Control a processor`s power supply in real time
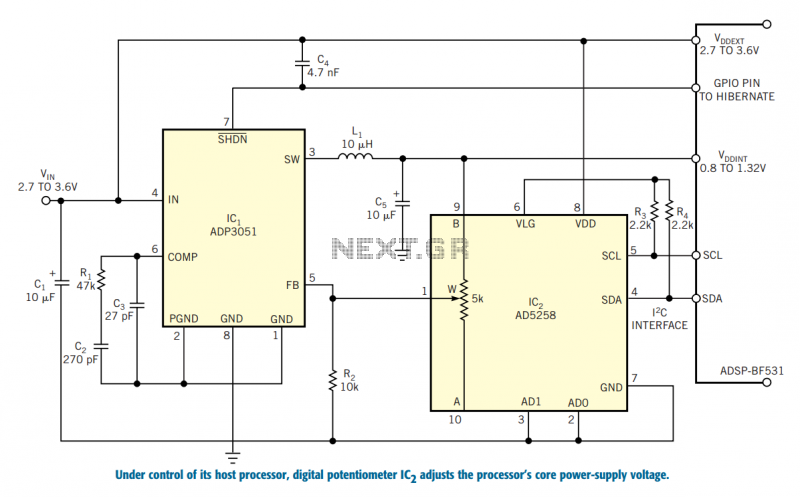
The described circuit integrates a microprocessor-based power management system that dynamically adjusts the supply voltage to optimize power consumption in battery-operated devices. The ADSP-BF531 Blackfin processor operates with a core voltage that can be finely tuned between 0.8V and 1.2V, with the ability to change in 50 mV increments. This adjustment capability is critical for maintaining operational efficiency, particularly during varying processing loads.
The AD5258 digital potentiometer serves as the key component for voltage regulation. It interfaces with the ADSP-BF531 through the I2C bus, allowing the processor to set the wiper position, which in turn alters the resistance in conjunction with an external resistor (R2). This configuration forms a voltage divider that determines the output voltage supplied by the ADP3051 step-down converter. The ADP3051 is designed to regulate output currents up to 500 mA while maintaining a minimum output voltage of 0.8V, ensuring that the requirements of the processor are met during both startup and normal operation.
To ensure stability and prevent overvoltage conditions, the design incorporates feedback mechanisms. The ADSP-BF531 monitors the output voltage and adjusts the resistance of the AD5258 accordingly. The algorithm implemented in the processor calculates the maximum resistance necessary for the desired output voltage, which is stored in the nonvolatile memory of the AD5258. This approach not only enhances the accuracy of the output voltage but also provides a safeguard against potential software errors that could lead to excessive voltage levels exceeding the 1.2V threshold.
Overall, the circuit exemplifies an efficient power management solution, combining a microprocessor, digital potentiometer, and step-down converter to achieve precise voltage control tailored for battery-powered applications, thereby extending battery life and improving device performance.In battery-powered applications in which power management is key, a microprocessor may adjust its core voltage corresponding to an increase or a decrease in clock speed, allowing full processing power when necessary but not wasting excess power when idle. The circuit of Figure 1 shows how an embedded processor can control its own supply voltage via a simple step-down converter and inexpensive digital potentiometer.
In this application, an embedded ADSP-BF531 Blackfin processor adjusts the wiper setting of IC2, an AD5258 digital potentiometer, via its I2C interface. In turn, IC2 controls the output of IC1, an ADP3051 current-mode, PWM step-down converter that supplies as much as 500 mA at output voltages as low as 0.8V.
When its output is in regulation, IC1's feedback input rests at 0.8V, and IC2 and R2 form a voltage divider.
The ADSP-BF531 imposes several design requirements: Its core power-supply voltage must maintain its accuracy to within 25 mV and offer an adjustment resolution of 50 mV per step from 0.8 to 1.2V. Also, the processor requires 1.2V at start-up to initialize its clocks. Finally, the power controller must prevent its output voltage from exceeding 1.2V if a software glitch occurs.
A digital potentiometer typically presents a highly variable absolute resistance value but can accurately set its internal resistance ratio. In this design, the AD5258's internal resistor forms a voltage divider with an external resistor to set the output voltage.
To improve the ADP3051's output-voltage accuracy, the ADSP-BF531 uses a simple algorithm to compute and store an appropriate maximum resistance for a given operating voltage in the AD5258's nonvolatile memory via its I2C port. Using the AD5258 with an external resistor provides hardware protection to prevent the output voltage from going above 1.2V.
If the AD5258 is set to zero resistance, the resulting output voltage is 0.8V×(0Ω+10 kΩ)/10 kΩ=0.8V.
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713