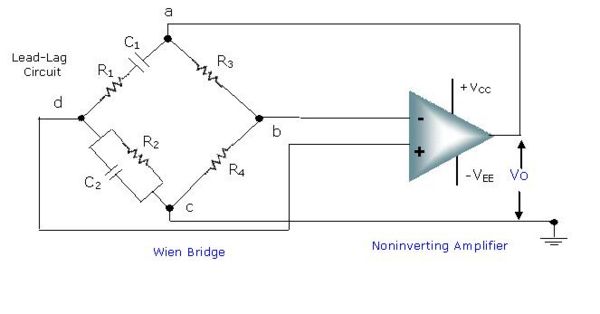
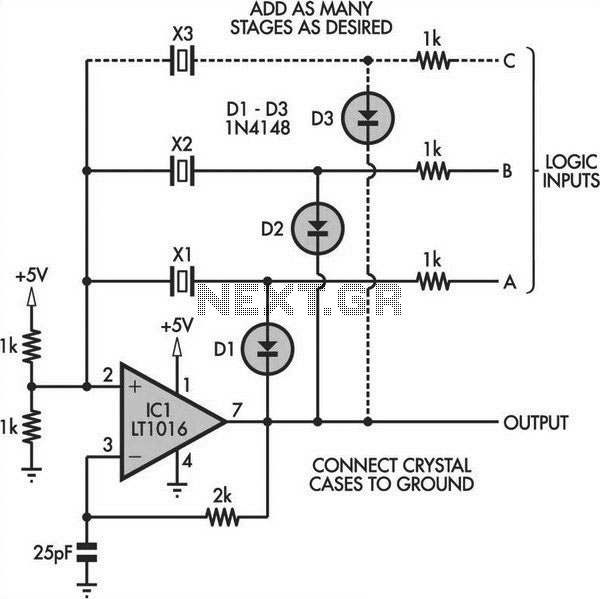
Colpitts oscillator
An early schematic of a Colpitts circuit utilizing a vacuum tube, redrawn from a patent publication. The Colpitts oscillator, invented in 1920 by American engineer Edwin H. Colpitts, is one of several designs for electronic oscillators.
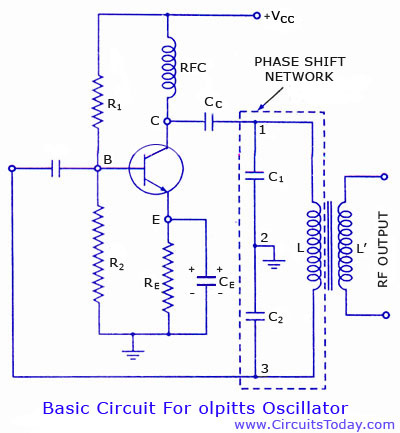
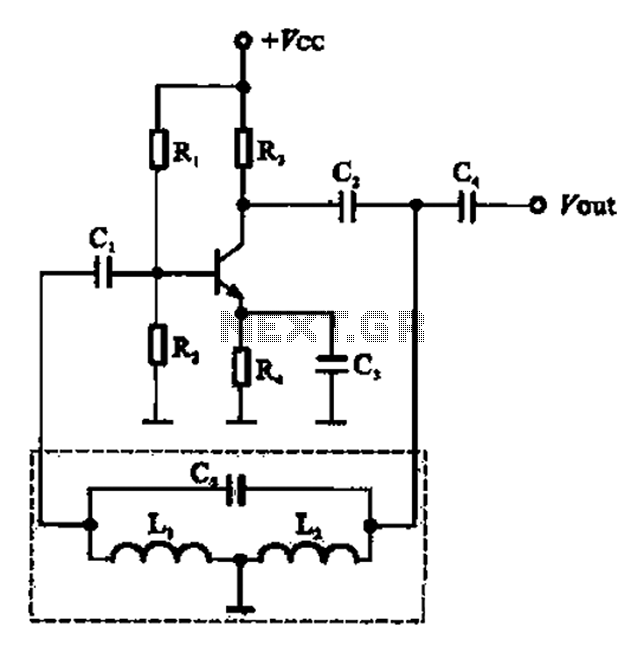
The Colpitts oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that generates sine waves and is characterized by its use of a combination of capacitors and an inductor in its feedback network. The fundamental operation of the Colpitts oscillator relies on the resonant frequency determined by the inductor and the capacitors connected in series.
In this particular schematic, the vacuum tube serves as the active element, providing the necessary gain for oscillation. The circuit typically consists of a vacuum tube, an inductor (L), and two capacitors (C1 and C2) arranged in a voltage divider configuration. The output frequency can be adjusted by varying the values of the capacitors or the inductor, allowing for flexibility in frequency generation.
The feedback loop is crucial for sustaining oscillations. It is established through the coupling of the output from the anode of the vacuum tube back to the junction of the two capacitors. This feedback ensures that the circuit maintains its oscillation at the resonant frequency determined by the LC network.
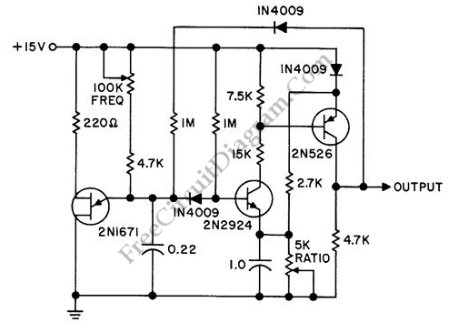
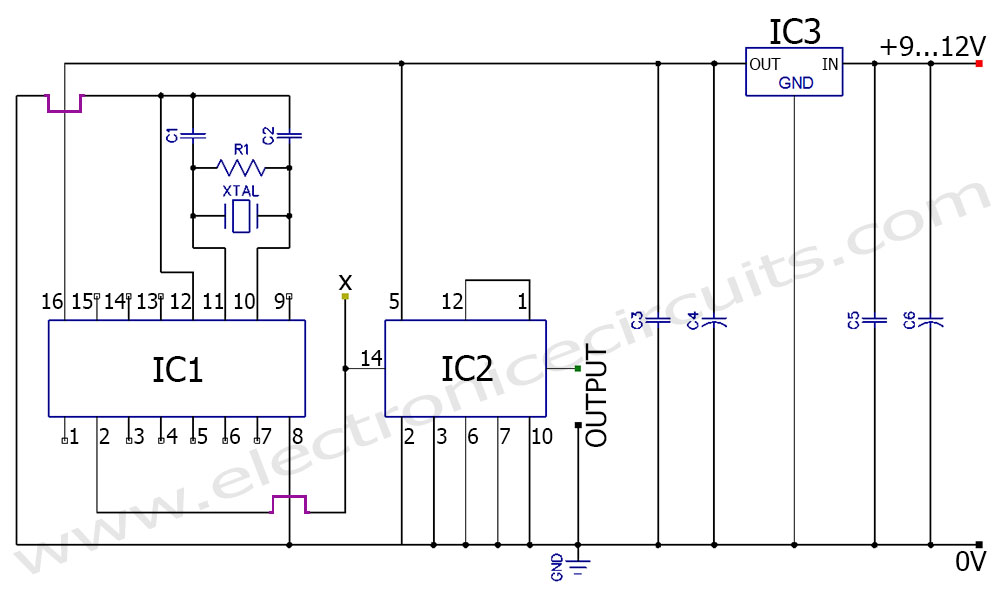
The Colpitts oscillator is known for its stability and is often used in applications requiring precise frequency generation, such as in radio transmitters and receivers. Its design can be modified to include additional components, such as resistors for biasing the vacuum tube and improving linearity, or additional filtering stages to enhance signal purity.
Overall, the early schematic of the Colpitts circuit showcases the foundational principles of oscillator design that remain relevant in modern electronic applications.Early schematic of a Colpitts circuit, using a vacuum tube, redrawn from the patent publication. A Colpitts oscillator, invented in 1920 by American engineer Edwin H. Colpitts, is one of a number of designs for electron.. 🔗 External reference
The Colpitts oscillator is a type of electronic oscillator that generates sine waves and is characterized by its use of a combination of capacitors and an inductor in its feedback network. The fundamental operation of the Colpitts oscillator relies on the resonant frequency determined by the inductor and the capacitors connected in series.
In this particular schematic, the vacuum tube serves as the active element, providing the necessary gain for oscillation. The circuit typically consists of a vacuum tube, an inductor (L), and two capacitors (C1 and C2) arranged in a voltage divider configuration. The output frequency can be adjusted by varying the values of the capacitors or the inductor, allowing for flexibility in frequency generation.
The feedback loop is crucial for sustaining oscillations. It is established through the coupling of the output from the anode of the vacuum tube back to the junction of the two capacitors. This feedback ensures that the circuit maintains its oscillation at the resonant frequency determined by the LC network.
The Colpitts oscillator is known for its stability and is often used in applications requiring precise frequency generation, such as in radio transmitters and receivers. Its design can be modified to include additional components, such as resistors for biasing the vacuum tube and improving linearity, or additional filtering stages to enhance signal purity.
Overall, the early schematic of the Colpitts circuit showcases the foundational principles of oscillator design that remain relevant in modern electronic applications.Early schematic of a Colpitts circuit, using a vacuum tube, redrawn from the patent publication. A Colpitts oscillator, invented in 1920 by American engineer Edwin H. Colpitts, is one of a number of designs for electron.. 🔗 External reference