a series of pulses, whose frequency and duty cycle can be modified based on the settings of the potentiometer R2 and the reference voltage.
In addition, capacitor C2 serves an important filtering function, smoothing out any high-frequency noise or ripple that may be present at the base of the transistor. This filtering is essential for maintaining the stability of the frequency output, as any noise could introduce jitter, affecting the performance of the pulse generator.
Overall, this circuit design provides flexibility and precision in generating variable-frequency pulse trains, making it suitable for various applications in signal processing, control systems, and waveform generation.The circuit consists of a variable current source that charges a capacitor, which is rapidly discharged by a Schmitt-trigger comparator. The sawtooth waveform thus produced is fed to another comparator, one with a variable switching level.
The output from the second comparator is a pulse train with an independently adjustable frequency and duty cycle. The variable-frequency ramp generator consists of capacitor Cl, which is charged by a variable and nonlinear current source.
The latter comprises a 2N2907A pnp transistor, plus resistor Rl and the potentiometer R2. Capacitor C2 eliminates any ripple or noise at the base of the transistor that might cause frequency jitter at the output. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit operates as a variable-frequency pulse generator, utilizing a combination of capacitive charging and comparator switching to produce a precise output waveform. The first stage involves the charging of capacitor C1 by a nonlinear current source, which is controlled by the 2N2907A PNP transistor. The transistor's base current is influenced by resistor R1 and the adjustable potentiometer R2, allowing for fine-tuning of the charging rate and, consequently, the frequency of the generated sawtooth waveform.
The Schmitt-trigger comparator plays a crucial role in ensuring that the capacitor discharges rapidly, creating sharp transitions in the voltage across C1. This rapid discharge leads to the generation of a sawtooth waveform, which is characterized by a linear rise followed by a quick drop, suitable for pulse-width modulation applications.
The second comparator receives the sawtooth waveform and compares it against a variable reference voltage, which is set by the user. This variable switching level allows the output pulse train's duty cycle to be adjusted independently of its frequency. The output of the second comparator is a series of pulses, whose frequency and duty cycle can be modified based on the settings of the potentiometer R2 and the reference voltage.
In addition, capacitor C2 serves an important filtering function, smoothing out any high-frequency noise or ripple that may be present at the base of the transistor. This filtering is essential for maintaining the stability of the frequency output, as any noise could introduce jitter, affecting the performance of the pulse generator.
Overall, this circuit design provides flexibility and precision in generating variable-frequency pulse trains, making it suitable for various applications in signal processing, control systems, and waveform generation.The circuit consists of a variable current source that charges a capacitor, which is rapidly discharged by a Schmitt-trigger comparator. The sawtooth waveform thus produced is fed to another comparator, one with a variable switching level.
The output from the second comparator is a pulse train with an independently adjustable frequency and duty cycle. The variable-frequency ramp generator consists of capacitor Cl, which is charged by a variable and nonlinear current source.
The latter comprises a 2N2907A pnp transistor, plus resistor Rl and the potentiometer R2. Capacitor C2 eliminates any ripple or noise at the base of the transistor that might cause frequency jitter at the output. 🔗 External reference